In the world of medicine, there are few things more unsettling than the thought of an organ in our body twisting and cutting off its own blood supply.
Yet, this is the unfortunate reality of ovarian torsion, a condition that brings excruciating pain and the looming threat of organ death.
But fear not, for modern technology and groundbreaking surgical techniques have come to the rescue, offering hope for a swift recovery.
Join us as we delve into the intricate world of torsion of ovarian tumors and explore how medical advancements are transforming the landscape of reproductive health.
torsion of ovarian tumor
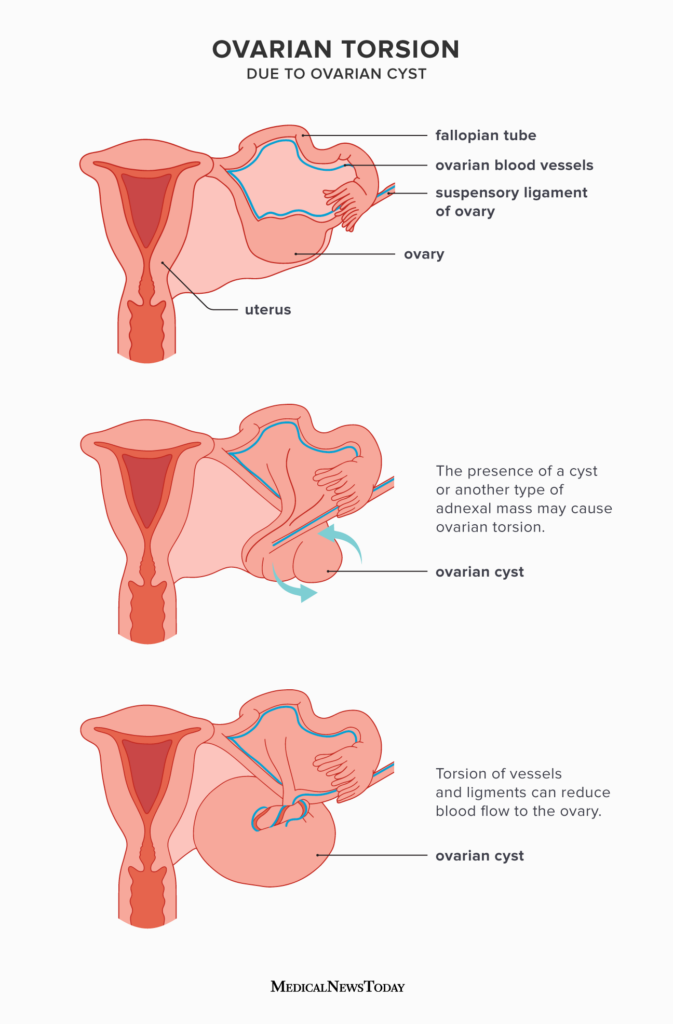
Ovarian torsion refers to the twisting of an ovarian tumor, resulting in the cutting off of blood supply to the ovary.
This condition can lead to organ death and is characterized by intense pain, vomiting, and peritonitis.
Ovarian torsion primarily affects women of reproductive age and can also occur in girls.
Prompt treatment, typically through surgery to untwist or remove the affected ovary, can result in full recovery.
If left untreated, ovarian torsion can have a negative impact on fertility.
Diagnosis of ovarian torsion often involves state-of-the-art ultrasound technology, while minimally invasive surgery is commonly used for treatment.
Adnexal torsion is another term used to describe ovarian torsion, which also involves the twisting of the fallopian tube and tissue death due to lack of blood supply.
Complications of ovarian torsion can include abdominal infection.
Diagnosis and treatment for ovarian torsion are available at Yale Medicine.
Key Points:
- Ovarian torsion is the twisting of an ovarian tumor, cutting off blood supply to the ovary.
- Symptoms of ovarian torsion include intense pain, vomiting, and peritonitis.
