In the labyrinth of the human body, there exists a complex passageway that connects hope and life.
Hidden within the woman’s reproductive system, lie the fallopian tubes – delicate conduits that hold the key to creation.
But what happens when these vital pathways become entangled in the clutches of disease?
Enter salpingectomy, a surgical dance that seeks to remove the obstacles and restore the symphony of biology.
Join us on a journey as we unravel the intricacies of this procedure, exploring the various methods and recovery times that pave the way to a brighter future.
salpingectomy
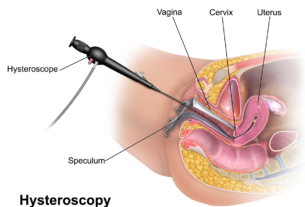
Salpingectomy is the surgical removal of one or both of a woman’s fallopian tubes.
It is performed to treat various conditions including fallopian tube cancer, ovarian cancer, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, blocked or infected fallopian tubes.
The surgery can be done under general anesthesia, either through a cut in the abdomen or laparoscopy.
Recovery may require a few days of hospital stay and it is generally faster with laparoscopy compared to laparotomy.
Salpingectomy may also be used as part of fertility treatment for blocked fallopian tubes or as a form of permanent contraception to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Key Points:
- Salpingectomy is the removal of one or both of a woman’s fallopian tubes.
- It is performed to treat conditions such as fallopian tube cancer, ovarian cancer, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, and blocked or infected fallopian tubes.
- The surgery can be done under general anesthesia, either through a cut in the abdomen or laparoscopy.
- Recovery may require a few days of hospital stay, with laparoscopy generally offering a faster recovery compared to laparotomy.
- Salpingectomy may also be used to treat blocked fallopian tubes as part of fertility treatment or as a form of permanent contraception to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
salpingectomy – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. In ancient Egypt, it was believed that women who had undergone a salpingectomy (surgical removal of the Fallopian tubes) were protected from evil spirits and curses.
2. Salpingectomy is also performed on animals, particularly birds, to prevent unwanted breeding and control population.
3. The first recorded successful human salpingectomy surgery was performed in the late 19th century by Dr. J. Marion Sims, an American physician who is often referred to as the “father of modern gynecology.”
4. Salpingectomy can sometimes be performed as a part of gender-affirming surgeries for transgender men, as it is a necessary step in the removal of internal reproductive organs.
5. The term “salpingectomy” is derived from the Greek words “salpinx,” meaning “trumpet,” and “ektom??,” meaning “excision.” This name was chosen due to the shape of the Fallopian tubes resembling trumpet valves.
Introduction To Salpingectomy – Surgical Removal Of Fallopian Tubes
Salpingectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing one or both of a woman’s fallopian tubes. The fallopian tubes have a crucial role in reproductive health, as they carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Removing the fallopian tubes is often recommended for treating conditions like fallopian tube cancer, ovarian cancer, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes, and infected fallopian tubes.
The procedure takes place in a hospital or surgical center, performed by a skilled surgeon. Before the surgery, patients meet with the surgeon and anesthesiologist to discuss the operation. This consultation involves the surgeon explaining the procedure, addressing any concerns or questions the patient may have, and assessing the patient’s overall health. Additionally, anesthesia options, potential risks, and post-operative care will be discussed.
Common Conditions Treated With Salpingectomy
Salpingectomy is a surgical procedure used to treat several gynecological conditions. One of the main reasons for performing this surgery is to address fallopian tube cancer or ovarian cancer. These types of cancers can spread quickly, so removing the fallopian tubes may be necessary to prevent further spread or recurrence.
Another condition that often requires salpingectomy is an ectopic pregnancy. In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants itself outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. Since this condition poses a significant health risk and can result in a life-threatening rupture, the affected tube is typically removed.
Salpingectomy can also be used to address blocked fallopian tubes. In some cases, the tubes can become obstructed due to scarring, inflammation, or infections. If alternative solutions, such as tubal reimplantation or tubal cannulation, have failed, salpingectomy may be a viable option. By removing the blocked tubes, the patient’s fertility may potentially be restored.
