Understanding the Ruptured Hymen: Myths, Facts, and Healing
– A ruptured hymen is a flimsy tissue that covers the vaginal opening
– Not all women bleed when their hymen breaks
– Bleeding from a ruptured hymen is typically a small amount and should not cause much discomfort
– Hymen does not fully protect the vaginal opening
– Inserting a tampon should not cause pain
– Symptoms of a ruptured hymen may include mild bleeding or spotting, discomfort or pain around the vaginal opening, and a broken layer near the vaginal opening
– Not all women are born with a hymen
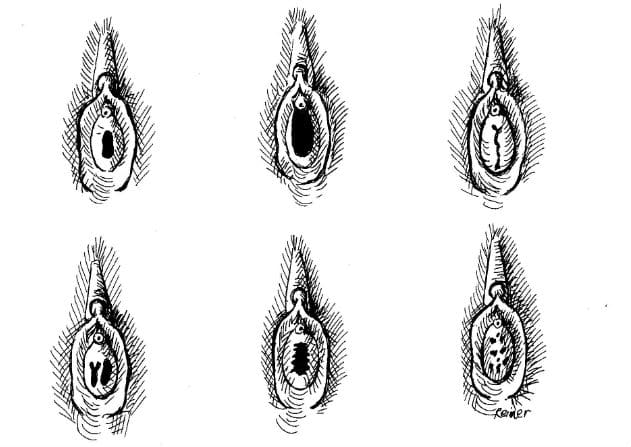
– The hymen may not be visible or noticeable, blending in with the color of the vagina
– Various activities can cause a ruptured hymen, such as penetrative sexual intercourse, horseback riding, riding bicycles, climbing trees or jungle gyms, playing on obstacle courses, gymnastics, dancing, using tampons, inserting menstrual cups, getting a Pap smear, and getting a transvaginal ultrasound
– Surgical options, such as hymenoplasty, can recreate a ruptured hymen
– Hymenoplasty aims to reconstruct the hymen located in the lower half of the vaginal area
– After hymenoplasty, there may be slight discomfort and pain, but patients can typically resume their daily routine within 24 to 48 hours
– Sutures used in hymenoplasty are dissolvable and do not need to be removed later
– Complete healing of a ruptured hymen may take up to 90 days during which sexual intercourse should be avoided
– The idea of a torn hymen is often associated with loss of virginity after sexual intercourse
– The hymen can tear or stretch through physical exercise, masturbation, vaginal speculums, injury, or tampon use
– Signs of a torn hymen may include light spotting or bleeding, slight discomfort or pain around the vaginal opening, and torn or broken skin around 1-2cm inside the opening
– The hymen naturally wears down over time and may tear in one go or gradually stretch and widen until it shrinks back to the vaginal walls
– Checking whether the hymen has torn can be done with a mirror, a chair, and fingers
– A thin, moon-shaped fleshy membrane across the lower section of the vaginal opening indicates an intact hymen, but the size and shape can vary