Summary:
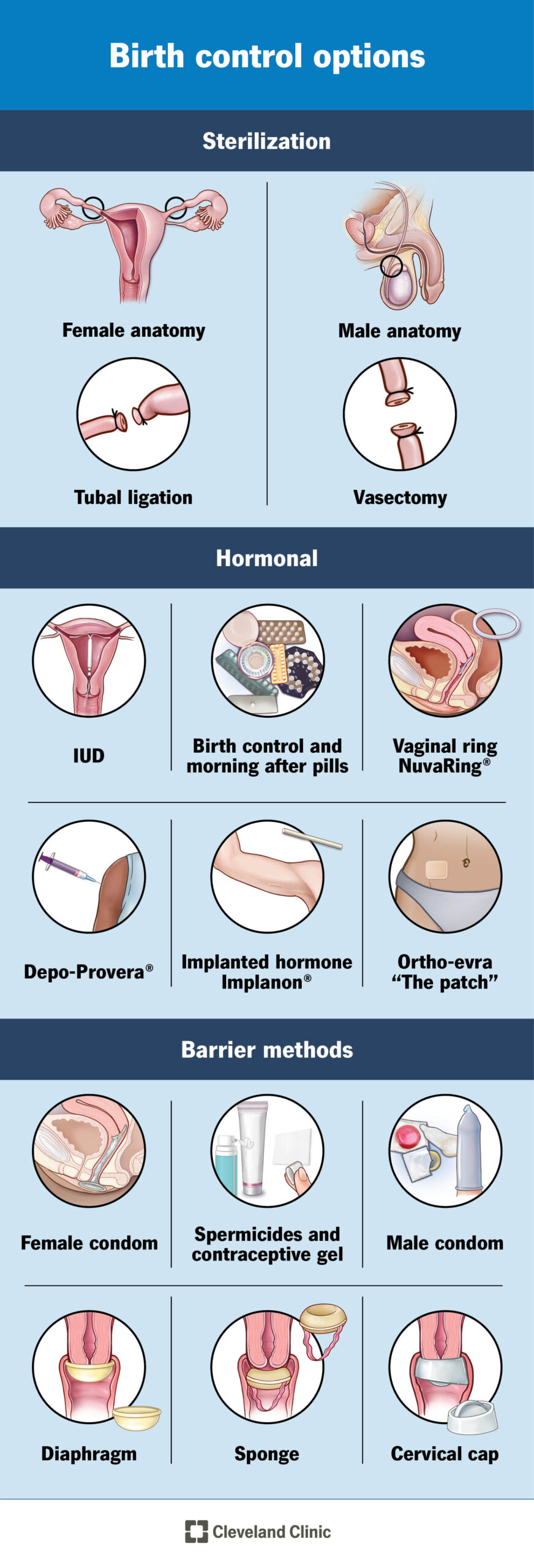
– An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small T-shaped plastic and copper device that is inserted into the womb to prevent pregnancy.
– When inserted correctly, IUDs are over 99% effective and can last for 5 to 10 years.
– IUDs can be inserted at any time during the menstrual cycle if the person is not pregnant.
– IUDs can be removed at any time by a trained medical professional.
– Side effects can include heavier, longer, or more painful periods, spotting or bleeding between periods, and a small risk of infection.
– The IUD does not protect against sexually transmitted infections, so additional protection may be needed.
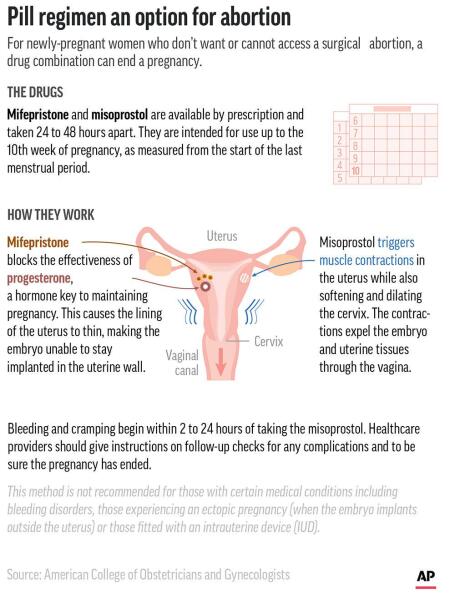
– The copper in the IUD alters cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach an egg and preventing the implantation of a fertilized egg.
