Difficult delivery: Understanding the causes, risks, and solutions
– Heavier infants weighing 8 pounds and 13 ounces or more may have a difficult delivery and are more prone to birth injuries.
– Premature births before the 37th week of pregnancy have higher rates of birth injuries due to underdeveloped muscles and nervous systems in the child.
– Infants born in abnormal positions, such as head-up, buttocks-first, or breech positions, are more likely to suffer birth injuries.
– Physical injuries during the birth process, such as from the use of forceps or vacuum extraction, can cause serious birth injuries.
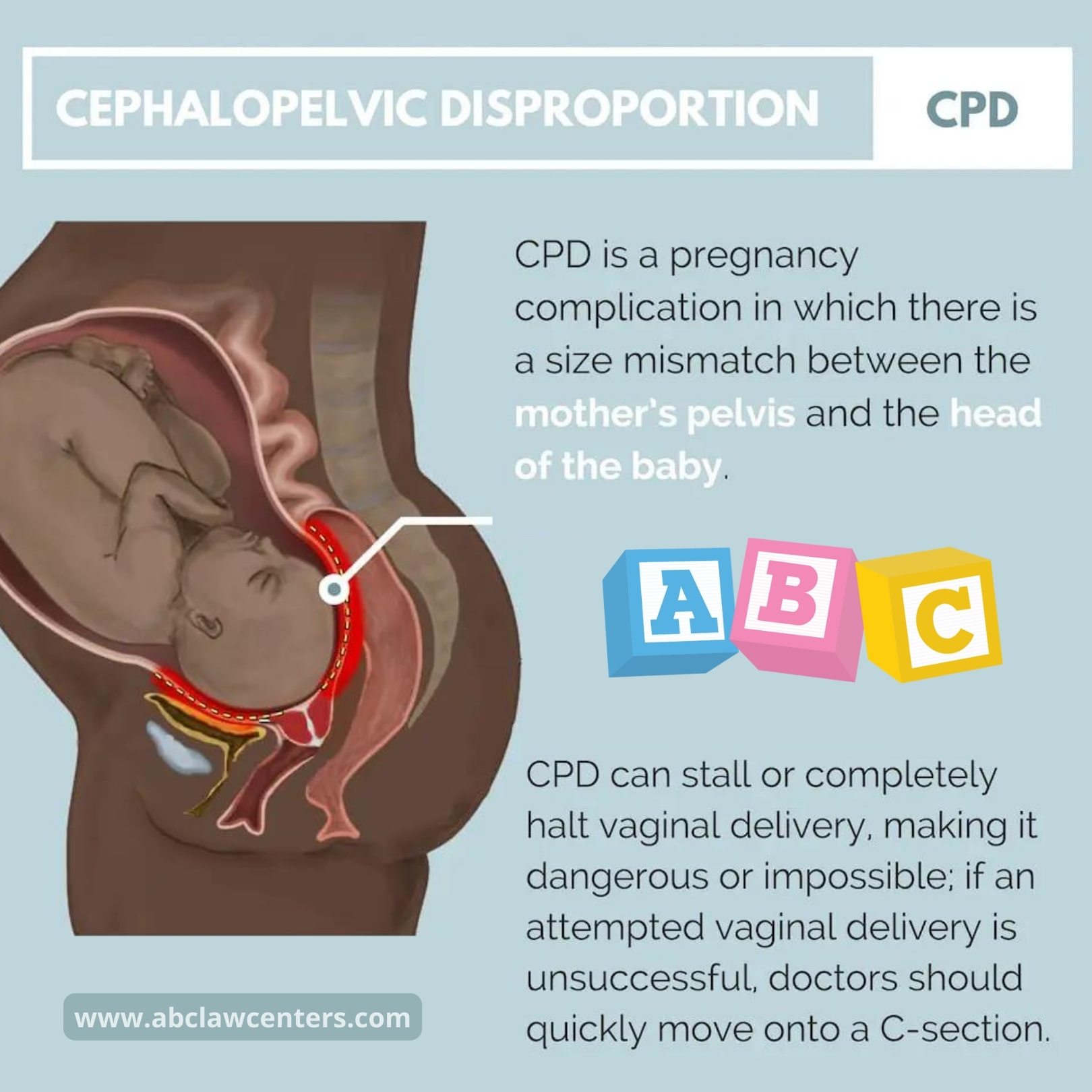
– Delayed birth lasting over 18 hours can increase pressure on the infant’s brain and lead to fetal distress, elevated blood pressure, and possible stroke or cardiovascular issues.
– Oxygen deprivation during birth caused by factors like a prolapsed umbilical cord or underdeveloped lungs can result in various injuries to newborns, including severe brain injuries.
– Medical malpractice, such as excessive force or negligence during delivery, can also lead to birth injuries, including brain damage.
– Other causes of birth injuries include improper manipulation of the child’s body during delivery, certain medications, and viral or bacterial infections in the mother or infant during pregnancy.
– A childbirth complication refers to any abnormal condition or event during pregnancy, labor, or delivery that can harm the mother or baby. Obstetric complications cause birth injuries.
– Uterine rupture is the most dangerous complication and can cause major brain damage or death for both the baby and mother.
– Shoulder dystocia is an emergency event during vaginal delivery where the baby’s shoulder becomes stuck in the birth canal, posing a risk of brain injury or death due to oxygen deprivation.
– Excessive force during delivery can cause physical injury to the baby, such as fractured collarbones or nerve damage.
– Prolapse of the umbilical cord can restrict or cut off the baby’s oxygen supply, leading to severe consequences.
– Chorioamnionitis, a bacterial infection in the amniotic fluid and/or fetal membranes, can cause brain injuries and increase the risk of major birth injuries.
– Fetal macrosomia, when undiagnosed, can be dangerous during delivery and increase the risk of the baby getting stuck in the birth canal and experiencing oxygen deprivation.
– Clinical risk factors for pregnancy complications include hypertension, gestational diabetes, breech presentation, multiples, and previous cesarean birth.
– The most commonly listed causes of maternal death in the US include uterine rupture, infection, and heart disease.