Endometroid Cysts: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention Strategies
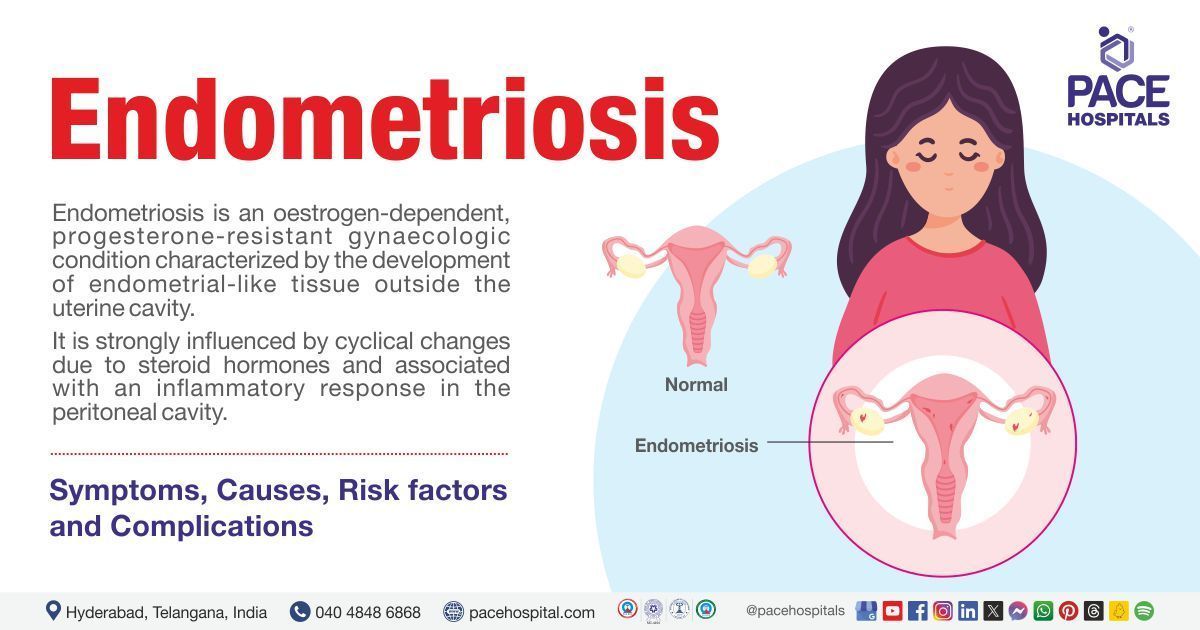
– Endometriosis is the growth of endometrium tissue in other areas of the body, such as the fallopian tubes, bladder, or peritoneum.
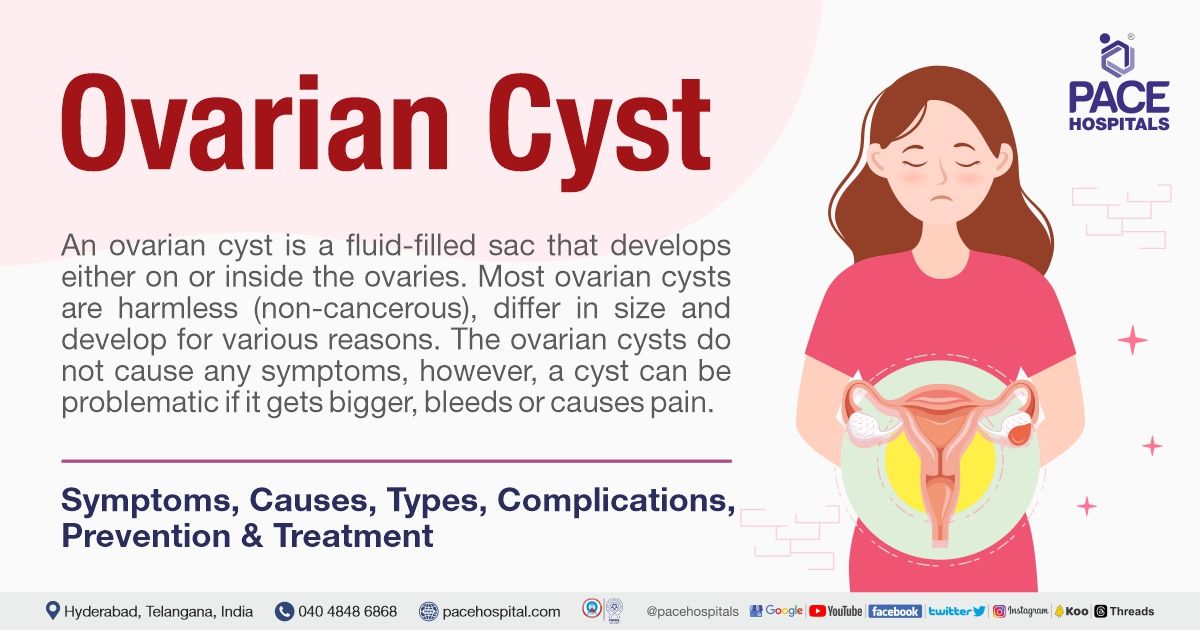
– Endometrioid cysts, also known as endometriomas, are a type of cyst that can form on the ovaries.
