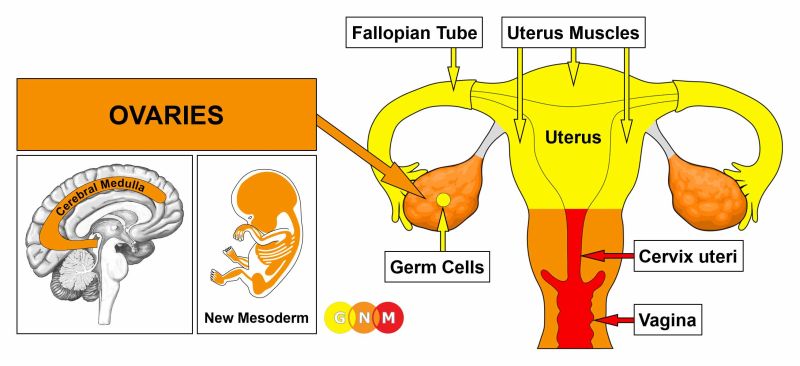
Primordial Uterus: Unveiling the Origins of Life
– Development of paramesonephric ducts in the female reproductive system
– Role of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) in the regression of paramesonephric ducts in males
– Persistence of paramesonephric ducts in males with mutations in AMH or AMH receptor genes
– Persistent Mullerian duct syndrome and its manifestations
– Abnormalities and complications associated with paramesonephric duct anomalies
– Difficulty in diagnosing paramesonephric duct anomalies
– Surgical advances improving the sexual function, fertility, and obstetric outcomes for women with these anomalies
– Assisted reproductive technology for women with paramesonephric duct anomalies
– Johannes Peter Müller and his discovery of paramesonephric ducts