Subserous myoma, lurking on the periphery of the uterus, possess an unsuspecting menace.
Benevolent yet troublesome, these benign tumors can wreak havoc on a woman’s health.
But fear not, for science has birthed an arsenal of treatments to combat this foe.
Join us as we unravel the mysteries of subserous myoma, delving into the realm of surgery and medication, where hope lies dormant, waiting to be awakened.
subserous myoma
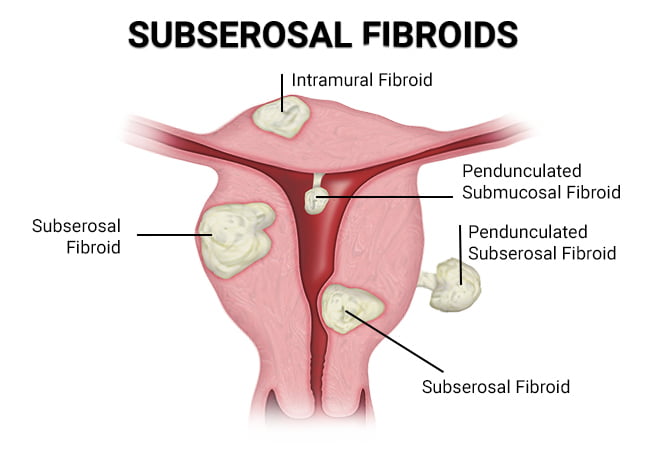
Subserous myoma, also known as subserosal fibroids, are benign tumors that grow on the exterior of the uterus.
The exact cause is unknown, but genetics and hormones may play a role.
African American women and those who have never had children or started puberty early have a higher risk.
Symptoms include a feeling of heaviness, frequent urination, constipation, and bloating.
Subserosal fibroids can cause complications during pregnancy and may require a cesarean delivery.
Diagnosis is made through a pelvic exam and additional tests.
Treatment options include uterine fibroid embolization, hysterectomy, and myomectomy.
Subserosal fibroids are non-cancerous and can impact nearby organs.
They may cause pain, infertility, and can lead to complications during childbirth.
Treatment depends on the condition, size, and location of the fibroids.
Key Points:
- Subserous myoma are benign tumors that grow on the exterior of the uterus.
- The cause is unknown, but genetics and hormones may be involved.
- African American women, those who haven’t had children or started puberty early are at a higher risk.
- Symptoms include heaviness, frequent urination, constipation, and bloating.
- Subserosal fibroids can lead to complications during pregnancy and require a cesarean delivery.
- Diagnosis is made through a pelvic exam and additional tests.
subserous myoma – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Subserous myomas are a type of uterine fibroid that grow on the outer layer of the uterus, just beneath the serosa.
2. Subserous myomas are usually benign and don’t often cause significant symptoms, making them the least problematic type of uterine fibroid.
3. While subserous myomas are generally non-cancerous growths, they can sometimes become cancerous in very rare cases. Regular monitoring is important to rule out any potential malignant transformation.
4. Subserous myomas can vary in size, ranging from tiny nodules to large masses that can distort the shape of the uterus.
5. Although the exact cause of subserous myomas is unknown, research suggests that hormonal imbalances, genetic factors, and estrogen dominance may contribute to their development.
Definition Of Subserosal Fibroids
Subserosal fibroids are a type of benign tumor that grows on the exterior surface of the uterus, specifically the uterine serosa. They are the most common type of uterine fibroid and are typically non-cancerous.
These fibroids can vary in size, ranging from small pea-sized growths to large masses that can distort the shape of the uterus. While they primarily develop on the outer layer of the uterus, subserosal fibroids may also extend inward and affect nearby organs such as the bladder and bowels.
Although these fibroids are generally harmless, they can cause symptoms and complications if left untreated.
- Subserosal fibroids are a type of benign tumor
- They grow on the exterior surface of the uterus, specifically the uterine serosa
- They are the most common type of uterine fibroid
- They are typically non-cancerous
- They can vary in size from small pea-sized growths to large masses
- They can distort the shape of the uterus
- They may extend inward and affect nearby organs such as the bladder and bowels
- If left untreated, they can cause symptoms and complications.
“Although these fibroids are generally harmless, they can cause symptoms and complications if left untreated.”