– These cysts can range in size from small (less than 2 inches) to large (up to 8 inches across).
– Endometriomas can cause chronic pelvic pain, make it harder to get pregnant, interfere with fertility treatments, and affect ovary function.
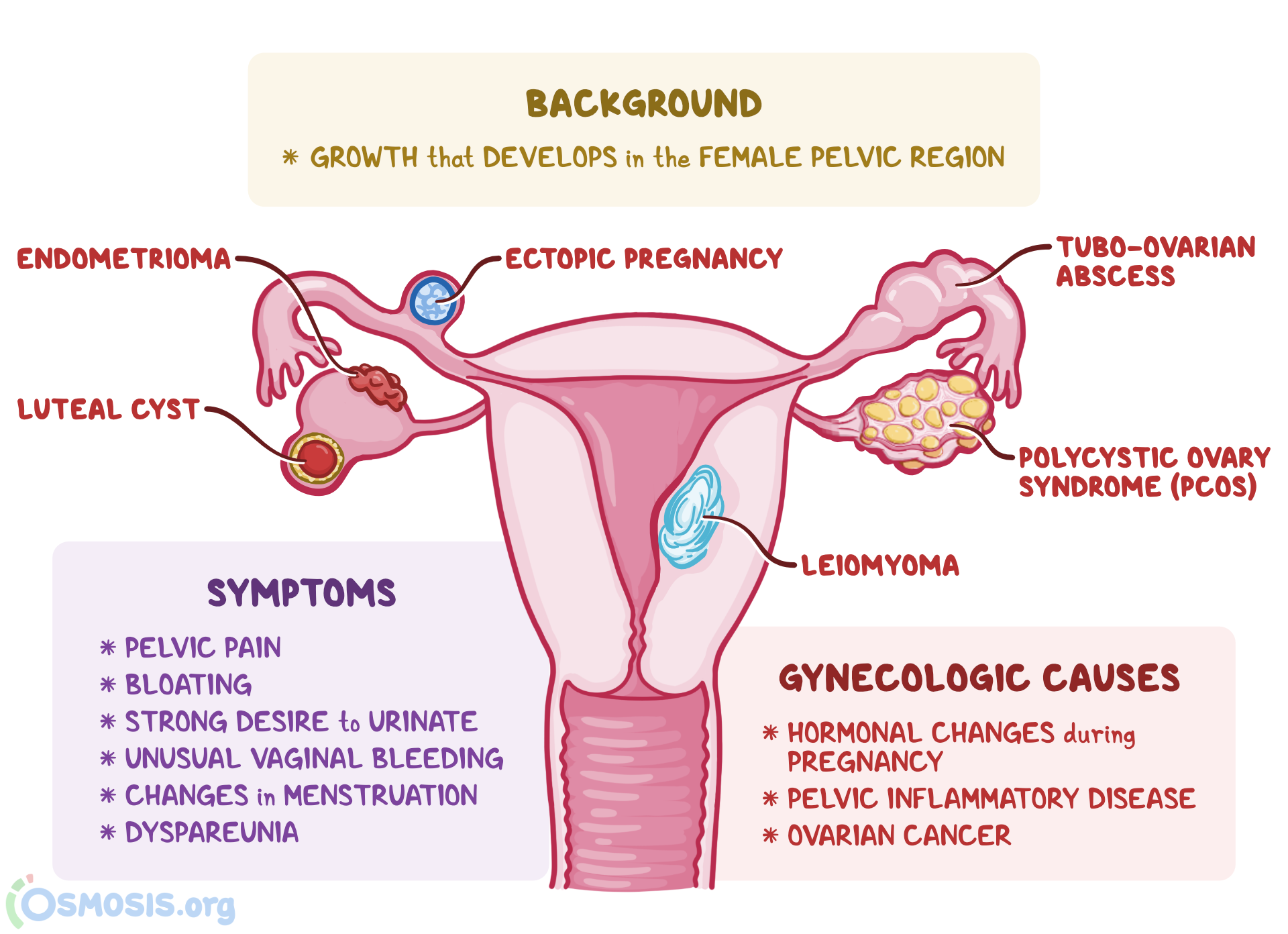
– The most common symptom of endometriosis is persistent lower belly pain, which can worsen before and during periods.
– Other symptoms may include heavy bleeding, pain during sex, soreness, pressure, or no symptoms at all.
– A doctor may discover an endometrioid cyst during a pelvic exam or through ultrasound.
– Ovarian endometrioma is a cyst filled with fluid that resembles chocolate syrup and is found in the ovaries.
– It is a sign of endometriosis, a condition where endometrial-like tissue grows outside the uterus.
– About 10% of people who menstruate have endometriosis.
– Ovarian endometriomas can cause pelvic pain, increase the risk of ovarian cancer, and make it more difficult to become pregnant.
– While ovarian cancer is rare among those with ovarian endometriomas, monitoring and discussing treatment options is necessary if there is concern about potential cancerous growth.