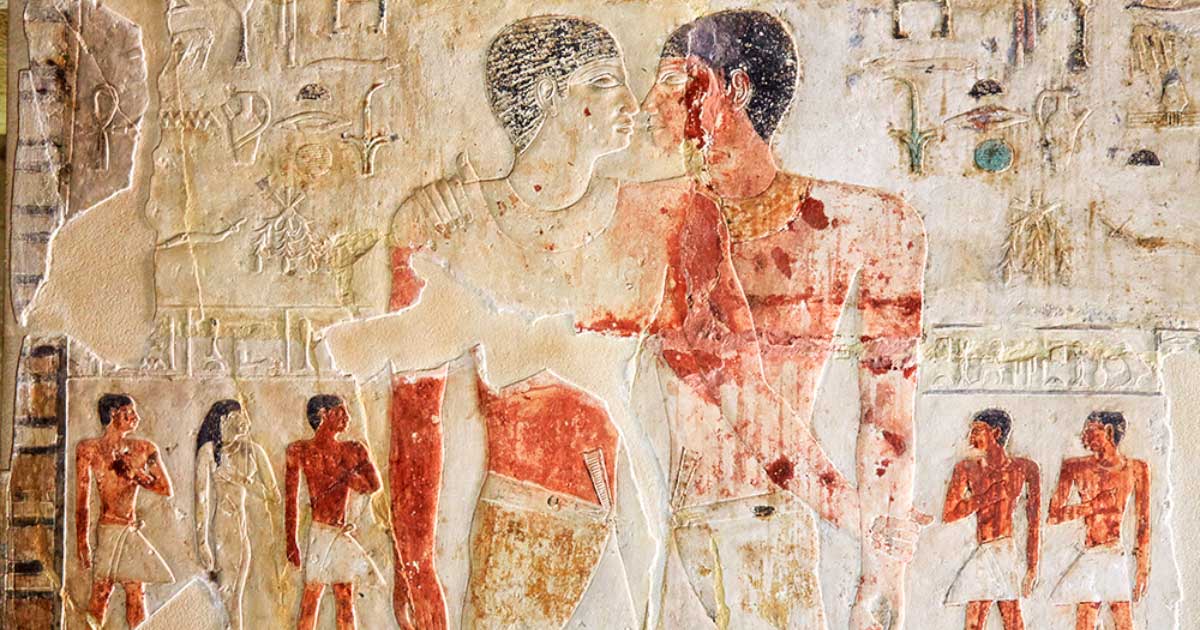
Acyeterion: Exploring the Origins and Significance of Greek Tragedy
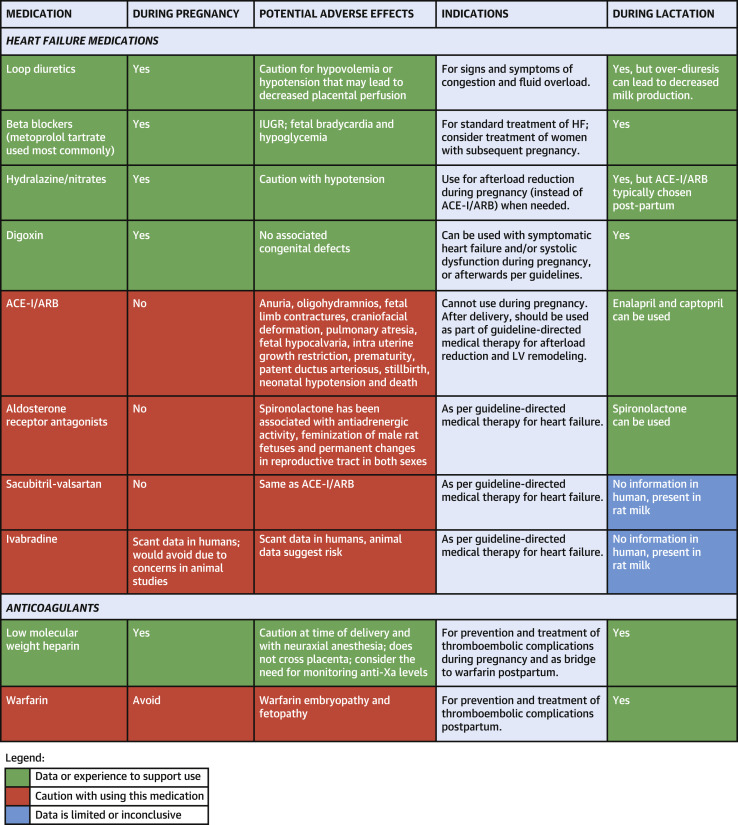
Emergency contraception, also known as morning-after pills or certain IUDs, refers to methods that can be used to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex. It should be used within 5 days (120 hours) of unprotected sex for best results. There are two types of morning-after pills: ulipristal acetate (ella) and levonorgestrel (Plan B, Take Action, etc.). Ulipristal acetate requires a prescription, while levonorgestrel pills can be bought over the counter. Morning-after pills work best when taken as soon as possible and may not be as effective if the body has already started ovulating.
Emergency contraception should not be used as a regular form of birth control. It does not cause long-term side effects, harm existing pregnancies, or affect future fertility. It is a safe method to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex. Different types of morning-after pills should not be used simultaneously or within 5 days of each other as they may counteract each other.
The effectiveness of emergency contraception can be affected by factors such as body weight. Levonorgestrel pills may be less effective for individuals weighing over 165 pounds, while ulipristal acetate is less effective for those weighing 195 pounds or more. The Paragard, Mirena, and Liletta IUDs are the most effective at preventing pregnancy and can be used within 120 hours of unprotected sex.
Emergency contraception can be purchased over the counter at drugstores and pharmacies without a prescription. It is recommended to use whichever method is available, even if not the most effective. The cost of emergency contraception varies, with Plan B One-Step typically costing around $40-$50 and levonorgestrel pills costing about $11-$45. ella, a different brand of morning-after pill, usually costs about $50 or more at the pharmacy but may be free with health insurance or Medicaid. The cost of getting an IUD can range from $0 to $1,300, but they may be free or low cost with health insurance plans, Medicaid, and some government programs.
Emergency contraception may cause temporary side effects such as nausea, vomiting, slight irregular vaginal bleeding, and fatigue. It does not have long-term side effects. It is not advisable to rely on home remedies for emergency contraception, as they are not effective. Morning-after pills do not require age or gender restrictions for purchase. Sometimes they may be locked up or kept behind the counter at stores, requiring assistance from a pharmacist or store clerk.
Insurance usually covers the cost of emergency contraception, but a prescription from a doctor or nurse may be required for coverage. Emergency contraception can also be obtained at family planning or health department clinics, as well as Planned Parenthood health centers. The first period after taking emergency contraception may come earlier or later than expected.
Continue Reading