List of pertinent information about acute salpingo-oophoritis:
– Oophoritis is the inflammation of one or both ovaries, often seen as a manifestation of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
– It is most commonly seen in younger women below 25 years of age.
– The inflammation can be caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, bacterial infections, insertion of intrauterine devices (IUDs) in a wrong manner, delivering a baby, having an abortion, miscarriage, or autoimmune oophoritis.
– The initial symptoms include abdominal discomfort, pain in the pelvic region, heavy menstrual bleeding, bleeding between periods, difficulty during urination, burning sensation during urination, abnormal vaginal discharge, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
– If left untreated, the symptoms can progress to severe pelvic pain, fever, chills, nausea, or vomiting.
– Diagnosis typically occurs after the patient experiences severe abdominal pain and seeks medical help.
– Diagnostic methods include pelvic examination, blood tests, urinary tests, and ultrasonography.
– Treatment methods for oophoritis depend on the cause, symptoms, and severity, and may involve antibiotics, painkillers, or surgical intervention.
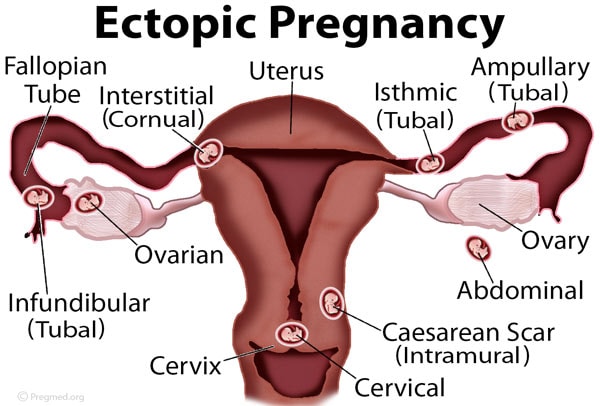
– Complications of oophoritis include damage to the fallopian tubes, increased risk of ectopic pregnancies, sepsis, scarring or blockages that can impact fertility, and the potential need for assisted reproductive techniques like in vitro fertilization.
– Safe sexual practices and limiting sexual partners can help prevent oophoritis.
– Acute salpingo-oophoritis, also known as salpingitis, is an infection in the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
– Symptoms of salpingitis can include abnormal vaginal discharge, spotting between periods, painful periods, pain during ovulation, painful sexual intercourse, fever, abdominal pain, lower back pain, frequent urination, and nausea/vomiting.
– Risk factors for salpingitis include engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse and prior infection with a sexually transmitted disease.
– Complications of salpingitis can include further infection spreading to nearby structures and infection of sexual partners.
– Diagnosis of acute salpingo-oophoritis involves general and pelvic examinations, blood tests, mucus swabs, and laparoscopy in some cases.
– Treatment options for acute salpingo-oophoritis include antibiotics (successful in 85% of cases), hospitalization, and surgery if necessary.
– Complications of acute salpingo-oophoritis can include tubo-ovarian abscess, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility.
Continue Reading