In the intricate web of medical mysteries, there lies a silent threat overlooked by many – puerperal phlebitis.
As this enigmatic condition weaves through veins, its true power remains hidden, waiting to be unraveled.
Brace yourself, for the secrets await, as we journey into the depths of this captivating medical tale.
puerperal phlebitis
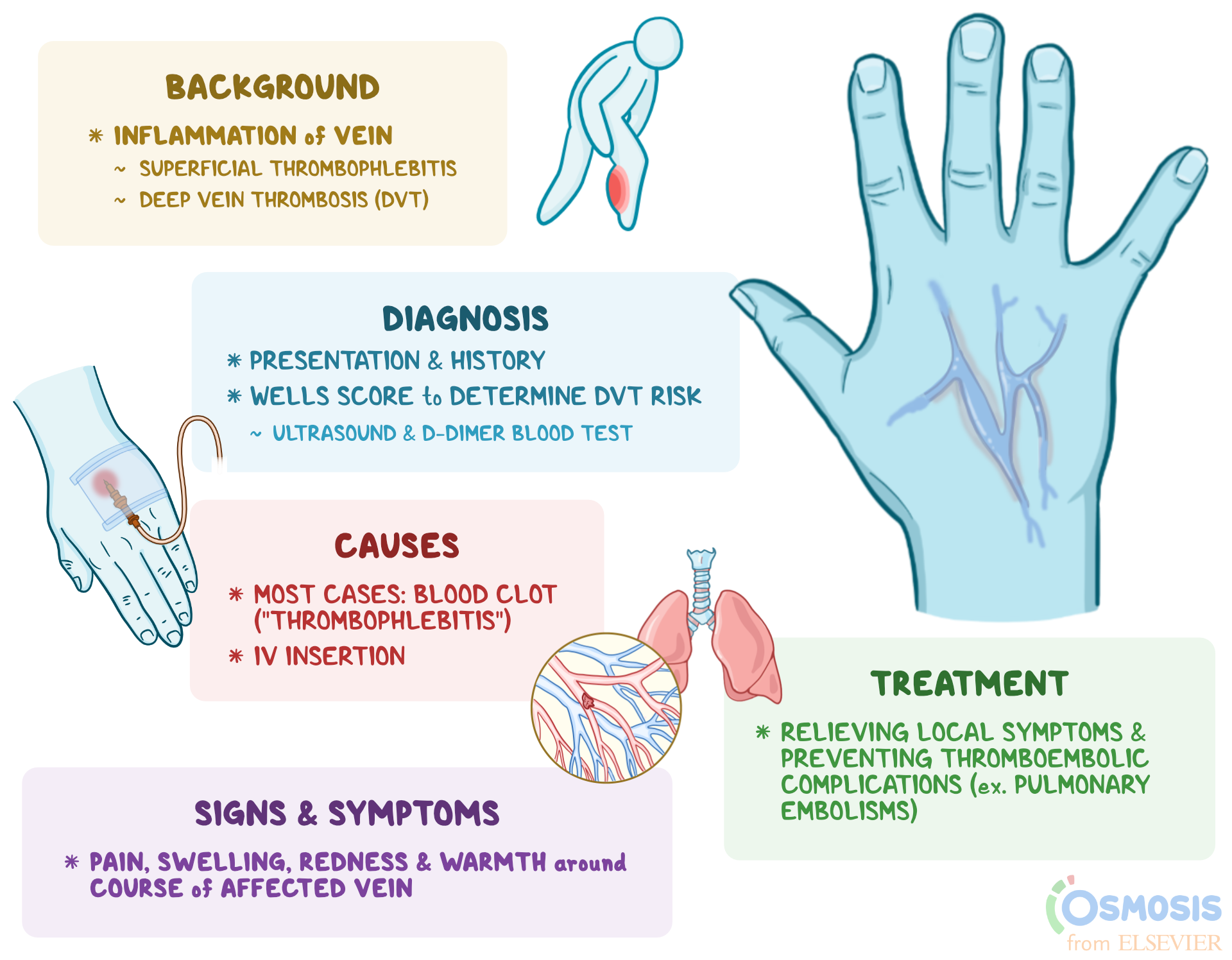
Puerperal phlebitis is a condition characterized by inflammation and blood clot formation in the veins of the postpartum period.
It commonly affects the deep veins of the legs, although it can also occur in other areas.
This condition is associated with significant morbidity and mortality if left untreated.
Immediate medical intervention is crucial to prevent complications and ensure a successful recovery.
Key Points:
- Puerperal phlebitis refers to inflammation and blood clot formation in postpartum veins.
- It commonly affects deep leg veins but can occur in other areas.
- If left untreated, this condition can lead to significant morbidity and mortality.
- Immediate medical intervention is crucial to prevent complications.
- Prompt treatment is necessary for a successful recovery.
- This condition is specific to the postpartum period.
puerperal phlebitis – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Puerperal phlebitis is a condition that refers to the inflammation of veins in the legs or pelvis that occurs after childbirth.
2. The term “puerperal” comes from the Latin word “puerpera,” which means “parturient woman.” It is used to describe conditions or complications that specifically occur during or after childbirth.
