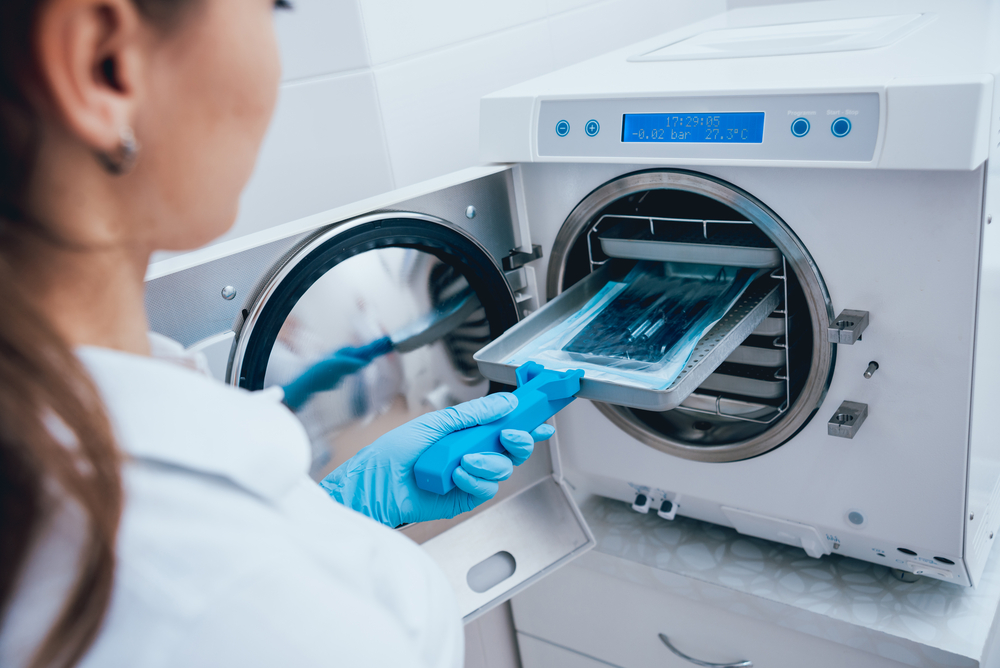
In the realm of medicine, sterile equipment is the unsung hero that protects us from the invisible threats lurking around us.
While heat has long been the go-to method for sterilization, modern technology has ushered in a wave of innovative techniques.
From ethylene oxide gas to hydrogen peroxide gas plasma and peracetic acid immersion, these cutting-edge methods have revolutionized the field.
Join us as we delve into the world of sterilization and uncover the intricate measures taken to keep us safe from disease transmission.
From the tried-and-true to the exciting new, discover why each medical device requires its own unique sterilization approach.
sterilization
Sterilization is a process that destroys all microorganisms on the surface of an article or in a fluid to prevent disease transmission.
It is essential for ensuring the safety of medical and surgical devices used in healthcare facilities.
While most devices undergo heat sterilization, there has been an increase in the use of materials that require low-temperature sterilization.
Ethylene oxide gas has been commonly used for heat- and moisture-sensitive devices since the 1950s.
In the past 15 years, new low-temperature sterilization systems such as hydrogen peroxide gas plasma and peracetic acid immersion have been developed.
The wide margin of safety in sterilization processes reduces the risk of pathogen transmission, although it is important to adequately sterilize critical items that come into contact with sterile body tissues or fluids.
Various sterilization technologies, including heat and low-temperature methods, have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Key Points:
- Sterilization destroys microorganisms to prevent disease transmission
- Sterilization is necessary for the safety of medical and surgical devices
- Heat sterilization is common, but low-temperature sterilization is increasing
- Ethylene oxide gas has been used for heat- and moisture-sensitive devices since the 1950s
- New low-temperature sterilization systems have been developed in the past 15 years
- Different sterilization technologies have their own pros and cons
sterilization – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The first recorded case of sterilization as a method of birth control occurred in ancient Egypt around 3000 BCE when women used a mixture of crocodile dung and sour milk as a spermicide.
2. In the early 20th century, eugenics programs in some American states led to the forced sterilization of individuals deemed “undesirable” or “unfit,” including those with mental illnesses, disabilities, or low socioeconomic status.
3. The largest recorded mass sterilization campaign took place in the 1970s in India, where millions of men were coerced or forced to undergo vasectomies as a means of population control.
4. The first successful animal sterilization experiments were conducted in the early 19th century by French scientist Jean Pierre M??gnin, who sterilized insects by using heat techniques.
5. One of the most well-known cases involving sterilization is that of Buck v. Bell in 1927, where the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that forced sterilization of those perceived as mentally unfit was constitutional, setting a precedent that was followed by more than 30 states.
1. Heat Sterilization For Medical And Surgical Devices
Heat sterilization is the primary method used to ensure the cleanliness and safety of medical and surgical devices in healthcare facilities. This technique involves subjecting the devices to high temperatures, with steam or dry heat being commonly used. The elevated heat effectively eliminates all microorganisms present on the surface of the devices, preventing the spread of diseases.