Possible Causes Of Subserosal Fibroids
The exact cause of subserosal fibroids is still unknown, but several factors have been identified as potential contributors. Genetics is believed to play a role, as having a family history of fibroids increases the risk of developing them. Hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, are also thought to influence fibroid growth. Research suggests that these hormones promote the development of fibroids, which explains why they tend to develop during the reproductive years.
Higher Risk Factors For Subserosal Fibroids
Certain factors increase the risk of developing subserosal fibroids. African American women have a higher susceptibility to fibroids compared to women of other ethnicities. Additionally, women who have never had children or started puberty early (before the age of 12) are more likely to develop fibroids. Furthermore, excess weight or obesity has been associated with an increased risk of fibroids.
Complications During Pregnancy
Subserosal fibroids can cause complications during pregnancy. They may lead to difficulties during childbirth if they grow larger and limit the space for the baby to grow. Complications such as lower birth weight and the need for a cesarean delivery can arise due to the presence of subserosal fibroids.
It is important for pregnant women with fibroids to receive appropriate monitoring and care to minimize potential risks.
- Subserosal fibroids can cause complications during pregnancy
- Difficulties during childbirth may arise if the fibroids grow larger and limit space for the baby
- Presence of subserosal fibroids can lead to lower birth weight and the need for a cesarean delivery
- Pregnant women with fibroids should receive appropriate monitoring and care to minimize risks
Common Symptoms Of Subserosal Fibroids
Subserosal fibroids are growths that develop in the outer layer of the uterus and can cause a range of symptoms with varying degrees of severity. It is important to be aware of the following signs and symptoms:
- Feeling of heaviness or fullness in the pelvic region
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Bloating
Additional symptoms may include:
- Abdominal cramping
- Pain in the lower back and legs
- Pain during sexual intercourse
These symptoms can have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life. It is crucial to seek proper medical evaluation and treatment for effective management of subserosal fibroids.
- For pelvic region: feeling of heaviness or fullness
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Bloating
- Abdominal cramping
- Pain in lower back and legs
- Pain during sexual intercourse
Diagnosis Of Subserosal Fibroids
Diagnosing subserosal fibroids typically involves a series of medical procedures and tests. A pelvic examination is often conducted to detect the presence of fibroids and assess their size and location. Additionally, imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be recommended to provide a more detailed view of the fibroids and their effects on the uterus and nearby organs. These diagnostic measures assist healthcare providers in formulating an appropriate treatment plan.
- Pelvic examination: A standard procedure used to detect the presence of fibroids and evaluate their size and location.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans provide a detailed view of fibroids and their impact on the uterus and nearby organs.
- These diagnostic measures help healthcare providers in devising an optimal treatment plan.
Importance Of Treating Subserosal Fibroids
Treating subserosal fibroids is crucial for various reasons. Alleviating symptoms such as pain, discomfort, and urinary or bowel issues can greatly improve a woman’s quality of life. Moreover, prompt treatment can help prevent complications during pregnancy and childbirth. The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s symptoms, fibroid size, and overall health. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment option.
Improvements:
- Emphasize the importance of treating subserosal fibroids.
- Highlight the impact on a woman’s quality of life.
- Stress the significance of preventing complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
- Make it clear that the choice of treatment depends on individual factors.
- Recommend consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options For Subserosal Fibroids
Non-surgical treatment options, such as Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE), are available to address subserosal fibroids. UFE is a minimally invasive procedure that effectively shrinks fibroids by cutting off their blood supply. This technique has demonstrated success in reducing fibroid-related symptoms and preserving the uterus.
Aside from UFE, there are additional treatment options for subserosal fibroids. These include hormone therapy which helps to regulate hormone levels and manage symptoms. Additionally, medication can be used to alleviate pain and discomfort associated with the condition.
Surgical Treatment Options For Subserosal Fibroids
In cases where non-surgical interventions are not effective or appropriate, surgical intervention may be necessary. Hysterectomy, the surgical removal of the uterus, is a permanent solution for fibroid treatment. However, this procedure is typically reserved for cases where fertility preservation is not a concern.
On the other hand, myomectomy involves the removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus. This option is suitable for women who wish to conceive in the future.
