In the world of medical conditions, there are some terms that may sound intimidating but hold fascinating stories.
One such term is “submucous myoma.” Though it might sound complex, the intrigue lies beneath the surface.
In this brief introduction, we will delve into the realm of submucous myomas, exploring their nature, impact, and the path to understanding.
So, let us embark on this captivating journey and uncover the mysteries that lie within.
submucous myoma
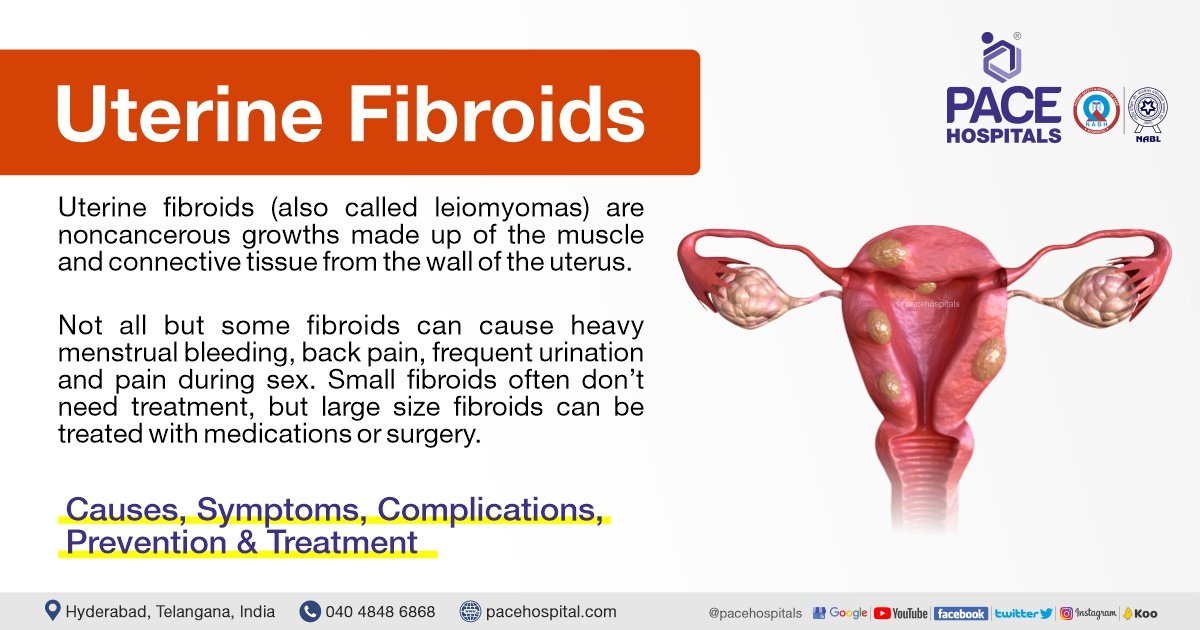
A submucous myoma is a type of uterine fibroid that grows within the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium.
It is a benign tumor composed of smooth muscle tissue.
Submucous myomas can cause symptoms such as heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, or infertility.
Surgical removal is often recommended for symptomatic cases, such as hysteroscopic myomectomy, to alleviate symptoms and improve fertility outcomes.
Key Points:
- Submucous myomas grow within the lining of the uterus (endometrium).
- They are benign tumors composed of smooth muscle tissue.
- Symptoms of submucous myomas can include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, or infertility.
- Surgical removal, such as hysteroscopic myomectomy, is often recommended for symptomatic cases.
- The surgical removal of submucous myomas can alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical removal can also improve fertility outcomes.
submucous myoma – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Submucous myomas are a subtype of uterine fibroids, which are noncancerous growths that develop in the muscular walls of the uterus.
2. Studies have shown that submucous myomas cause heavy menstrual bleeding in approximately 30% of women who have them.
3. The size of submucous myomas can vary significantly, ranging from as small as a seed to as large as a grapefruit.
4. Despite their common occurrence, submucous myomas often go undiagnosed because they may not cause any noticeable symptoms.
5. Surgical removal called hysteroscopic myomectomy is considered the gold standard treatment for submucous myomas, as it allows the fibroids to be removed without making any incisions in the abdomen.