It is important to note that heat sterilization is suitable for heat-resistant items that can endure high temperatures without sustaining any damage or deformation. Metal surgical instruments, glassware, and certain plastics are examples of materials that can be safely sterilized using heat.
2. Increase In Low-Temperature Sterilization Devices
In recent years, the use of medical devices made of low-temperature sterilization-compatible materials has significantly risen. This is due to the fact that certain plastics and electronics are not compatible with high temperatures and can be damaged or warped when subjected to heat sterilization methods.
To overcome this issue, new low-temperature sterilization systems have been developed. These technologies allow for the sterilization of heat- and moisture-sensitive items without compromising their integrity. Two commonly used low-temperature sterilization methods are hydrogen peroxide gas plasma and peracetic acid immersion.
3. Ethylene Oxide Gas For Heat- And Moisture-Sensitive Devices
Since its introduction in the 1950s, ethylene oxide gas has been an effective method for sterilizing heat- and moisture-sensitive medical devices. This widely accepted technique allows for efficient sterilization without subjecting the devices to harmful high temperatures or excessive moisture.
Ethylene oxide gas is capable of penetrating the materials of the devices and successfully eliminating any microorganisms present. This makes it particularly suitable for sterilizing endoscopes, rubber tubing, and certain plastic components.
It is important to exercise caution when handling ethylene oxide gas since it can be flammable and toxic. Adequate ventilation and careful handling are necessary to ensure safety.
In summary, ethylene oxide gas is a widely used method for sterilizing heat- and moisture-sensitive medical devices. However, its potential flammability and toxicity require careful handling and ventilation.
- Key points:
- Ethylene oxide gas is used for sterilizing heat- and moisture-sensitive medical devices.
- It effectively destroys microorganisms by penetrating the device materials.
- Ethylene oxide gas is particularly suitable for endoscopes, rubber tubing, and certain plastic components.
- Caution is required due to its flammability and toxicity.
4. New Low-Temperature Sterilization Systems
In the past 15 years, new low-temperature sterilization systems have emerged as alternatives to ethylene oxide gas. These technologies offer improved effectiveness and safety in sterilizing heat- and moisture-sensitive medical devices.
One such system is hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilization. This method involves exposing the devices to a low-temperature plasma created by the interaction of hydrogen peroxide vapor and radiofrequency energy. The plasma effectively destroys microbial contaminants and leaves no harmful residues.
Another emerging technology is peracetic acid immersion sterilization. This method utilizes a solution of peracetic acid, hydrogen peroxide, and acetic acid, which is applied to the devices. The solution effectively kills microorganisms and breaks down into harmless byproducts.
5. Preventing Disease Transmission Through Sterilization
Sterilization is a crucial process that aims to destroy all microorganisms on the surface of an article or in a fluid, preventing the transmission of diseases. By ensuring that medical devices and instruments are sterile, healthcare facilities can significantly reduce the risk of infection for patients and healthcare professionals.
Critical items that come into contact with sterile body tissues or fluids, such as surgical instruments and catheters, should always be sterile. Failure to adequately sterilize these items can have severe consequences, including the transmission of pathogens and the development of infections.
- Sterilization destroys microorganisms on surfaces or in fluids.
- It prevents the transmission of diseases.
- Sterile medical devices reduce infection risk.
- Critical items must be sterile to avoid severe consequences.
- Failure to sterilize can lead to pathogen transmission and infections.
“Sterilization is a crucial process that aims to destroy all microorganisms on the surface of an article or in a fluid, preventing the transmission of diseases.”
6. Rare Transmission Of Pathogens Due To Sterilization Processes
Despite the importance of proper sterilization, cases of pathogen transmission due to inadequately sterilized critical items are relatively rare. This is primarily because sterilization processes provide a wide margin of safety.
- It is crucial to recognize that although the risk of transmission is low, the potential consequences can be severe.
- Healthcare facilities should therefore maintain rigorous sterilization protocols and continuously monitor the effectiveness of their sterilization methods.
“Even though the risk of transmission is low, the potential consequences can be severe.”
- Healthcare facilities must prioritize proper sterilization to prevent pathogen transmission.
- Continuous monitoring of sterilization methods ensures effectiveness and safety.
7. Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) Explained
The sterility assurance level (SAL) is a crucial concept in the field of sterilization. It refers to the probability of a single viable microorganism occurring on a product after sterilization. A lower SAL value signifies a higher level of confidence in the device’s sterility.
Typically, a SAL of 10^-6 is considered acceptable for medical devices intended to come into contact with sterile body tissues or fluids. This means that there is a one in a million chance of a viable microorganism being present on the device after sterilization.
To ensure the desired SAL, healthcare facilities must:
- Adhere to stringent sterilization processes
- Closely monitor the efficacy of their chosen sterilization methods.
Note: The sterility assurance level (SAL) plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
8. Ensuring Sterility For Critical Items
To prevent disease transmission, critical items that come into contact with sterile body tissues or fluids must be sterile. Ensuring sterility for these items requires a rigorous approach to sterilization.
Heat sterilization remains the preferred method for heat-resistant critical items. However, for heat- and moisture-sensitive items, low-temperature sterilization technologies must be used. Healthcare facilities should assess the materials and properties of each item to determine the appropriate sterilization method.