- Salpingectomy is employed as a treatment for several gynecological conditions, including:
- Fallopian tube cancer or ovarian cancer
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Blocked fallopian tubes
“Salpingectomy is a surgical procedure used to treat several gynecological conditions, including fallopian tube cancer or ovarian cancer, ectopic pregnancy, and blocked fallopian tubes.”
Preparing For Salpingectomy Surgery
Before undergoing salpingectomy surgery, patients must engage in a comprehensive preparation process. The surgeon and medical team will provide the necessary guidance and instructions to ensure optimal patient preparation.
Patients may be required to undergo certain pre-operative tests to assess their overall health and confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include:
- Blood work
- Imaging studies
- Possibly a pregnancy test, depending on the reason for the surgery.
To minimize the risk of complications during the procedure, patients may need to avoid eating or drinking anything for several hours prior to surgery. This fasting period allows the gastrointestinal system to empty completely, reducing the risk of vomiting or regurgitation during anesthesia.
Additionally, patients may be instructed to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or herbal supplements, before the surgery. It is crucial to follow all pre-operative instructions provided by the surgical team to ensure a smooth and successful procedure.
Blockquote: Following the surgeon’s instructions before salpingectomy surgery is important for a safe and effective procedure.
- Engage in a comprehensive preparation process
- Undergo pre-operative tests
- Avoid eating or drinking before surgery
- Stop taking certain medications.
Fasting Requirements Before The Surgery
In preparation for salpingectomy surgery, patients are often required to adhere to specific fasting requirements. These requirements help minimize the risk of complications associated with anesthesia and ensure a safe surgical experience.
Generally, patients are instructed to avoid consuming any solid foods for at least six hours prior to the surgery. This fasting period allows the stomach to empty completely, reducing the likelihood of aspiration during anesthesia.
For liquids, patients are typically instructed to abstain from drinking anything for at least two hours before the surgery. Clear fluids, such as water or apple juice, may be allowed up to two hours before the operation, as these liquids are more rapidly digested.
Adhering to the fasting requirements is crucial for patient safety and the success of the surgery. Patients should make sure to follow these guidelines meticulously and inform their surgical team if they have any concerns or questions regarding the fasting protocol.
Key Points:
- Avoid consuming any solid foods for at least six hours prior to the surgery.
- Abstain from drinking anything for at least two hours before the surgery.
- Clear fluids, such as water or apple juice, may be allowed up to two hours before the operation.
“Adhering to the fasting requirements is crucial for patient safety and the success of the surgery.”
Types Of Anesthesia Used In Salpingectomy
Salpingectomy can be performed under different types of anesthesia depending on the patient’s individual needs and the complexity of the procedure. The choice of anesthesia is made by the anesthesiologist in collaboration with the surgeon, taking into consideration factors such as the patient’s health condition, the duration of the surgery, and the patient’s preferences.
-
General anesthesia is commonly used for salpingectomy surgeries. It involves administering medications that induce a state of unconsciousness and render the patient completely unaware during the procedure. With general anesthesia, patients will not experience pain or have any memory of the surgery.
-
Alternatively, laparoscopic salpingectomy may be performed under regional anesthesia, such as spinal or epidural anesthesia. In these cases, patients are awake during the procedure but are numbed in the lower part of their body to eliminate pain. This option may be considered when the salpingectomy is less invasive or for patients who are not suitable candidates for general anesthesia.
The choice of anesthesia will be discussed during the pre-operative consultation, and patients can express their concerns, preferences, and any previous experiences with anesthesia to ensure a comfortable and safe surgical experience.
Surgical Methods For Removing Fallopian Tubes
There are two primary surgical methods available for removing fallopian tubes: laparotomy and laparoscopy. The choice of method depends on factors such as the underlying condition being treated, the surgeon’s preference, and the patient’s individual circumstances.
Laparotomy is a more traditional approach that involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to access and remove the fallopian tubes. This method may be used when the surgery is complex, or when there is a large mass or adhesions present. While a longer recovery period and a larger scar are potential disadvantages, laparotomy may be the best choice for certain cases.