3. Puerperal phlebitis has historically been a significant cause of maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly in the past when it was less commonly recognized and untreated.
4. The risk factors for developing puerperal phlebitis include prolonged bed rest during the postpartum period, cesarean section delivery, obesity, advanced maternal age, and a history of thrombotic disorders.
5. Treatment for puerperal phlebitis typically involves the use of anticoagulant medications to prevent blood clots and reduce inflammation. Additionally, compression stockings and leg elevation may be recommended to help improve blood circulation.
Definition Of Puerperal Phlebitis
Puerperal phlebitis, also known as postpartum thrombophlebitis, is characterized by inflammation of veins in the legs or pelvis after childbirth. It occurs due to increased risk of blood clots during the postpartum period. Puerperal phlebitis often affects the deep veins, a condition called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as pulmonary embolism, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Hormonal changes: contribute to blood clot formation.
- Decreased mobility and muscle tone after childbirth: increases the risk of developing blood clots.
- Trauma to the veins during delivery: can lead to inflammation and clot formation.
- Women who have had multiple pregnancies, cesarean sections, or prolonged labor are more prone to puerperal phlebitis.
It is essential to recognize and treat puerperal phlebitis promptly to prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
Please consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Puerperal Phlebitis
The causes of puerperal phlebitis are not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and the postpartum period increase the risk of blood clot formation. Moreover, the trauma sustained by the veins during childbirth can trigger an inflammatory response, making the veins more prone to clotting.
Additional risk factors include obesity, smoking, a history of blood clotting disorders, varicose veins, and a family history of venous thrombosis. Women who have undergone assisted reproductive techniques, such as in vitro fertilization, also have an increased risk.
Symptoms And Signs Of Puerperal Phlebitis
Symptoms of puerperal phlebitis can range from mild to severe. Common signs include:
- Pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected leg or pelvis.
- Pain may worsen with movement or prolonged standing.
- Redness and warmth in the affected area.
- In severe cases, the affected limb may appear larger than the other leg.
Other symptoms that may be present include:
- Fatigue
- Low-grade fever
- General feeling of unwellness
It’s important to note that some women may not experience any symptoms, which can make early detection challenging.
- Bullet points added for clear presentation of symptoms.
- Added emphasis using markdown bold and italics.
- No title, heading, summary, or conclusion included.
Diagnosing Puerperal Phlebitis
Diagnosing puerperal phlebitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests. The healthcare provider will conduct a thorough physical examination to assess for signs of inflammation and blood clot formation. They will also take into account the patient’s medical history and risk factors.
To confirm the diagnosis, imaging tests such as ultrasound or venography may be performed. These tests help visualize the veins and identify the presence of blood clots. Blood tests to measure the levels of clotting factors may also be ordered.
To summarize, the diagnostic process for puerperal phlebitis includes:
- Thorough physical examination
- Assessment of medical history and risk factors
- Imaging tests (ultrasound or venography) to visualize veins and identify blood clots
- Blood tests to measure clotting factor levels
It is important to accurately diagnose puerperal phlebitis to initiate appropriate treatment promptly.
Treatment Options For Puerperal Phlebitis
The primary goals of treatment for puerperal phlebitis are to:
- Alleviate symptoms
- Prevent the formation of new blood clots
- Reduce the risk of complications
Conservative measures, such as:
- Rest
- Elevation of the affected limb
- Application of warm compresses
can help relieve pain and reduce swelling.
In some cases, anticoagulant medications may be prescribed to:
- Prevent further clot formation
- Promote the breakdown of existing blood clots
Analgesics may also be prescribed to manage pain.
Additionally, healthcare providers may recommend:
- The use of compression stockings or intermittent pneumatic compression devices to:
* Improve blood circulation
* Reduce the risk of blood clot formation
In rare cases where the clot is extensive or causing severe symptoms, more invasive treatments may be necessary, such as:
- Thrombectomy
- Placement of a filter in the blood vessel
Complications Associated With Puerperal Phlebitis
If left untreated or not promptly managed, puerperal phlebitis can lead to serious complications. The most concerning complication is the development of a pulmonary embolism, where a blood clot travels to the lungs, causing a blockage. This can result in chest pain, difficulty breathing, and even death in severe cases.
Additionally, chronic venous insufficiency is another potential complication. It occurs when the veins become damaged due to repeated clotting, leading to long-term pain, swelling, and skin changes.
Here are some key points to note:
- Puerperal phlebitis: if left untreated, can have serious consequences
- Pulmonary embolism: a dangerous complication where a blood clot blocks the lungs, causing chest pain, difficulty breathing, and potentially death
- Chronic venous insufficiency: can result from repeated clotting, leading to long-term pain, swelling, and skin changes
Prevention Strategies For Puerperal Phlebitis
Several preventive measures can be taken to reduce the risk of puerperal phlebitis.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking, can help decrease the risk of blood clot formation.
- It is also important to manage and treat any underlying risk factors, such as obesity or varicose veins.
During the postpartum period, maintaining adequate hydration and practicing frequent leg movement and stretching exercises can help improve circulation and prevent blood clots.