Definition Of Submucous Myoma
Submucous myoma, also known as submucosal fibroids, is a type of uterine fibroid that develops within the muscular wall of the uterus, just beneath the lining of the uterine cavity. These growths are typically benign and can vary in size, ranging from small, pea-sized nodules to larger masses that distort the shape of the uterus. Submucous myomas are often categorized as a subtype of uterine leiomyomas, which are noncancerous tumors that arise from the smooth muscle cells of the uterus.
Causes Of Submucous Myoma
The exact cause of submucous myoma is still unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to their development. Hormonal imbalances, specifically an excess of estrogen, are thought to play a role in the growth and progression of submucous myomas. Genetic predisposition and certain medical conditions, such as obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), may also increase the risk of developing these fibroids. Additionally, there is evidence to suggest that long-term use of certain medications, such as tamoxifen, may increase the likelihood of developing submucous myomas.
Symptoms Of Submucous Myoma
The presence of submucous myomas can lead to a variety of symptoms. However, it is important to note that not all women may experience noticeable signs. Common symptoms associated with submucous myomas include:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Enlarged abdomen
In addition, some women may also experience fertility issues or recurrent miscarriages as a result of submucous myomas. It is worth mentioning that the severity and frequency of these symptoms can vary depending on factors such as the location, size, and number of fibroids present.
To summarize:
- Submucous myomas can cause various symptoms, but they may not always be noticeable.
- Symptoms can include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, difficulty emptying the bladder, and an enlarged abdomen.
- Fertility issues and recurrent miscarriages can also be associated with submucous myomas.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management of submucous myomas.
Note: The content could be further improved with additional details or explanations, if desired.
Diagnosis Of Submucous Myoma
If submucous myoma is suspected, a healthcare provider will perform a thorough evaluation to confirm the diagnosis. This may include a pelvic examination, ultrasound imaging, MRI, or hysteroscopy. Pelvic exams can help identify any abnormalities in the uterus, while ultrasounds and MRIs provide detailed images of the fibroids and allow for accurate measurements. Hysteroscopy, a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the uterus, can provide direct visualization of the fibroids and aid in diagnosis.
Treatment Options For Submucous Myoma
The treatment options for submucous myoma depend on several factors, including:
- severity of symptoms
- patient’s desire for future fertility
- size and location of the fibroids
The range of treatment options includes:
- Conservative approaches to surgical intervention
- Watchful waiting with regular monitoring for minimal symptoms or small fibroids
- Hormonal medications such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists or progestins to alleviate severe symptoms
- Non-surgical treatments like uterine artery embolization (cuts off blood supply to fibroids) and focused ultrasound surgery (destroys fibroids using ultrasound waves)
However, surgical procedures are often necessary for complete removal of submucous myomas.
Surgical Procedures For Submucous Myoma Removal
Several surgical options exist for the removal of submucous myomas. Hysteroscopic myomectomy is a minimally invasive procedure in which fibroids located within the uterine cavity are removed using a hysteroscope. This procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis and allows for a quick recovery.
Another surgical option is laparoscopic myomectomy, which involves making small incisions in the abdomen to access and remove the fibroids.
In cases where the size or location of the fibroids makes these approaches challenging, an abdominal myomectomy, which requires a larger incision, may be necessary.
In some cases, a hysterectomy, the complete removal of the uterus, may be recommended if fertility is not a concern or if other treatment options have been exhausted.
Some key points to note about surgical options for submucous myomas are:
- Hysteroscopic myomectomy is a minimally invasive procedure using a hysteroscope.
- Laparoscopic myomectomy involves small incisions in the abdomen.
- Abdominal myomectomy may be necessary for challenging cases.
- Hysterectomy is an option if fertility is not a concern or other treatments have failed.
“Surgical options for submucous myomas include hysteroscopic myomectomy, laparoscopic myomectomy, and abdominal myomectomy. In some cases, a hysterectomy may be recommended. These procedures vary in their invasiveness and are chosen based on factors such as fibroid size, location, and patient preferences.”