- It primarily affects women of reproductive age and can also occur in girls.
- Prompt treatment, typically through surgery, can result in full recovery.
- If left untreated, it can negatively impact fertility.
- Diagnosis involves ultrasound technology and treatment often involves minimally invasive surgery.
torsion of ovarian tumor – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. The term “torsion” in “torsion of ovarian tumor” refers to the twisting or rotation of the organ around its ligaments, which can lead to severe complications.
2. Although torsion of an ovarian tumor is rare, it is most commonly observed in women of reproductive age.
3. One of the symptoms of torsion of an ovarian tumor is sudden and severe pelvic pain, which may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
4. One interesting aspect of torsion of an ovarian tumor is that it can occur in both benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) tumors of the ovary.
5. In some cases of torsion, the blood supply to the affected ovary can be compromised, leading to tissue death, and prompt surgical intervention is needed to prevent further complications.
Torsion Of Ovarian Tumor – Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion is a serious condition where an ovarian tumor twists, cutting off the blood supply to the ovary. It can result in organ death and cause intense pain. To ensure a positive outcome, it is essential to understand the risks associated with ovarian torsion and the appropriate treatment options.
- Ovarian torsion can lead to the disruption of blood supply to the ovary.
- This condition can cause organ death and intense pain.
- Prompt intervention is crucial for a positive outcome.
“Ovarian torsion can have severe consequences, including organ death and intense pain.”
- It is important to understand the risks and appropriate treatment options for ovarian torsion.
Twisting Of Ovarian Tumor
The twisting of an ovarian tumor occurs when the tumor rotates on its axis, resulting in the twisting of the surrounding supportive structures such as the blood vessels and fallopian tubes. This rotation can lead to a complete or partial occlusion of the blood vessels, cutting off the blood supply to the affected ovary.
Cutting Off Blood Supply To The Ovary
When the blood supply to the ovary is compromised due to torsion, the tissues within the ovary begin to suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients. This can eventually lead to tissue death, also known as necrosis. The longer the blood supply is cut off, the greater the damage to the ovary, potentially resulting in the need for surgical intervention or removal of the affected organ.
Organ Death Due To Ovarian Torsion
The lack of blood supply caused by ovarian torsion can result in the death of the affected ovary. This can have significant implications for a woman’s fertility and hormonal balance. It is essential for healthcare providers to recognize the signs and symptoms of ovarian torsion to ensure prompt diagnosis and intervention to preserve ovarian function.
Intense Pain Caused By Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion typically manifests as intense pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis. The twisting of the tumor and subsequent restriction of blood flow can cause nerve irritation and inflammation, intensifying the pain. This pain usually occurs suddenly and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Symptoms of ovarian torsion include:
- Intense pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sudden onset
“Ovarian torsion often presents with intense pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis. The twisting of the tumor and the subsequent compromise of blood flow can lead to nerve irritation and inflammation, contributing to the severity of the pain experienced by the patient. The pain may come on suddenly and may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting.”
Vomiting As A Symptom Of Ovarian Torsion
In some cases, vomiting can occur as a symptom of ovarian torsion. This is believed to be a result of the intense pain and the body’s response to the disruption of normal ovarian function. Vomiting should be taken seriously as it can be a sign of a serious medical condition and should prompt immediate medical attention.
Peritonitis Caused By Ovarian Torsion
In severe cases of ovarian torsion, the twisting of the tumor can lead to the rupture of the affected organ and the subsequent leakage of its contents into the abdominal cavity. This can result in peritonitis, which is an infection and inflammation of the peritoneum, the lining of the abdominal cavity. Peritonitis is a serious complication that requires immediate medical intervention.
- Ovarian torsion can cause rupture and leakage of tumor contents into the abdominal cavity
- This can lead to peritonitis
- Peritonitis is characterized by infection and inflammation
- Immediate medical intervention is necessary to address this serious complication.