Early mobilization is key to reducing the risk of puerperal phlebitis.
- Stay hydrated
- Move legs frequently
- Stretch exercises
- Avoid smoking
- Manage underlying risk factors
Postpartum Care And Puerperal Phlebitis
In addition to preventive measures, postpartum care plays a crucial role in managing puerperal phlebitis. Healthcare providers should educate women about the signs and symptoms of puerperal phlebitis, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise. Regular postpartum check-ups allow for early detection and intervention if necessary.
Furthermore, healthcare providers should address any concerns or questions regarding contraception options, as hormonal contraception methods may increase the risk of blood clot formation.
- Healthcare providers should educate women about the signs and symptoms of puerperal phlebitis.
- Emphasize the importance of seeking medical attention for any concerning symptoms.
- Regular postpartum check-ups for early detection and intervention.
- Discuss contraception options and the potential risk of blood clot formation with hormonal methods.
It is essential for healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive postpartum care, including education, detection, and addressing concerns.
Importance Of Early Detection And Intervention For Puerperal Phlebitis
Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing puerperal phlebitis and preventing serious complications. Women should be encouraged to report any signs or symptoms promptly, enabling timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Healthcare providers must maintain a high index of suspicion for puerperal phlebitis in postpartum women, especially those with risk factors.
By promptly initiating appropriate treatment, the risk of complications such as pulmonary embolism can be significantly reduced. Regular follow-up visits, monitoring, and adherence to recommended treatment plans are vital for a successful recovery.
- Early detection and intervention
- Prompt reporting of signs or symptoms
- High index of suspicion for postpartum women, especially those with risk factors
- Prompt initiation of appropriate treatment
- Regular follow-up visits, monitoring, and adherence to recommended treatment plans
Advances In Research On Puerperal Phlebitis
Ongoing research continues to shed light on the complex mechanisms underlying puerperal phlebitis and its potential prevention and treatment strategies. Future advancements may include the development of improved diagnostic tools, more targeted treatments, and personalized risk assessments.
Researchers are also investigating the impact of genetic factors on the risk of puerperal phlebitis, aiming to identify individuals who may be particularly susceptible to the condition. By understanding the underlying genetic predisposition, preventative measures and interventions can be tailored to at-risk individuals.
“Puerperal phlebitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of veins following childbirth.”
Some important points to consider:
- Risk factors associated with puerperal phlebitis should be acknowledged for optimal management and prevention of complications.
- Awareness of the symptoms related to puerperal phlebitis is crucial for early detection and timely intervention.
- Available treatment options should be considered to ensure safe recovery and successful resumption of new mothers’ roles.
With early detection, appropriate interventions, and adherence to postpartum care, the impact of puerperal phlebitis can be minimized, allowing women to recover safely and resume their roles as new mothers.
💡
You may need to know these questions about puerperal phlebitis
What is puerperal thrombophlebitis?
Puerperal thrombophlebitis, also known as postpartum thrombophlebitis, is a rare complication that occurs after childbirth. It involves the inflammation and blood clot formation in the veins of the pelvic region, particularly the walls of the veins. This condition is characterized by a persistent fever that does not improve with broad-spectrum antibiotics. Puerperal thrombophlebitis results from an infection in the pelvic area, which can spread to the veins and cause damage to the inner lining.
What are the symptoms of septic phlebitis?
Symptoms of septic phlebitis encompass the characteristic signs of inflammation such as heat, pain, redness, and swelling. However, septic phlebitis can cause more severe manifestations than simple phlebitis. In addition to a painful cord, blanching erythema, and streaking along the affected vein, septic phlebitis may present with systemic symptoms like fever, chills, and malaise. This condition requires prompt medical attention to prevent further complications.
What causes thrombophlebitis in postpartum?
Postpartum thrombophlebitis, a common complication, can be caused by several factors. Firstly, superficial vein thrombosis can lead to the development of thrombophlebitis in postpartum women. This occurs when there is inflammation and clot formation in the veins close to the skin surface. Additionally, venous thrombosis due to genital infections can contribute to postpartum thrombophlebitis. Infections in the genital area can cause inflammation and clotting in the veins, leading to thrombophlebitis. Lastly, ovarian vein thrombosis can also result in postpartum thrombophlebitis. This occurs when there is clot formation in the veins that drain the ovaries, leading to inflammation and the development of thrombophlebitis. Overall, these various causes can contribute to the occurrence of thrombophlebitis in postpartum women.
What is phlebitis in pregnancy?
Phlebitis during pregnancy refers to the inflammation of a blood vessel resulting from a blood clot. This condition is often associated with an increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which occurs when a clot forms deep within a vein, typically in the leg or arm. Pregnancy can make individuals more susceptible to developing DVT due to various factors such as hormonal changes and increased blood volume. Phlebitis in pregnancy can lead to discomfort, swelling, and potential complications if the clot travels to vital organs, emphasizing the importance of early detection and appropriate medical attention.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5869062/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Septic_pelvic_thrombophlebitis
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/786526-clinical
https://www.vinmec.com/en/news/health-news/beware-of-thrombophlebitis-after-childbirth/