Cervical Carcinoma in Situ: Risk Factors, Prevention, Treatment
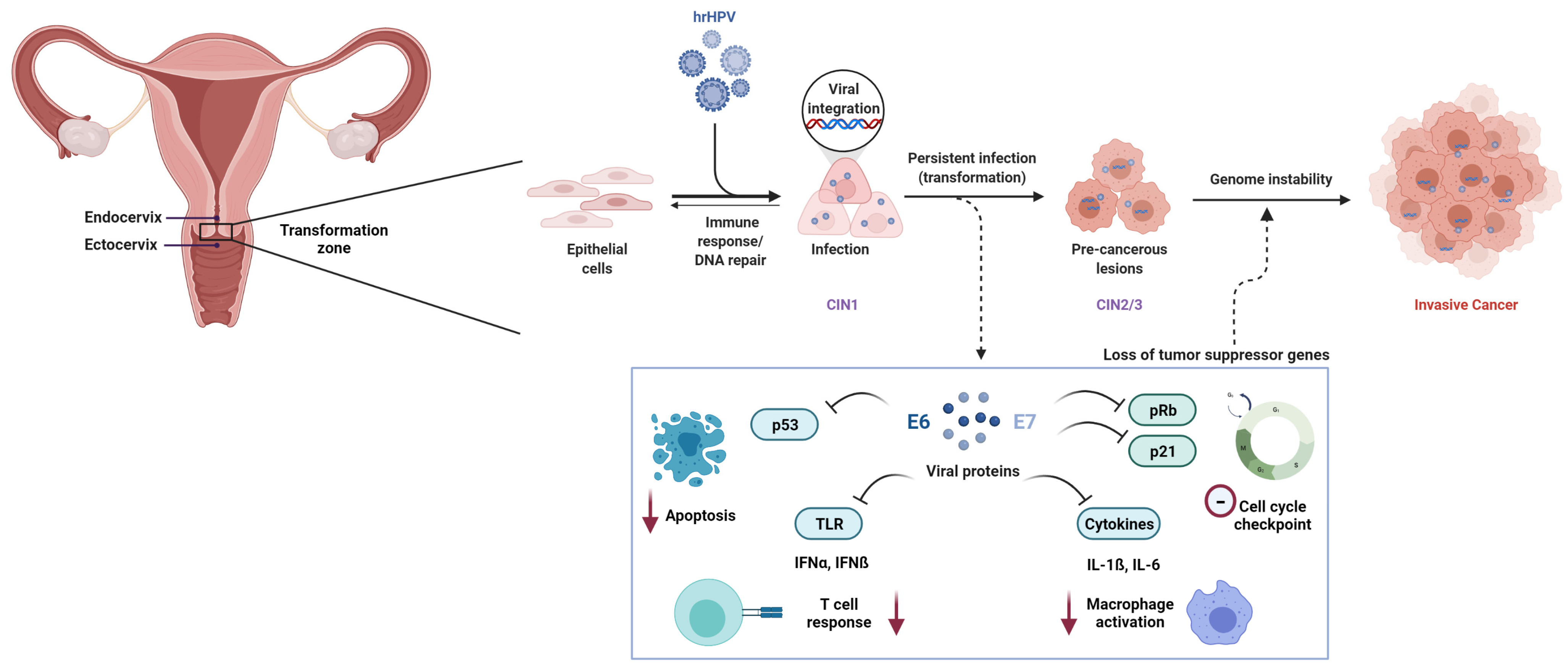
– Carcinoma in situ
– Cervical cancer
– International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO)
– Staging system
– Stage 0
– Surface layer of cells lining the cervix
– Pre-cancer
– Cancer treatment
– Roman numerals
– Advanced cancer
– Stage I
– Stage IA1
– Stage IA2
– Stage IB1
– Stage IB2
– Stage IB3
– Tumor size and depth
– Microscopic examination
– Visible tumor
– Lymph nodes
– Pelvis
– Vagina
– Bladder
– Rectum
– Metastasis
– Lungs
– Liver
– Brain
– Bone
– Treatment options
– Local ablative measures
– Excisional measures
– Cryosurgery
– Laser ablation
– Loop excision
– Surgical removal
– Total hysterectomy
– Radical hysterectomy
– Conization
– Lymph node dissection
– Radiation therapy
– Pelvic radiation therapy
– High-risk factors
– Combined external beam radiation
– Brachytherapy
– Radical vaginal trachelectomy
– Fertility preservation
– Pretrachelectomy MRI
– Minimally invasive surgical techniques
– Laparoscopic techniques
– Robotically assisted laparoscopic techniques
– Extensive lymphadenectomy
– Postoperative irradiation
– Chemotherapy
– Platinum-based doublet
– Docetaxel
– Gemcitabine
– Ifosfamide
– 5-fluorouracil
– Mitomycin
– Irinotecan
– Topotecan
– Pemetrexed
– Vinorelbine
– Bevacizumab
– FDA approval
– Persistent cancer
– Recurrent cancer
– Metastatic cancer
– Overall survival
– Tumor shrinkage
– Hypertension
– Thromboembolic events
– GI fistulas
– Pembrolizumab
– PD-L1 expression
– Tumor mutational burden
– KEYNOTE-158 trial
– Objective response rate
– Complete response rate
– Partial response rate
– Duration of response