Pyometra in Dogs: A Potentially Fatal Uterine Infection
– Pyometra: An infection inside the uterus of an unneutered female dog
– Unneutered female dogs over six years old are especially susceptible to pyometra
– Pyometra can lead to sepsis, kidney failure, peritonitis, and death
– There are two types of pyometra: open and closed
– Open pyometra is characterized by visible blood and pus from the dog’s vulva
– Closed pyometra is particularly dangerous as it can cause the womb to burst
– Neutered dogs can also develop a rare type of pyometra called stump pyometra
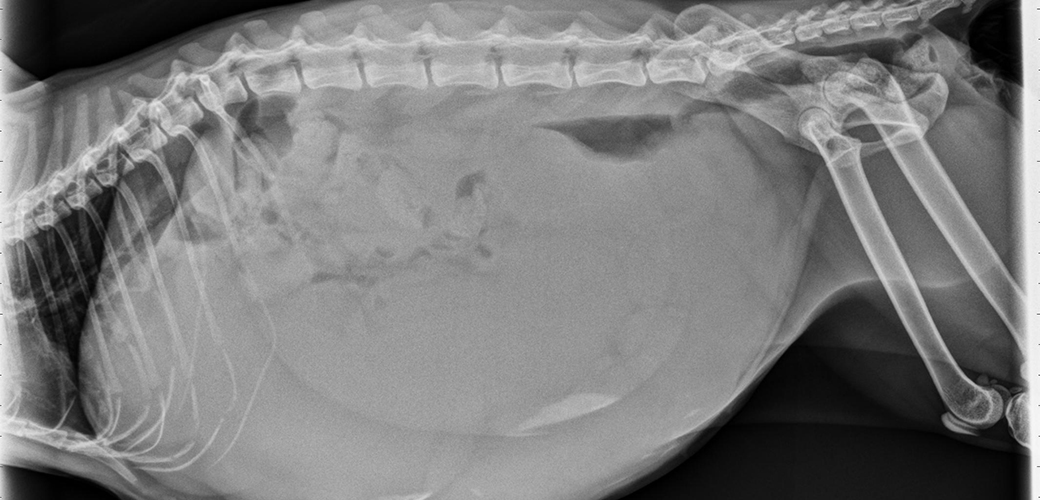
– Pyometra is a serious infection of the uterus
– It can lead to complications such as kidney failure, toxaemia, dehydration, and death
– Mostly affects older, un-spayed female dogs, but can occur in any un-spayed female dog
– Caused by a bacterial infection, commonly E. coli, which often occurs after a female dog’s season
– Symptoms include loss of appetite, lethargy, excessive thirst, and sometimes vaginal discharge
– Diagnosis is done through questioning, abdominal examination, and possibly ultrasound
– Urgent surgery to remove the infected womb is the usual treatment
– Earlier surgery increases the chances of survival
– Preventative spaying can help prevent pyometra
– Most spayed dogs will not get pyometra, but there is a rare condition called uterine stump pyometra.