In the world of biology, there are endless marvels that never cease to fascinate.
Imagine a scenario where a tiny part of the uterus, barely developed, becomes the unlikely host of a growing life.
This curious phenomenon, known as rudimentary horn pregnancy, defies the odds and poses unique challenges for medical professionals.
Join us on a thrilling journey as we uncover the mysteries surrounding this rare and intriguing condition.
Brace yourself for a captivating exploration into the depths of human biology and the urgent need for timely intervention to safeguard both mother and child.
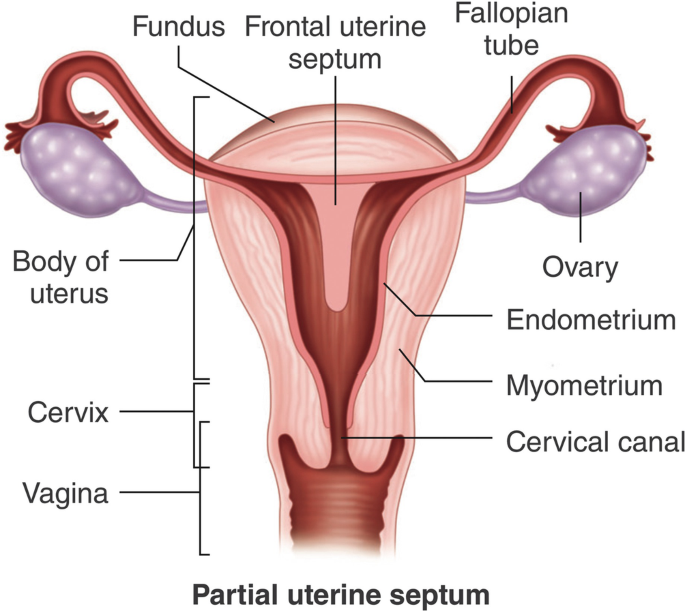
rudimentary horn of uterus
A rudimentary horn of the uterus is an underdeveloped part of the uterus that can result in a rare type of ectopic pregnancy.
It occurs in women with congenital uterine anomalies, such as a unicornuate uterus, which affects less than 5% of women.
A unicornuate uterus is characterized by incomplete development and failure of fusion of the Mullerian ducts, and about two-thirds of women with a unicornuate uterus may also have a rudimentary horn.
Diagnosis of a rudimentary horn pregnancy can be challenging, but symptoms may include amenorrhea, vaginal bleeding, abdominal or pelvic pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Transvaginal ultrasound scan is the preferred method for diagnosis, and additional imaging techniques may be used to confirm the diagnosis if necessary.
Prompt treatment is essential to prevent life-threatening complications, and options include medical treatment, laparoscopic surgery, or abdominal surgery.
Excision of the rudimentary horn and fallopian tube may be recommended to prevent recurrence and future complications.
Follow-up appointments should be scheduled to discuss chances of a healthy future pregnancy and any necessary precautions.
Key Points:
- Rudimentary horn of the uterus is an underdeveloped part of the uterus that can cause a rare ectopic pregnancy.
- It is commonly found in women with congenital uterine anomalies, such as a unicornuate uterus.
- Symptoms of a rudimentary horn pregnancy may include amenorrhea, vaginal bleeding, abdominal or pelvic pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Transvaginal ultrasound scan is the preferred method for diagnosis.
- Prompt treatment is essential to prevent life-threatening complications, and options include medical treatment or various types of surgeries.
- Excision of the rudimentary horn and fallopian tube may be recommended to prevent recurrence and future complications.
rudimentary horn of uterus – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. In extremely rare cases, women can be born with a rudimentary horn of the uterus, which is a developmental anomaly where a small, non-functional horn-like structure is present in the uterus.
2. A rudimentary horn of the uterus is formed when the two tubes that normally develop into the upper part of the uterus fail to fuse properly during embryonic development.
3. One of the main risks associated with a rudimentary horn of the uterus is a condition known as a “unicornuate uterus,” where the functional uterus is smaller in size, potentially leading to complications during pregnancy.
4. The rudimentary horn of the uterus is often not detected until complications arise, such as a ruptured horn or an ectopic pregnancy occurring in the non-functional horn portion.
