Hydrocephalus: Understanding The Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
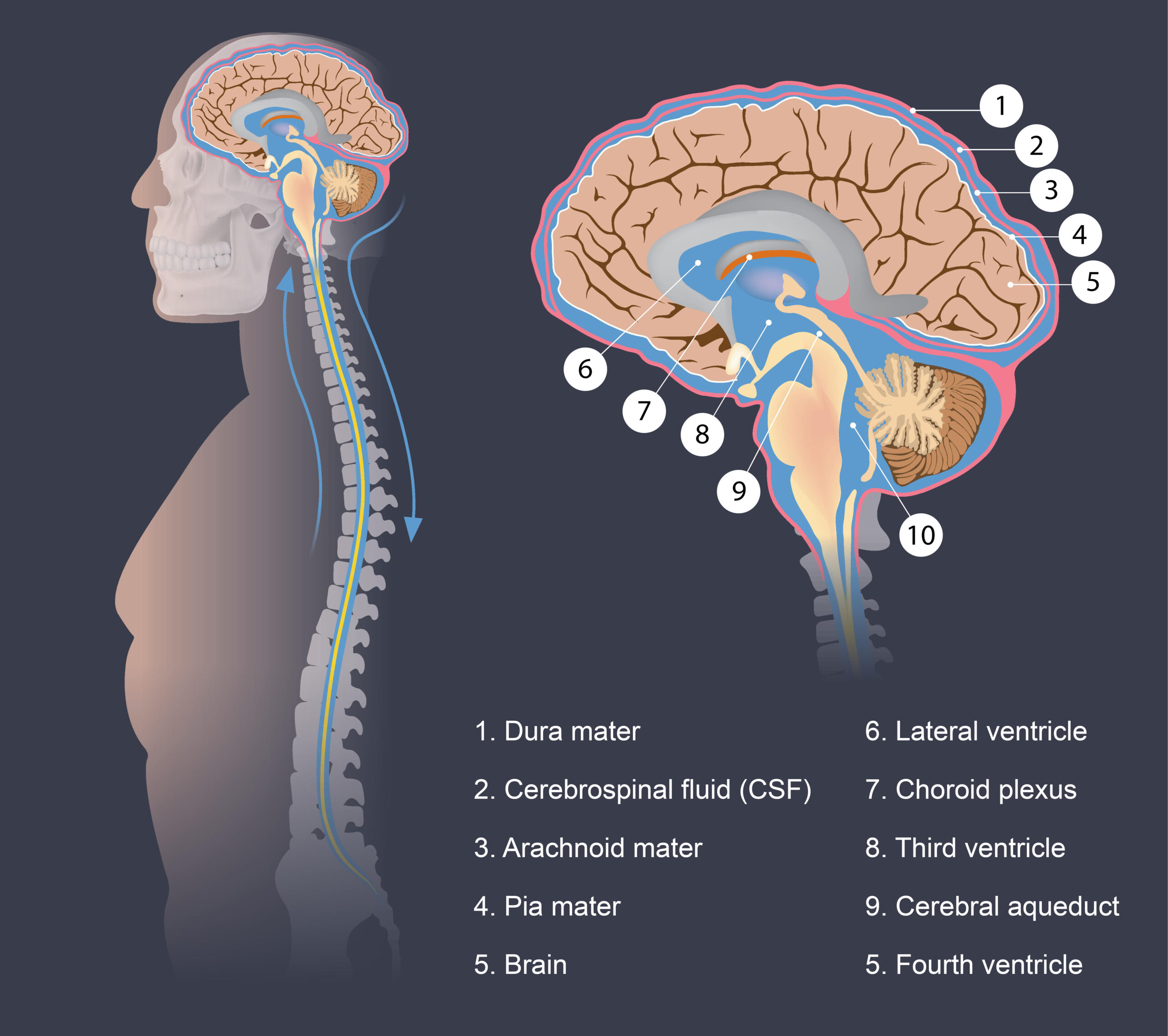
– Hydrocephalus is a neurological disorder caused by an abnormal buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain
– Symptoms in infants include rapid head size increase, bulge on the soft spot, vomiting, and seizures
– Symptoms in older children and adults include headache, blurred or double vision, nausea or vomiting, and problems with balance
– It is estimated that one to two out of every 1,000 babies are born with hydrocephalus
– Factors that increase the risk of hydrocephalus include brain or spinal cord tumors, infections, and injuries or strokes that cause bleeding in the brain
– There are different types of hydrocephalus, including communicating hydrocephalus, non-communicating hydrocephalus, Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH), and hydrocephalus ex-vacuo
– Hydrocephalus is diagnosed through a clinical neurological exam and brain imaging techniques
– Treatment for hydrocephalus involves surgery, with options including inserting a shunt into the brain to drain excess fluid or performing endoscopic third ventriculostomy
– Hydrocephalus can have long-term complications if left untreated, prompt diagnosis and treatment are important
– Rehabilitation therapies, educational interventions, and support from healthcare professionals are important for individuals with hydrocephalus
– The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) conducts research and clinical studies to find better ways to prevent, treat, and cure hydrocephalus
– NINDS supports the Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network (HCRN) to study improved treatments for hydrocephalus
– Research topics include cellular mechanisms, gene mutations, brain nerve networks, and neural stem cell behavior related to hydrocephalus
– New imaging methods are being developed to determine if shunt surgery can improve cognitive and motor difficulties associated with hydrocephalus
– Shunt malfunctions are common, and researchers are working on developing a safe and cost-effective method for diagnosing shunt malfunctions using ultrasound
– Shunts carry a high risk of infection, and scientists are researching microorganisms present in CSF during shunt placement, revision, and infection to improve prevention and treatment
– More information on hydrocephalus research supported by NINDS and other NIH Institutes and Centers can be found using NIH RePORTER
– The article suggests participating in clinical trials to help further research and improve care for people with hydrocephalus. It provides links to resources for finding clinical trials related to hydrocephalus