Understanding the Risks, Symptoms, and Treatment Options: Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix
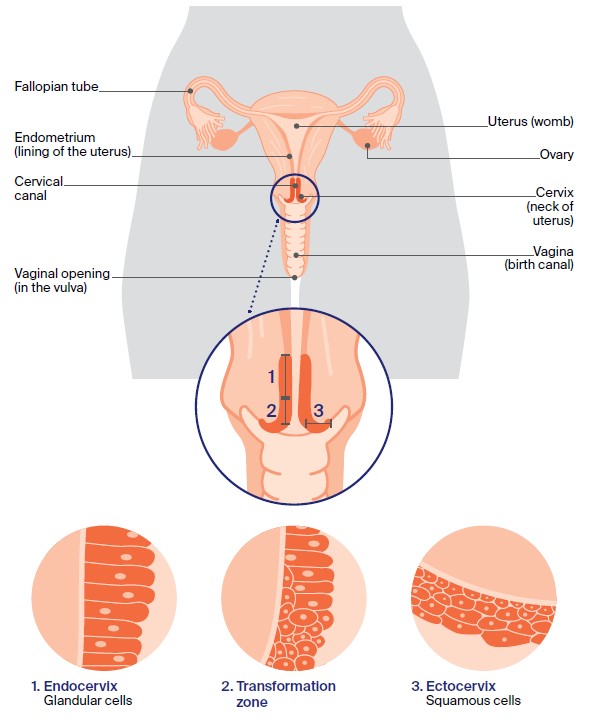
– Squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix occurs when cells in the cervix become abnormal and start to multiply uncontrollably.
– Advances in medical technology and Pap tests have helped identify cervical cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix, earlier.
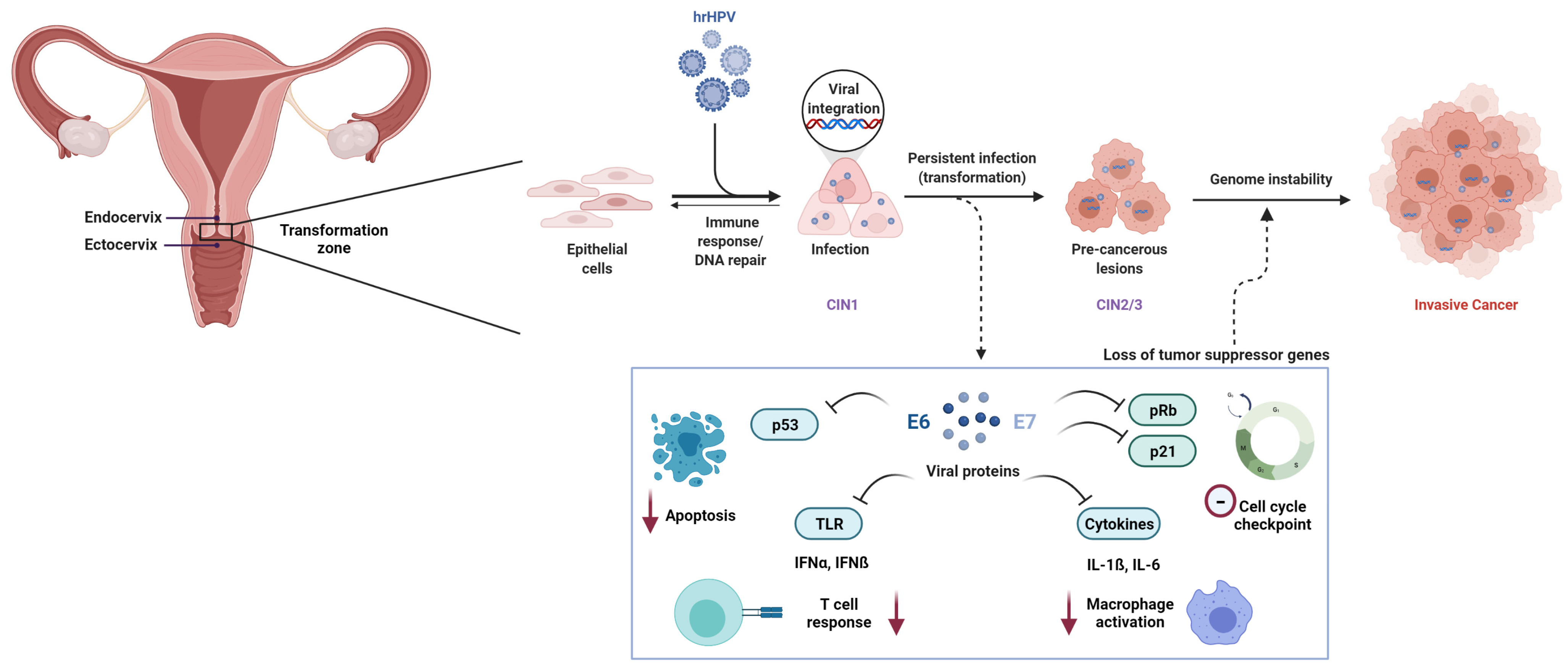
– Human papillomavirus (HPV) plays a role in causing squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix, but not everyone with HPV develops it.
– Risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix include multiple sexual encounters, weakened immune system, smoking, and exposure to the drug DES during pregnancy.
– Early stages of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix do not usually show signs or symptoms, emphasizing the importance of regular Pap smears and pelvic exams.
– Symptoms of advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix may include unusual vaginal bleeding, watery or bloody discharge, and pelvic pain.
– Regular screening for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix is recommended to start at age 21.
– HPV DNA tests and Pap tests are used to detect cervical abnormalities, including squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix, and HPV infection.
– If squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix is suspected, a colposcopy may be performed to examine the cervix more thoroughly, potentially including a punch biopsy to collect cell samples.
– The article discusses various treatment options for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted drug therapy, and immune therapy. It emphasizes the importance of considering individual health and preferences when deciding on a treatment plan.
– The article also suggests ways to cope with a squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix diagnosis, such as seeking information, finding support, setting achievable goals, and taking care of oneself.