5. Surgical removal of a rudimentary horn of the uterus is necessary to prevent potential life-threatening complications, and the procedure typically involves excising the horn along with the fallopian tube and ovary on the affected side.
Introduction: Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy In Unicornuate Uteruses
Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy:
Rudimentary horn pregnancy is a rare condition where a fertilized egg implants and grows in the underdeveloped portion of the uterus called the rudimentary horn of a unicornuate uterus. This makes it an ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants outside of the main cavity of the uterus.
Incidence and Causes:
With an incidence rate of approximately 1 in 75,000 to 150,000 pregnancies, rudimentary horn pregnancy is an extremely rare occurrence. This condition is primarily caused by the presence of a unicornuate uterus, which is a type of congenital uterine anomaly. Unicornuate uteruses account for around 10-20% of all uterine malformations and are found in less than 5% of women.
Prevalence Of Congenital Uterine Anomalies
Congenital Uterine Anomalies
Congenital uterine anomalies, such as unicornuate uteruses, are relatively uncommon and affect less than 5% of all women. These anomalies occur due to abnormal development of embryonic structures called Mullerian ducts during fetal life. The unicornuate uterus, a variation in these anomalies, occurs when there is incomplete fusion of the Mullerian duct with the opposite side. It is estimated that around 10-20% of all uterine malformations can be attributed to the unicornuate uterus.
Demographics: Incidence Of Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy
Rudimentary horn pregnancy is a rare occurrence, with an incidence rate of 1 in 75,000 to 150,000 pregnancies. The majority (85%) of these pregnancies occur in non-communicating rudimentary horns. Non-communicating means that the rudimentary horn does not share a direct connection with the main uterine cavity, further complicating the diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
It is important to note that rudimentary horn pregnancies can cause serious complications if left untreated, including life-threatening bleeding. Therefore, prompt diagnosis and appropriate management are imperative.
Developmental Origins Of Uterine Anomalies
The development of uterine anomalies, including the unicornuate uterus, begins during fetal life. It results from the abnormal development of the Mullerian ducts, which are embryonic structures responsible for the formation of the female reproductive system. In the case of a unicornuate uterus, incomplete fusion and failure of the Mullerian duct to connect with the opposite side leads to its formation. Interestingly, approximately two-thirds of women with a unicornuate uterus may also have a rudimentary horn.
Understanding the developmental origins of uterine anomalies provides insight into how and why rudimentary horn pregnancy occurs. It highlights the importance of early detection and appropriate management to prevent potential complications.
Understanding The Unicornuate Uterus And Rudimentary Horn
The unicornuate uterus is a rare congenital anomaly characterized by the incomplete development and failure of fusion with the opposite side of the Mullerian duct. It is typically associated with a single fallopian tube and ovary.
This type of uterus is elongated and has one-sided development, resulting in a smaller capacity compared to a normal uterus.
Within the unicornuate uterus, the rudimentary horn is an underdeveloped and non-functional portion of the uterus that lacks a direct connection with the main uterine cavity.
This rudimentary horn is where rudimentary horn pregnancy occurs, with the fertilized egg implanting and growing in this anatomical anomaly. It is important to note that the rudimentary horn lacks the necessary structures and blood supply to support a developing fetus, making rudimentary horn pregnancy extremely dangerous.
Location And Characteristics Of Rudimentary Horn Pregnancies
Most rudimentary horn pregnancies occur in non-communicating rudimentary horns, meaning there is no direct connection between the rudimentary horn and the main uterine cavity. This lack of communication often makes diagnosis challenging, and the condition may go undetected during routine pelvic exams.
Symptoms of a rudimentary horn pregnancy can vary but may include:
- Amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods)
- Vaginal bleeding (which may be light or prolonged/intermittent)
- Pain in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or lower back
- Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
It is important to note that a rudimentary horn pregnancy is a rare and potentially dangerous condition that requires prompt medical attention.
Symptoms And Diagnosis Of Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy
Diagnosing a rudimentary horn pregnancy can be difficult as it may not always cause symptoms and can be missed during routine pregnancy scans. However, it is crucial to detect the condition early to prevent life-threatening complications.