Laparoscopic salpingectomy, commonly referred to as keyhole surgery, is a minimally invasive procedure that involves making a few small incisions in the abdomen. A laparoscope, a thin and flexible instrument with a camera, is inserted through one of the incisions to visualize the pelvic organs. Surgical instruments are then inserted through the remaining incisions to perform the removal of the fallopian tubes. Laparoscopic surgery offers several benefits, including smaller incisions, reduced post-operative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to laparotomy.
The decision between laparotomy and laparoscopy is made based on a combination of factors, including the patient’s condition, the surgeon’s expertise, and the available resources. The surgeon will assess each case individually and determine the most appropriate surgical method for optimal results.
Summary:
- There are two primary surgical methods for removing fallopian tubes: laparotomy and laparoscopy
- Laparotomy involves a larger incision in the abdomen, while laparoscopy is minimally invasive
- The choice of method depends on factors such as the underlying condition, surgeon’s preference, and patient’s circumstances
- Laparoscopic surgery offers benefits such as smaller incisions, reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery
Post-Operative Recovery And Hospital Stay
Following a salpingectomy surgery, patients should expect a recovery period that may require a few days of hospital stay. It is common for patients to experience pain, discomfort, and fatigue after the surgery, which can vary depending on the surgical technique used and the patient’s tolerance.
Pain management is an essential aspect of the post-operative recovery process. Patients will be closely monitored for any signs of complications, such as excessive bleeding or infection. Pain medication will be prescribed to alleviate discomfort, and patients are encouraged to communicate their pain levels with the medical team to ensure appropriate adjustments in pain management.
In the hospital, patients may receive specific instructions regarding wound care, movement limitations, and activities to avoid during the recovery period. It is crucial to follow these instructions diligently to promote proper healing and minimize the risk of complications.
Once the patient’s condition stabilizes, they may be discharged from the hospital. Having a support system in place is essential to assist with daily activities during the initial phase of recovery, which may involve limited mobility, and certain restrictions on lifting heavy objects or engaging in rigorous physical activities.
Regular post-operative check-ups will be scheduled to monitor the healing process and address any concerns or complications that may arise. Patients should follow the recommended post-operative care plan and attend all follow-up appointments to ensure a smooth recovery.
Salpingectomy For Fertility Treatment
Salpingectomy is a key component of fertility treatment plans that are designed to address blocked fallopian tubes with fluid build-up. When the fallopian tubes become obstructed, natural conception may be difficult or even impossible.
Salpingectomy plays a crucial role in restoring fertility by removing the blocked tubes and providing an alternative pathway for eggs.
By removing the damaged or obstructed fallopian tubes, the chances of successful conception can be significantly improved, especially when assisted reproductive techniques like in vitro fertilization (IVF) are utilized.
IVF allows for the fertilization of eggs to take place in a laboratory environment, bypassing the fallopian tubes entirely. The resulting embryos are then transferred into the uterus for implantation.
The decision to undergo salpingectomy as part of fertility treatment is typically made after thorough investigations and evaluation of the couple’s fertility potential. The medical team will discuss the benefits, risks, and success rates of this approach, taking into account the patient’s unique circumstances and fertility goals.
Other Reasons For Salpingectomy
Salpingectomy is a surgical procedure that is not limited to treating conditions such as cancer, ectopic pregnancy, or blocked fallopian tubes. It can also be performed for other reasons, including permanent contraception and reduction of the risk of ovarian cancer.
As a form of permanent contraception, salpingectomy is an effective alternative to tubal ligation or the use of contraceptive devices such as intrauterine devices. The removal of the fallopian tubes ensures that the route for egg-sperm interaction is blocked entirely, providing an irreversible contraceptive method.
Additionally, recent research has shown a link between the removal of fallopian tubes and a reduced risk of ovarian cancer. As the fallopian tubes are believed to be the site of origin for some types of ovarian cancer, removing these tubes can considerably lower the risk of developing this potentially life-threatening disease. Salpingectomy may be considered for women at high risk of ovarian cancer due to genetic predisposition or other factors.
