Anovulatory Dysfunction: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
– Abnormal uterine bleeding: menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, menometrorrhagia, intermenstrual bleeding, midcycle spotting, postmenopausal bleeding, amenorrhea
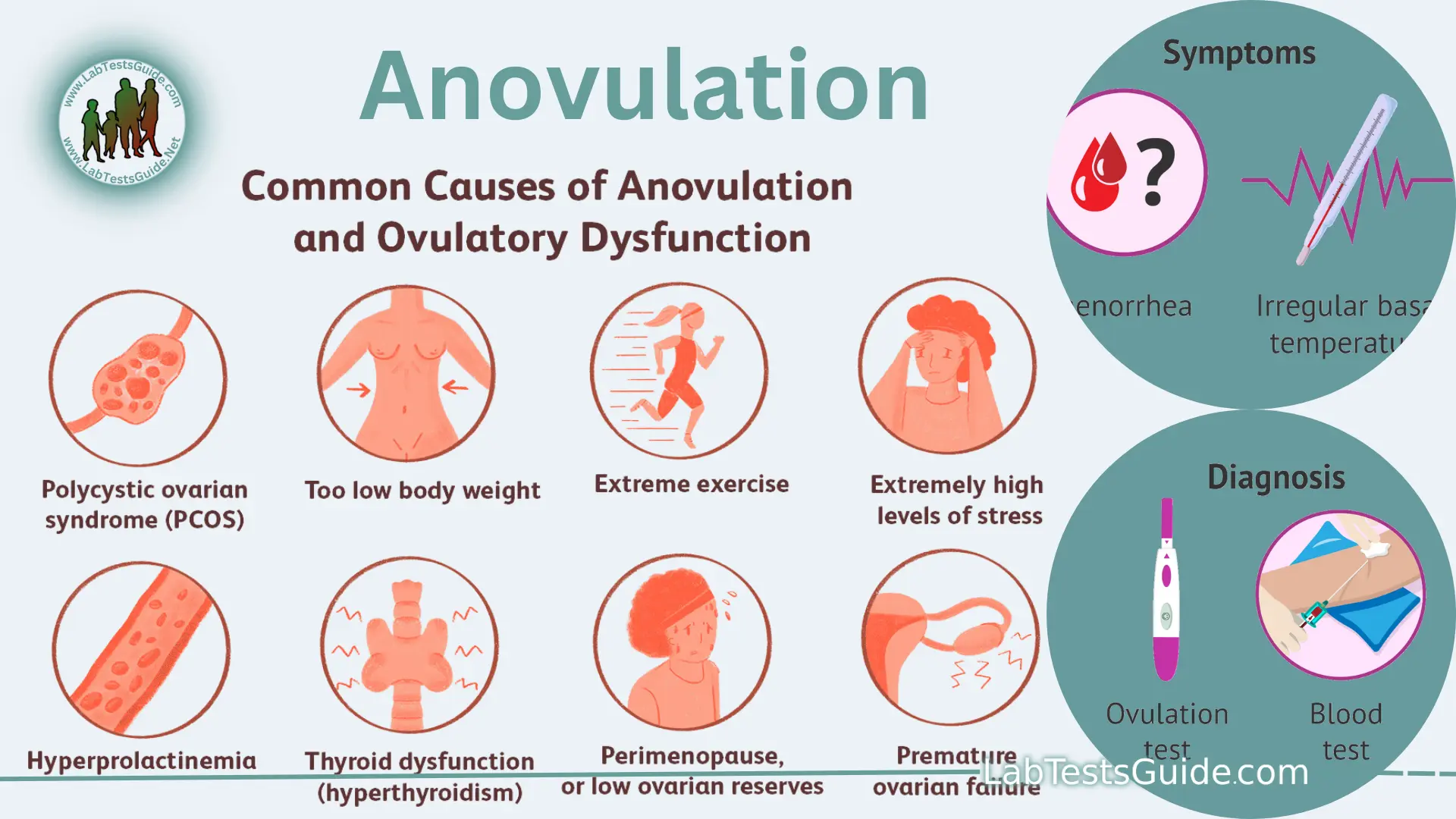
– Anovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding: disturbance of the normal hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, irregular bleeding episodes, amenorrhea, metrorrhagia, menometrorrhagia, changes in prostaglandin concentration, increased endometrial responsiveness to vasodilating prostaglandins, changes in endometrial vascular structure
– Ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding: bleeding occurs cyclically, menorrhagia, defects in the control mechanisms of menstruation, blood loss rates 3 times faster than women with normal menses
– Menstrual cycle: 28 days, starts on the first day of menses, endometrium thickens under the influence of estrogen, rising estrogen levels stimulate pituitary gland to secrete follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), ovum release at midpoint of cycle, corpus luteum dies if implantation does not occur, hormone withdrawal causes vasoconstriction in the spiral arterioles of the endometrium leading to menses