It is essential to:
- carefully follow manufacturer instructions
- maintain proper sterilization equipment
- regularly monitor the sterilization process
This will ensure the consistent sterility of critical items.
“Proper sterilization of critical items is crucial in preventing disease transmission.”
9. Choosing The Right Sterilization Technology
Choosing the right sterilization technology for medical devices is crucial to ensure both effectiveness and safety. The selection process should consider factors such as:
- Device material compatibility
- Device complexity
- Required turnaround time
- Cost-effectiveness
Heat sterilization methods, such as steam sterilization and dry heat sterilization, are suitable for heat-resistant items and offer proven efficacy.
Low-temperature sterilization technologies, such as hydrogen peroxide gas plasma and peracetic acid immersion, are ideal for heat- and moisture-sensitive items. These technologies provide effective sterilization while mitigating the risk of damage to delicate materials.
The decision of which sterilization technology to use should be based on a thorough assessment of the device’s requirements and the facility’s resources.
- Steam sterilization and dry heat sterilization are suitable for heat-resistant items.
- Hydrogen peroxide gas plasma and peracetic acid immersion are ideal for heat- and moisture-sensitive items.
“Choosing the right sterilization technology is crucial to ensure both effectiveness and safety.”
10. Summary Of Sterilization Technologies
To summarize the advantages and disadvantages of commonly used sterilization technologies:
- Heat sterilization methods, such as steam sterilization and dry heat sterilization, offer proven effectiveness but are limited to heat-resistant items.
- Ethylene oxide gas provides an effective means of sterilizing heat- and moisture-sensitive devices but requires careful handling due to its flammability and toxicity.
- Hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilization offers a low-temperature alternative that leaves no harmful residues but may require longer cycle times.
- Peracetic acid immersion sterilization is a safe and efficient method for heat- and moisture-sensitive items but may require additional drying time.
Each sterilization technology has its own merits and limitations, and the choice should be made based on the specific requirements of the medical devices and the healthcare facility’s capabilities.
In conclusion, sterilization plays a crucial role in maintaining hygiene and preventing the transmission of diseases in healthcare settings.
Heat sterilization methods are widely used for heat-resistant items, while low-temperature sterilization technologies have emerged to address the increasing number of heat- and moisture-sensitive devices. Ensuring sterility for critical items is essential to prevent disease transmission, and selecting the appropriate sterilization technology requires careful consideration of factors such as device compatibility and facility resources.
By adhering to strict sterilization protocols and monitoring the effectiveness of sterilization processes, healthcare facilities can provide a safe environment for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
- Heat sterilization methods are effective but limited to heat-resistant items.
- Ethylene oxide gas is effective for heat- and moisture-sensitive devices but requires careful handling.
- Hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilization is a low-temperature alternative.
- Peracetic acid immersion sterilization is safe and efficient but requires additional drying time.
💡
You may need to know these questions about sterilization
What happens when a woman is sterilized?
When a woman undergoes sterilization, her fallopian tubes are blocked, cutting off the pathway for eggs to meet with sperm and be fertilized. As a result, the eggs are released from the ovaries, but they are naturally absorbed by the woman’s body instead of being fertilized in the womb. Sterilization is a surgical procedure that permanently prevents pregnancy.
What is human sterilization?
Human sterilization is a permanent form of birth control that can be done for both men and women. For men, it involves the removal or blocking of the testicles, which are responsible for producing sperm and testosterone. This can be achieved through surgical procedures such as vasectomy, rendering the individual unable to impregnate a woman. In women, tubal sterilization is the most common method, where the fallopian tubes are either tied, banded, clipped, or sealed with electric current. This prevents the eggs from reaching the uterus and thus avoids pregnancy. These procedures provide a reliable and irreversible means to prevent conception.
What is sterilization birth control?
Sterilization birth control refers to the process of female sterilization, which is an outpatient surgical procedure that aims to permanently prevent pregnancy. The procedure involves blocking the fallopian tubes, which hinders the movement of eggs from the ovaries to the uterus, thereby preventing fertilization by sperm. By obstructing the natural pathway of conception, sterilization birth control provides a reliable and long-term solution for individuals seeking to avoid pregnancy. This method of contraception has gained popularity due to its effectiveness and permanence, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their reproductive choices.
What are the 3 types of sterilization?
Alongside steam sterilization, dry heat and ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization are also widely used methods. Dry heat sterilization involves the use of high temperatures, typically between 160-180 degrees Celsius, to eliminate microorganisms. It is commonly used for heat-resistant equipment that cannot be sterilized using steam or other methods. Ethylene oxide sterilization, on the other hand, utilizes a combination of temperature, humidity, and gas concentration to effectively disinfect products. This method is particularly effective for temperature-sensitive items, such as plastics and electronics. Overall, these three sterilization methods play vital roles in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical and scientific equipment.
Reference source
https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/disinfection/sterilization/index.html
https://www.nhsinform.scot/healthy-living/contraception/female-sterilisation
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/sterilization-for-women-and-men
https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/fact-sheet/sterilization-as-a-family-planning-method/