– Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
– The virus can be spread through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity.
– Some people may have no symptoms or very mild symptoms but can still spread the virus.
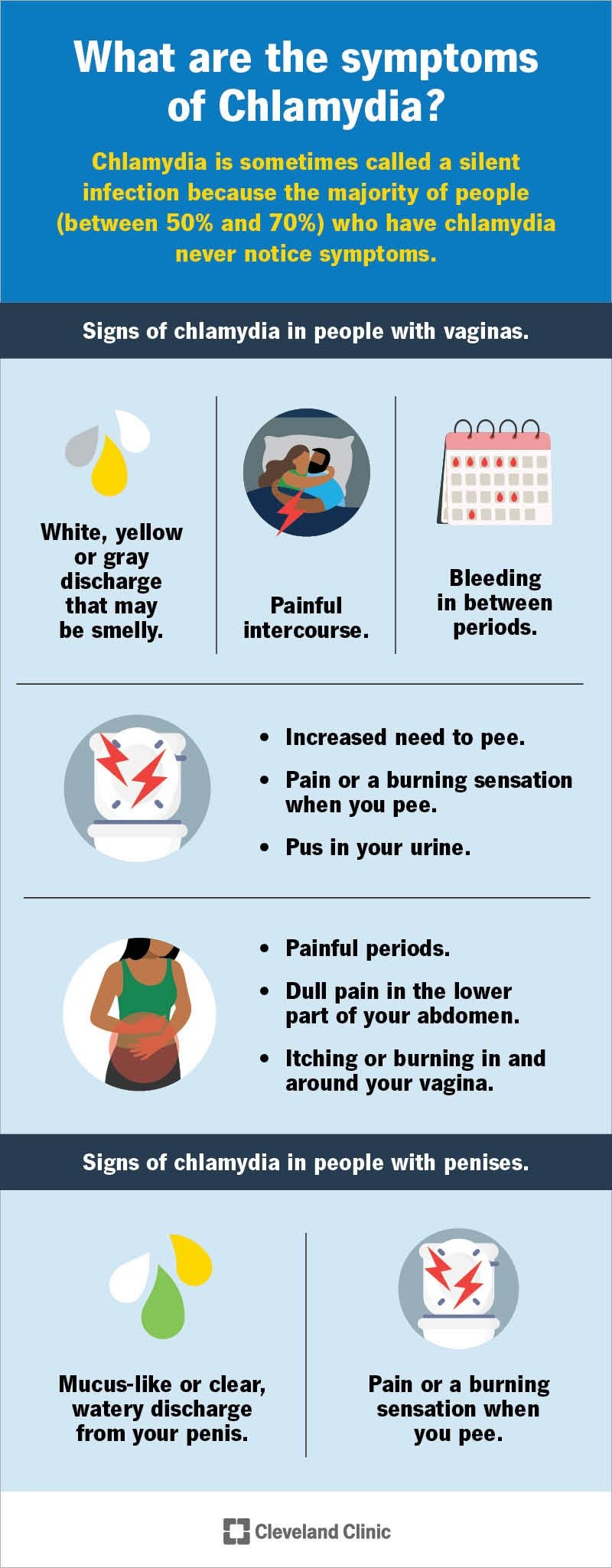
– Symptoms include pain, itching, and sores around the genitals, anus, or mouth.
– There is no cure for genital herpes, but medicine can help ease symptoms and reduce the risk of infecting others.
– Condoms can help prevent the spread of genital herpes.
– Symptoms usually appear 2 to 12 days after exposure to the virus.
– Sores can develop on the buttocks, thighs, rectum, anus, mouth, urethra, vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, or scrotum.
– After the first outbreak, recurrent outbreaks may occur, but they are usually less severe and don’t last as long.
– Warning signs of a recurrent outbreak may include genital pain, tingling, or shooting pain in the legs, hips, or buttocks.
– It is recommended to see a healthcare provider if you suspect you have genital herpes or any other sexually transmitted infection.
– Genital herpes is caused by two types of herpes simplex virus – HSV-2 and HSV-1.
– HSV-2 is the most common cause of genital herpes and can be present on blisters and ulcers, in the mouth, vagina, or rectum.
– HSV-1 is a version of the virus that causes cold sores and can be transmitted through close skin-to-skin contact.
– Recurrent outbreaks of genital herpes caused by HSV-1 are often less frequent.
– Neither HSV-1 nor HSV-2 survives well at room temperature and is not likely to spread through surfaces.
– However, the virus can spread through kissing or sharing objects like drinking glasses or silverware.
– Risk factors for contracting genital herpes include having unprotected sexual contact, especially without using barriers like condoms or dental dams, and having sex with multiple partners.
– Women are at a higher risk of getting genital herpes, and the virus spreads more easily from men to women than from women to men.
– Genital herpes is often undiagnosed, with many people unaware that they have it.
– Having multiple sexual partners increases the risk of contracting genital herpes.
– Genital herpes is spread through sexual activity and contact with infected genitals.
– Medication can help limit outbreaks of genital herpes, but there is no cure.
– Certain groups, including women, those with a history of sexually transmitted diseases, older people, Black people in the United States, and men who have sex with men, are diagnosed with genital herpes at higher rates.
– Complications of genital herpes can include other sexually transmitted infections, newborn infection during delivery, internal inflammatory disease, finger infections, eye infections, swelling of the brain, and infection of internal organs.
– Prevention of genital herpes involves practicing safe sex and having a long-term sexual partner.
Continue Reading