The decision to undergo salpingectomy for contraception or risk reduction purposes should be made after thorough discussions and consideration of the individual’s overall health, reproductive goals, and personal preferences. The medical team will provide the necessary information and support to help patients make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
- Salpingectomy can be performed for multiple reasons including cancer treatment, ectopic pregnancy, blocked fallopian tubes, and permanent contraception.
- The procedure ensures irreversible contraceptive method by blocking the route for egg-sperm interaction.
- Recent research suggests that removing fallopian tubes can considerably reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Women at high risk of ovarian cancer may consider salpingectomy as a preventative measure.
- The decision to undergo salpingectomy should be based on thorough discussions and consideration of overall health, reproductive goals, and personal preferences.
Comparison Of Recovery Time Between Keyhole Surgery And Laparotomy
One significant advantage of laparoscopic salpingectomy, or keyhole surgery, over traditional laparotomy is the difference in recovery times. Patients who undergo keyhole surgery tend to experience a faster recovery and shorter hospital stay compared to those who undergo laparotomy.
The smaller incisions used in laparoscopic surgery result in less tissue damage, leading to reduced post-operative pain and discomfort. Patients often require less pain medication and can resume regular activities, including walking and self-care, sooner than patients who undergo laparotomy.
The shorter recovery time associated with laparoscopic salpingectomy is also beneficial in terms of hospital stays. Patients typically spend fewer days in the hospital following keyhole surgery, allowing them to recover in the comfort of their own homes sooner.
However, it is important to note that the choice of surgical method is determined by various factors, including the complexity of the procedure, the patient’s overall health, and the surgeon’s expertise. While laparoscopic salpingectomy generally offers a faster recovery, laparotomy may be necessary in certain cases where a more extensive surgery is required.
💡
You may need to know these questions about salpingectomy
What is removed in a salpingectomy?
During a salpingectomy, one or both fallopian tubes are removed entirely. These structures, also known as oviducts, serve as pathways for eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. The procedure can involve the complete extraction of the tubes or the removal of specific sections within them. Removing the fallopian tubes through a salpingectomy is typically done to address conditions like ectopic pregnancies, tubal blockages, or to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Why would you have a salpingectomy?
A salpingectomy may be considered as a preventive measure for individuals at a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer. By removing one or both fallopian tubes, which have been identified as a common site for certain types of ovarian cancer, the chances of developing the disease can be significantly reduced. This preventive approach allows individuals to proactively manage their health and minimize the risk of potential complications in the future. Additionally, salpingectomy is sometimes performed in cases of recurrent ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus. Removing the affected tube can help prevent future ectopic pregnancies and the associated health risks they pose.
Furthermore, salpingectomy can be beneficial in cases of severe tubal blockage or infection. If the fallopian tubes are blocked due to factors such as scarring from previous infections or conditions like endometriosis, fertility may be compromised. In some instances, removing the affected tubes may increase the chances of successful conception through alternative fertility treatments or in vitro fertilization (IVF). Similarly, in cases of chronic infection, such as a persistent or recurring tubal infection, removing the fallopian tubes can help prevent further complications and promote better overall reproductive health.
What happens to your body when your fallopian tubes are removed?
When the fallopian tubes are removed from the body, it does not affect the functioning of the ovaries and uterus. Therefore, if one fallopian tube is removed, the individual will still have regular menstrual periods and will need contraception to prevent pregnancy. However, if both fallopian tubes are removed, it becomes impossible for the egg to meet the sperm, resulting in infertility. In such cases, the need for contraception is eliminated as conception is no longer possible. It’s important to note that the removal of fallopian tubes does not have any immediate impact on menstrual cycles or the overall hormonal functioning of the body.
Is a salpingectomy a major surgery?
Yes, a salpingectomy is considered a major surgery. During a salpingectomy, the fallopian tube is surgically removed, which requires anesthesia and may involve an overnight hospital stay. Additionally, since the procedure involves the removal of body parts, it is classified as a major surgery. Recovery from a salpingectomy typically takes 3-6 weeks to heal completely.
Reference source
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/salpingectomy
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/salpingectomy
https://www.webmd.com/women/what-is-a-salpingectomy
https://www.healthline.com/health/salpingectomy