Symptoms that may indicate a rudimentary horn pregnancy include:
- severe abdominal or pelvic pain
- fainting
- shock
If a rudimentary horn pregnancy is suspected, further medical examination and diagnostic procedures are necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tools: Transvaginal Ultrasound And MRI
Transvaginal ultrasound scan (TVS) is the preferred diagnostic tool for detecting ectopic pregnancies, including rudimentary horn pregnancies. This imaging technique utilizes sound waves to create images of the pelvic organs from inside the vagina. It provides detailed visualization and can help identify the location of the pregnancy and other relevant anatomical features.
In equivocal cases, three-dimensional ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be utilized to provide additional information and confirm the diagnosis of a rudimentary horn pregnancy.
Treatment Options For Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy
There are several treatment options available for rudimentary horn pregnancy, including medical treatment with drugs, laparoscopic surgery, or abdominal surgery. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, such as:
- Location and characteristics of the pregnancy
- Patient’s overall health
- Preferences of the medical team
If left untreated, a rudimentary horn pregnancy can lead to life-threatening bleeding. Therefore, prompt intervention is essential to prevent complications. Depending on the specific case, medical treatment may be attempted first, but in most instances, surgical intervention is necessary to remove the rudimentary horn and prevent future complications.
- Medical treatment with drugs
- Laparoscopic surgery
- Abdominal surgery
“Prompt intervention is essential to prevent complications.”
Long-Term Considerations And Follow-Up For Rudimentary Horn Pregnancies
After treatment for a rudimentary horn pregnancy, follow-up appointments should be scheduled to monitor the patient’s recovery and discuss any long-term considerations. During these follow-up visits, the chances of a healthy future pregnancy can be discussed, along with the timing for attempting another pregnancy and any special precautions that may be advised.
It is important to note that the risk of recurrence of a pregnancy in the rudimentary horn is extremely rare with appropriate medical treatment and the excision of the rudimentary horn and fallopian tube. However, routine follow-up and discussions with healthcare professionals are recommended to ensure the best possible outcomes for future pregnancies.
Rudimentary horn pregnancy is a rare and complex condition that occurs in the underdeveloped portion of the uterus known as the rudimentary horn of a unicornuate uterus. It is crucial to understand the prevalence of congenital uterine anomalies, the developmental origins of uterine anomalies, as well as the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for rudimentary horn pregnancies. By increasing awareness and knowledge about this condition, healthcare professionals can provide prompt and appropriate care for those affected, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
💡
You may need to know these questions about rudimentary horn of uterus
What causes rudimentary horn of the uterus?
The rudimentary horn of the uterus is primarily caused by a developmental abnormality known as defective fusion of the Müllerian duct. This anomaly is estimated to occur in approximately one out of every 76,000 pregnancies, leading to a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn. Unfortunately, pregnancies occurring in this rudimentary horn can be life-threatening, often resulting in heavy and dangerous bleeding. Proper identification and management of such pregnancies are crucial to ensure the safety of the mother.
How do you treat a rudimentary horn uterus?
The treatment for a rudimentary horn uterus typically involves surgical resection of the horn, along with the fallopian tube on the same side, while preserving the ovary. This procedure also requires cutting and fixing the round ligament to the normal uterus. By removing the rudimentary horn and fallopian tube, potential complications such as ectopic pregnancy and endometriosis can be prevented, while maintaining the functionality of the ovary for reproductive purposes. This surgical approach aims to promote normal reproductive health and improve fertility outcomes for individuals with a rudimentary horn uterus.
Should a rudimentary horn be removed?
Yes, the removal of a rudimentary horn is necessary. When diagnosed, excising the rudimentary horn is the recommended course of action to mitigate potential complications. By removing the horn, the risk of associated issues can be minimized, ensuring the well-being and health of the individual. This medical intervention is crucial in preventing any future complications that may arise from the presence of the rudimentary horn.
Can rudimentary horn affect pregnancy?
Yes, a rudimentary horn can potentially affect pregnancy. Due to the limited space and ability of the horn to expand, a rudimentary horn pregnancy cannot progress normally and may lead to severe complications. If left untreated, the fertilized egg can continue to grow within the horn, increasing the risk of rupture and potentially life-threatening bleeding. Therefore, it is crucial for medical intervention to prevent such complications. In most cases, rudimentary horn pregnancies unfortunately end with rupture before reaching the third trimester.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3916269/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5510148/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2004571/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3015690/