Hypertonic Uterine Contraction: Understanding Causes, Risks, and Management
List of Pertinent Information:
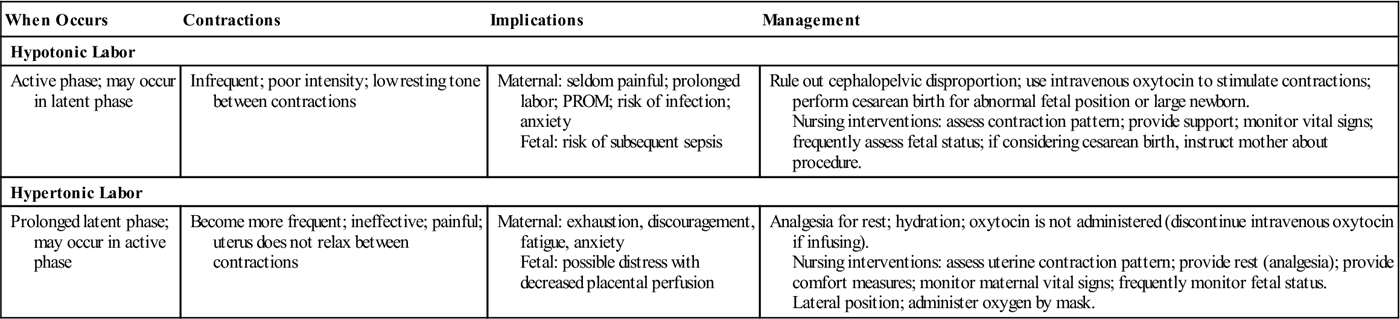
1. Uterine hyperstimulation, also known as hypertonic uterine dysfunction, can occur as a complication of labor induction.
2. It is characterized by frequent contractions (more than five in 10 minutes) or contractions lasting more than two minutes.
3. Uterine hyperstimulation can result in fetal heart rate abnormalities, uterine rupture, or placental abruption.
4. The drug Misoprostol, used for peptic ulcers, can cause uterine hyperstimulation when used to induce labor.
5. Terbutaline is commonly used to treat uterine hyperstimulation.
6. Prostaglandin E2 can be administered before labor to minimize the risk of hyperstimulation and its effects on the fetal heart rate.
7. Tocolytic treatment with β2-adrenergic drugs has been used to stabilize uterine contractions and lower fetal heart rate.
8. Using a balloon catheter for labor induction instead of Prostaglandin E2 can reduce the risk of uterine hyperstimulation and its impact on the fetal heart rate.