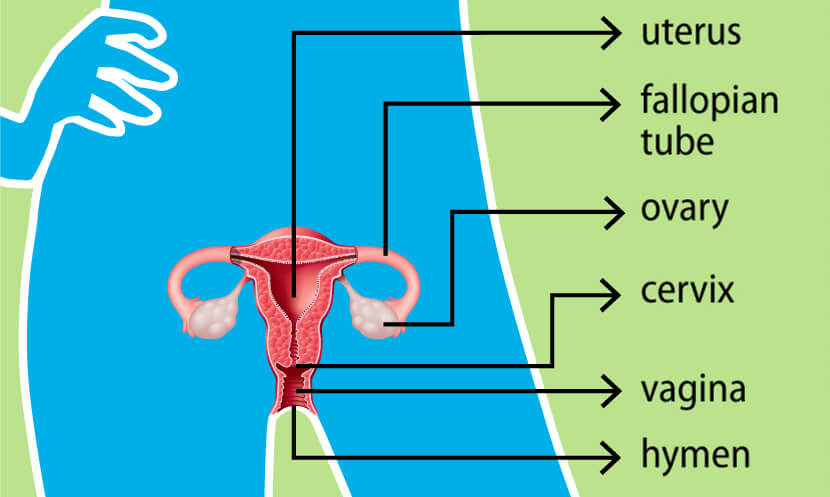
The Importance of Arteria Ovarica in Female Reproduction:
1. The ovarian artery is an artery that supplies oxygenated blood to the ovary in females.
2. It arises from the abdominal aorta below the renal artery.
3. It can be found within the suspensory ligament of the ovary, anterior to the ovarian vein and ureter.
4. The ovarian arteries are paired structures that arise from the abdominal aorta, usually at the level of L2.
5. After emerging from the aorta, the artery travels within the suspensory ligament of the ovary and enters the mesovarium.
6. The ovarian arteries may anastomose with the uterine artery in the broad ligament.
7. Small branches are given to the ureter and the uterine tube.
8. One branch passes on to the side of the uterus and unites with the uterine artery.
9. Other offsets are continued on the round ligament of the uterus, through the inguinal canal, to the integument of the labium majus and groin.
10. In 20% of cases, the ovarian arteries arise from the renal arteries.
11. They may also arise from adrenal, lumbar, or internal iliac arteries.
12. The ovarian artery supplies blood to the ovary and uterus.
13. The ovarian arteries swell during pregnancy, in order to increase the uterine blood supply.