Ovarian Torsion In Women Of Reproductive Age
Ovarian torsion primarily affects women in the reproductive age, typically between 20 and 40. The presence of an ovarian tumor elevates the risk of torsion, while factors like hormonal changes, pregnancy, or physical activity can exacerbate this risk. Healthcare providers should be vigilant about the potential for ovarian torsion in this demographic and include it as a consideration when diagnosing acute abdominal pain.
Ovarian Torsion In Girls
Ovarian torsion, although less common, can occur in girls of all ages, from infants to adolescents. Risk factors for ovarian torsion in girls are similar to those in adults and include the presence of ovarian tumors or hormonal changes. It is important to note that timely diagnosis and intervention are crucial in this population to preserve ovarian function and prevent complications.
- Some key points to remember:
- Ovarian torsion can occur in girls of all ages.
- Risk factors include ovarian tumors and hormonal changes.
- Timely diagnosis and intervention are vital.
- Preserving ovarian function is a priority.
“Timely diagnosis and intervention are crucial in this population to preserve ovarian function and prevent complications.”
Surgery For Untwisting Or Removal Of The Ovary
Ovarian torsion occurs when the ovary twists, leading to a disruption in blood flow. Surgical intervention is typically necessary to untwist the ovary or remove it, depending on the severity and viability of the tissue. Minimally invasive techniques, like laparoscopy, are commonly used for these procedures.
Benefits of using minimally invasive techniques include:
- Smaller incisions
- Reduced postoperative pain
- Faster recovery times
In the management of ovarian torsion, prompt diagnosis and the utilization of state-of-the-art ultrasound technology are crucial. Healthcare providers should remain vigilant and consider ovarian torsion as a possible diagnosis in women of reproductive age, as well as in girls experiencing acute abdominal pain.
To ensure early intervention and a positive outcome, understanding the risks and treatment options for ovarian torsion is essential. With early intervention, individuals affected by this condition can experience a full recovery and preserve their fertility.
- Blockquote:
“Understanding the risks and treatment options for ovarian torsion is essential to ensure early intervention and a positive outcome.”
💡
You may need to know these questions about torsion of ovarian tumor
What is the main cause of ovarian torsion?
The primary cause of ovarian torsion is the presence of ovarian cysts. Ovarian torsion predominantly occurs in women during their reproductive years, although it may occasionally affect prepubescent girls. The existence of an ovarian cyst increases the risk of torsion as the cyst can disrupt the balance of the ovary, leading to its twisting and potential consequences.
What is the most common tumor to cause ovarian torsion?
The most common tumor to cause ovarian torsion is dermoid cyst, also known as mature cystic teratoma. This type of tumor is typically benign and consists of various types of tissue such as hair, skin, and teeth. Although rare, it can cause the ovary to twist on its own axis, leading to ovarian torsion and potentially severe abdominal pain.
How serious is ovarian torsion?
Ovarian torsion is a condition that should be taken seriously due to the potential consequences it can entail. If left untreated, the risk of losing the affected ovary or experiencing infertility increases substantially. This occurs as the blood supply to the ovary becomes compromised, leading to necrosis, a situation where the tissue dies due to inadequate blood flow. Swift medical intervention is vital to prevent such severe outcomes and preserve reproductive health.
How do you treat a twisted ovarian tumor?
When facing a twisted ovarian tumor, prompt medical intervention is essential. In cases where the cyst has burst and caused internal bleeding or when ovarian torsion occurs, emergency surgery becomes necessary. The preferred method for treating this condition is cystectomy, which involves removing the cyst while preserving the ovary. This procedure can be performed using minimally invasive laparoscopy or through a larger incision in the abdomen known as laparotomy. The choice of approach depends on the specifics of the case and the expertise of the medical team.
Reference source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5615993/
https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/ovarian-torsion
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3307215/
https://www.webmd.com/women/what-to-know-ovarian-torsion