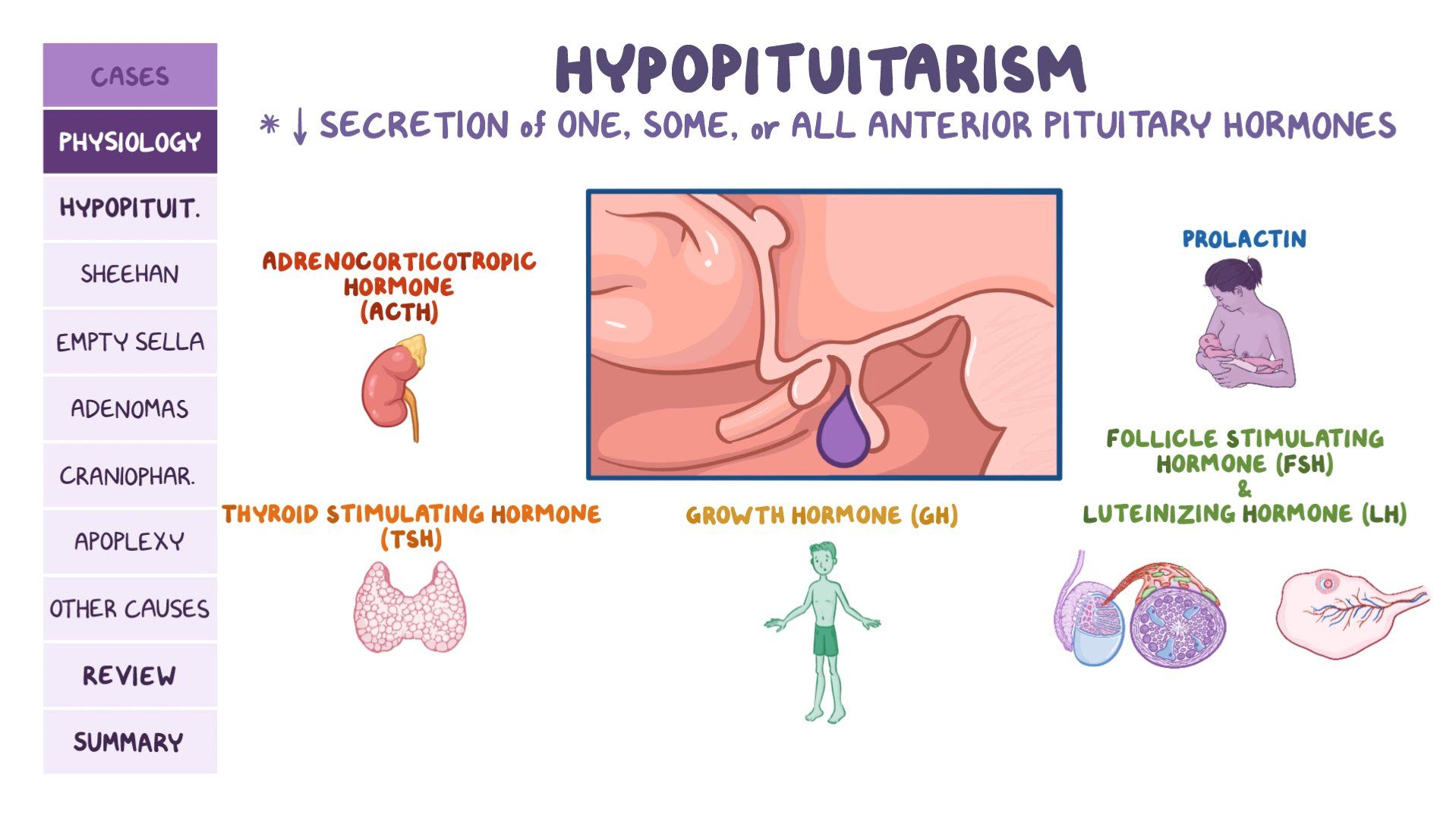
Hypopituitarism is a rare condition in which the pituitary gland doesn’t produce enough hormones. The pituitary gland is a kidney-bean-sized gland located at the base of the brain. It is part of the endocrine system, which includes other glands like the thyroid and adrenal glands. Hypopituitarism can affect various functions of the body, such as growth, blood pressure, and fertility. Symptoms of hypopituitarism depend on which hormones are deficient, and can include fatigue, muscle weakness, changes in body fat, loss of interest in activities, infertility, hot flashes, irregular periods, loss of pubic hair, erectile dysfunction, mood changes, tiredness, weight gain, dry skin, constipation, and sensitivity to cold. Treatment usually involves taking medications to replace the missing hormones.
Some important facts about hypopituitarism include:
– Symptoms can include severe tiredness, low blood pressure, frequent infections, nausea/vomiting/abdominal pain, and confusion.
– If symptoms occur suddenly or come with a bad headache, changes in vision, confusion, or a drop in blood pressure, it could indicate a medical emergency called pituitary apoplexy caused by bleeding into the pituitary gland.
– Common causes of hypopituitarism include pituitary tumors, head injuries, brain surgery, radiation treatment to the head or neck, stroke or bleeding in the brain, certain medications, inflammation of the pituitary gland, infections of the brain, diseases that affect multiple organs, significant blood loss during childbirth, and genetic factors.
– Tumors or diseases of the hypothalamus, located just above the pituitary gland, can also cause hypopituitarism.
Note: The provided text excerpts have been consolidated to remove duplication and ensure relevance to the keyword “hypopituitarism.”
Continue Reading