Potential Complications Of Submucous Myoma
While submucous myomas are generally noncancerous and pose minimal health risks, they can sometimes lead to complications. The most common complications include:
- Anemia due to excessive bleeding
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
- Pregnancy complications such as miscarriage or preterm labor
In rare cases, submucous myomas may undergo a process called degeneration, in which the cells of the fibroid break down and cause severe pain. Additionally, larger submucous myomas may cause significant distortion of the uterine cavity, potentially impacting the function of other organs or leading to urinary or bowel problems.
Bullet points:
- Anemia due to excessive bleeding
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
- Pregnancy complications such as miscarriage or preterm labor
Prevention Strategies For Submucous Myoma
The exact cause of submucous myoma is still unknown, making it difficult to prevent their development. However, several lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: This can contribute to overall hormonal balance and potentially lower the risk of developing submucous myomas.
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can also help maintain hormonal balance and minimize the risk of submucous myoma.
- Managing stress levels: High levels of stress can have an impact on hormonal imbalance, so finding effective stress management techniques can be beneficial in reducing the risk.
In addition to lifestyle changes, it is important to undergo regular gynecological check-ups and promptly address any abnormal symptoms. This is crucial for the early detection and management of submucous myomas.
Steps to reduce the risk of submucous myomas:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly
- Manage stress levels
- Regular gynecological check-ups
- Promptly address any abnormal symptoms.
Prognosis For Patients With Submucous Myoma
The prognosis for patients with submucous myoma can vary depending on the individual and the specific characteristics of the fibroids. In general, submucous myomas are benign and do not pose significant health risks. However, the impact of these fibroids on fertility and pregnancy outcomes can vary. With appropriate medical intervention, management of symptoms is often successful, and many women are able to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. It is essential for individuals with submucous myoma to consult with their healthcare provider to receive personalized treatment and guidance.
Research Advancements In Submucous Myoma Treatment
Advancements in research are continuously being made to improve the understanding and treatment of submucous myoma. Studies are exploring new medication options, such as selective progesterone receptor modulators (SPRMs), for nonsurgical management of symptoms. Additionally, researchers are investigating novel techniques for the minimally invasive removal of submucous myomas, such as:
- Robotic-assisted surgery
- Transvaginal ultrasound-guided procedures
Further advancements in the field may lead to more effective and less invasive treatment options for women diagnosed with submucous myoma, improving their quality of life and reproductive outcomes.
💡
You may need to know these questions about submucous myoma
What is submucous myoma?
Submucous myoma refers to a type of benign tumor that grows underneath the lining of the uterus. This condition often leads to abnormal uterine bleeding and can contribute to infertility in women. Prior to the 1970s, the options for removing submucous myomas that did not protrude through the cervix were limited to abdominal myomectomy or hysterectomy. However, thanks to the introduction of hysteroscopic resection by Neuwirth, a less invasive technique became available for treating this condition.
Is submucosal myoma cancerous?
No, submucosal myomas are not cancerous. They are benign growths that develop in the inner lining of the uterus. Although they are not cancerous, submucosal fibroids can cause various symptoms such as heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and fertility issues. It is important for women experiencing these symptoms to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
How do you treat a submucous myoma?
The treatment for submucous myoma involves the use of ultrasound-guided intratumor injection of lauromacrogol. This procedure is known for its simplicity and effectiveness in reducing tumor size and volume. Additionally, it improves blood flow, minimizes postoperative complications, and alleviates the patient’s pain. Overall, this approach provides a valuable solution for managing submucous myoma of the uterus.
What causes a submucous myoma?
While the exact cause of submucous myoma remains unclear, hormonal factors seem to have a significant influence. The interplay between estrogen and progesterone levels is believed to contribute to the development of these fibroids. Additionally, genetic predisposition and being overweight have been identified as potential risk factors. However, further research is necessary to fully understand the underlying cause of submucous myoma.
Reference source
https://journals.lww.com/clinicalobgyn/fulltext/2006/12000/hysteroscopic_treatment_of_submucous_myomas.10.aspx
https://njgyncancer.com/news-events/fibroid-management/what-is-a-submucosal-fibroid-and-how-can-it-be-treated/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5876458/
https://midcityobgyn.com/posts/fibroids/what-is-a-submucosal-fibroid-and-how-can-it-be-treated/