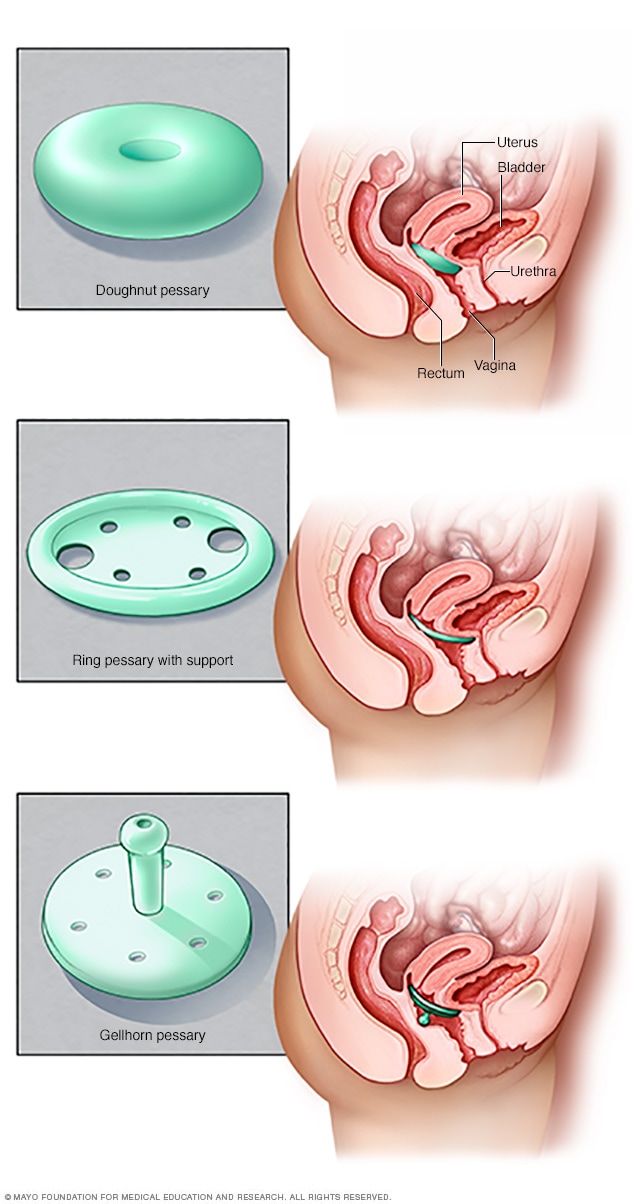
Uterine Prolapse: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention Strategies
– Uterine prolapse occurs when muscles and tissue in the pelvis weaken, allowing the uterus to drop into the vagina
– Nearly half of all women between ages 50 and 79 have uterine prolapse
– The main cause is weakened muscles and tissue in the pelvic floor that can’t support the weight of the uterus
– Risk factors include giving birth (highest risk), vaginal delivery, menopause, being Caucasian, being overweight, and smoking
– Many women with uterine prolapse have no symptoms, but possible symptoms include leakage of urine, inability to completely empty the bladder, feeling of heaviness or fullness in the pelvis, bulging in the vagina, lower-back pain, aching or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvis, and constipation
– Diagnosing uterine prolapse involves a physical exam, possibly a cystoscopy to examine the bladder and urethra, and an MRI to get a better look at the kidneys and other pelvic organs.