Exploring the Climacteric Period: Understanding the Transition
Here is the revised list pertinent to the keyword ‘climacteric period’:
– The climacteric period refers to the midlife transition when fertility declines.
– Men may experience a reduction in their ability to reproduce during the climacteric period.
– Women lose their ability to reproduce once they reach menopause.
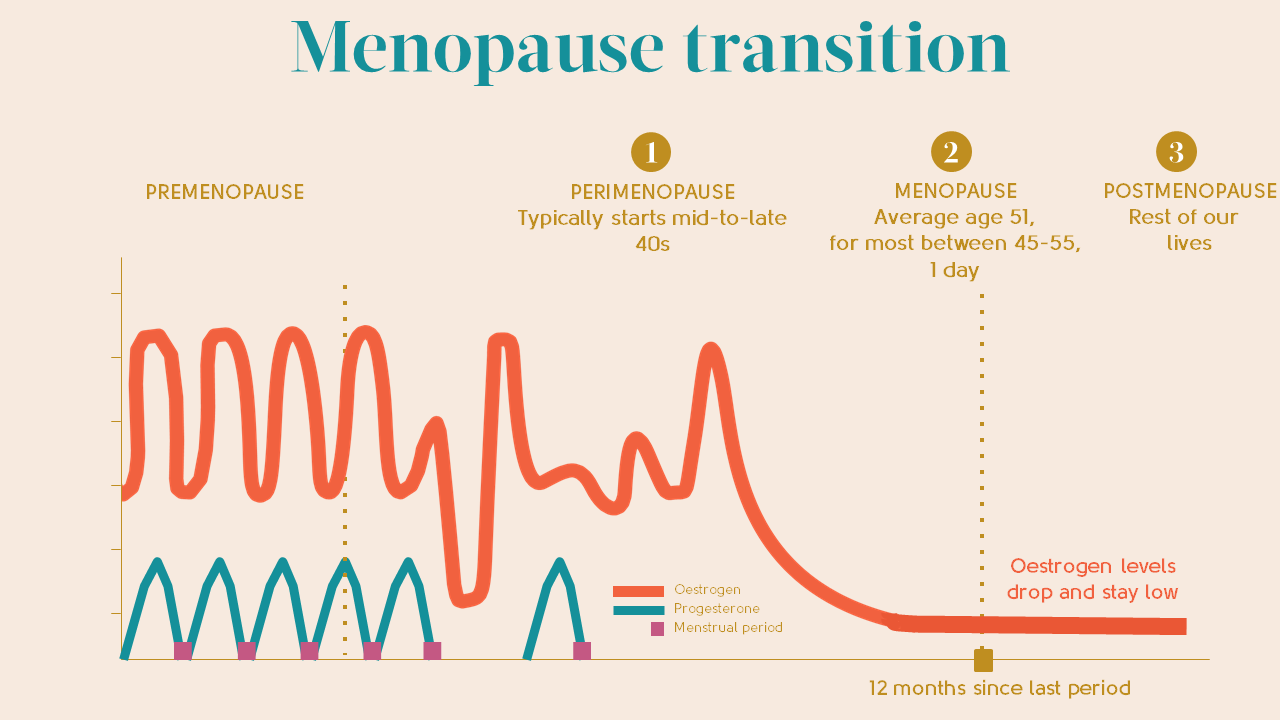
– Perimenopause is a period of transition in which a woman’s ovaries stop releasing eggs and the production of estrogen and progesterone decreases.
– Menopause is defined as 12 months without menstruation, and the average age is around 51.
– Symptoms of perimenopause and menopause are caused by decreased production of estrogen and progesterone.
– Symptoms include difficulty falling asleep, hot flashes, vaginal dryness and pain during intercourse, thinning of the vaginal wall, decreased bone mass leading to osteoporosis, depression, irritability, and weight gain.
– Concerns about hormone replacement therapy have led to a decrease in its prescription for menopausal women.
– Hormone replacement therapy has been associated with breast cancer, stroke, and the development of other conditions.
– Most women do not have severe enough symptoms to warrant estrogen or hormone replacement therapy.
– Other treatment options include lower doses of estrogen, frequent exams, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, eating soy, remaining sexually active, practicing relaxation techniques, and using water-based lubricants.
– Studies have found that menopausal symptoms vary greatly across countries, regions, and ethnic groups.
– White women were more likely to report symptoms of depression, irritability, forgetfulness, and headaches compared to other racial/ethnic groups.
– African American women experienced more night sweats, but this varied across research sites.
– Chinese and Japanese American women reported fewer menopausal symptoms compared to women in other groups.
– Cultural influences play a role in how menopause is experienced.
– Some cultures do not have specific words for menopausal symptoms, and women in these cultures may not experience certain symptoms.
– Women in different cultures have differing perceptions of menopause, with some viewing it as a loss and others as a liberating experience.
– In India, 94% of women welcomed menopause as they gained status and no longer had to follow menstrual restrictions.
– Erectile dysfunction (ED) becomes more common in middle adulthood.
– Intermittent ED affects as many as 50% of men between 40 and 70 years old.
– Approximately 30 million men in the United States experience chronic ED.
– Causes for ED include medical conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, alcoholism, and atherosclerosis.
– Plaque build-up in the arteries can restrict blood flow and cause ED.
– Diseases account for 70% of chronic ED, while psychological factors account for 10%-20%.
– Prostate enlargement and deficient testosterone levels are common in middle adulthood.
– Low testosterone levels can cause symptoms such as low sex drive, ED, fatigue, loss of muscle, loss of body hair, or breast enlargement.
– Low testosterone is associated with medical conditions such as diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, and testicular cancer.
– Supplemental testosterone effectiveness is mixed, and long term replacement therapy can increase the risk of prostate cancer, blood clots, heart attack, and stroke.
– Most men with low testosterone do not have related problems.