– IUDs can be left in place until menopause or when contraception is no longer needed for those over 40 years old.
– Before insertion, a GP or nurse will check the position and size of the womb and may test for existing infections.
– The fitting process takes about 20 to 30 minutes, with the IUD being inserted through the cervix into the womb.
– Local anesthesia can be used to minimize discomfort during insertion.
– After having an IUD fitted, period-type cramps and bleeding may occur for a few days.
– A GP may recommend checking the IUD after 3 to 6 weeks.
– If there are any problems or if removal is desired, the GP should be consulted.
– If there is a risk of sexually transmitted infection (STI), it may lead to an infection in the pelvis and should be addressed with a GP.
– IUDs have two thin threads that can be checked by the user to make sure it is still in place.
– If the threads cannot be felt or if the IUD has moved, there may be a risk of pregnancy, and additional contraception should be used until checked by a GP.
– If the partner can feel the IUD during sex, a check-up should be scheduled.
– Additional contraception should be used for 7 days before IUD removal if not replacing the IUD.
– Most individuals with a womb can use an IUD, with exceptions for those who may be pregnant, have untreated STIs or pelvic infections, have womb or cervix issues, or experience unexplained bleeding.
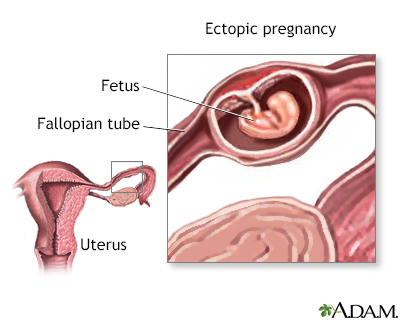
– People who have had an ectopic pregnancy or have an artificial heart valve should consult their GP before getting an IUD.
– IUDs can usually be fitted 4 weeks after giving birth, and alternative contraception should be used until then.
– IUDs have an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
– IUDs can be obtained for free from contraception clinics, sexual health or genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinics, GP surgeries, and some young people’s services.
– Contraception services are free and confidential for people under 16.
– Healthcare professionals will not inform parents or caregivers if under 16 seeking contraception, as long as they believe the person fully understands the information and decisions being made.
– Professionals may only disclose information if they believe the individual is at risk of harm, such as abuse.
– An IUD can last between 5 to 10 years, depending on the type.
– Periods may become heavier, longer, or more painful in the first 3 to 6 months after insertion.
– Spotting or bleeding between periods may occur.
– There is a small risk of infection or expulsion of the IUD.
– Previous pelvic infections may make IUDs unsuitable.
– IUDs do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
– IUDs release copper into the womb, which alters cervical mucus and makes it difficult for sperm to reach an egg and implant itself.
– Before insertion, a GP or nurse will check the position and size of the womb and test for existing infections.
– The appointment takes about 20 to 30 minutes, with fitting taking no longer than 5 minutes.
– IUD insertion can be uncomfortable or painful, but local anesthesia can be used to help.
– Painkillers can be taken after insertion if needed.
– There is a small chance of getting thrush that keeps coming back after having an IUD fitted.
– If the IUD fails and a woman becomes pregnant, there is an increased risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
– IUDs can be obtained for free from contraception clinics, sexual health or genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinics, GP surgeries, and some young people’s services.
– Contraception services are free and confidential for people under 16.
– Healthcare professionals will not inform parents or carers about a person under 16 seeking contraception, as long as they believe the person understands the information and decisions being made.
– Professionals may disclose information if they believe the person is at risk of harm, such as abuse.
Continue Reading