- Hysterectomy: Surgical removal of the uterus
- Permanent solution for fibroid treatment
-
Typically used when fertility preservation is not a concern
-
Myomectomy: Removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus
- Suitable for women who wish to conceive in the future
“In cases where non-surgical interventions are not effective or appropriate, surgical intervention may be necessary.”
Impact On Fertility And Pregnancy Complications
Subserosal fibroids and their impact on fertility
Subserosal fibroids, although they may have less impact on fertility compared to other types of fibroids, can still affect a woman’s ability to conceive. Depending on their size and location, they can obstruct the cervix or fallopian tubes, hindering the fertilization process.
During pregnancy, the growth of subserosal fibroids may also limit the space available for the developing baby, potentially leading to difficulties during childbirth and other pregnancy-related complications.
It is therefore important for women planning to conceive to consult with their healthcare provider to address any underlying fibroids and optimize their chances of a successful pregnancy.
- Subserosal fibroids may obstruct the cervix or fallopian tubes, hindering fertilization
- The growth of subserosal fibroids during pregnancy can lead to complications
- Consultation with a healthcare provider is important for optimizing chances of a successful pregnancy
Women planning to conceive should consult with their healthcare provider to address any underlying fibroids and optimize their chances of a successful pregnancy.
With timely medical intervention, symptoms can be managed, pregnancy-related complications can be prevented, and fertility can be preserved. Treatment options, both surgical and non-surgical, are available and should be tailored to each individual’s needs and preferences.
- Subserosal fibroids can be managed and prevented with timely medical intervention
- Treatment options should be tailored to individual needs and preferences
In summary:
Subserosal fibroids are a common type of benign tumor that grows on the exterior of the uterus. While the exact cause of these fibroids remains unknown, factors such as genetics, hormones, and certain risk factors can contribute to their development.
Recognizing the symptoms of subserosal fibroids and seeking appropriate medical intervention is crucial to improving quality of life and reproductive health for women with this condition.
- Subserosal fibroids are a common type of benign tumor
- The cause of subserosal fibroids is unknown, but genetics, hormones, and risk factors can contribute to their development
- Timely medical intervention is important for managing symptoms and improving reproductive health.
💡
You may need to know these questions about subserous myoma
What is the treatment for subserous myoma?
The treatment for subserous myoma, a type of fibroid that grows outside of the uterus, varies depending on the severity and symptoms. In some cases, hormone therapy may be prescribed to help shrink the fibroid and alleviate symptoms. Another non-invasive option is focused ultrasound surgery, which uses high-intensity ultrasound waves to heat and destroy the fibroid tissue. This procedure effectively treats the fibroid while preserving fertility. It is important for a woman to consult with her healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on her specific situation and future reproductive goals.
Do Subserosal fibroids need to be removed?
In most cases, it is not necessary to remove small asymptomatic subserosal fibroids. These fibroids can be simply observed through regular ultrasounds without any treatment. However, if the fibroids grow larger and start causing symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding due to the increased size of the uterus, removal may be considered. It is important to monitor the fibroids and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action based on the individual’s specific circumstances.
Is Subserosal myoma cancerous?
No, subserosal fibroids are not cancerous. These fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that develop within the outer wall of the uterus, known as the serosa. Although they can cause discomfort and potentially lead to various symptoms, subserosal fibroids are not cancerous and do not pose a cancer risk. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance regarding the management of subserosal fibroids.
Do myomas need to be removed?
While women without symptoms may not require immediate treatment for myomas, regular evaluation by their doctors is crucial. Symptoms caused by fibroids can vary greatly and can range from mild discomfort to severe pain or fertility issues. Treatment options for symptomatic women include both non-surgical and surgical approaches. Non-surgical treatments such as medication can be opted for to alleviate symptoms and preserve fertility, while surgical procedures may be considered if symptoms are severe or if fertility is not a concern. Ultimately, the decision to remove myomas is dependent on the individual’s specific circumstances, symptoms, and desire to conceive.
Reference source
https://www.azuravascularcare.com/infoufe/what-is-a-myoma/
https://www.usafibroidcenters.com/uterine-fibroids/subserosal-fibroid/
https://www.advancedgynaecologymelbourne.com.au/fibroids/types
https://www.astraveinvascular.com/subserosal-fibroids/