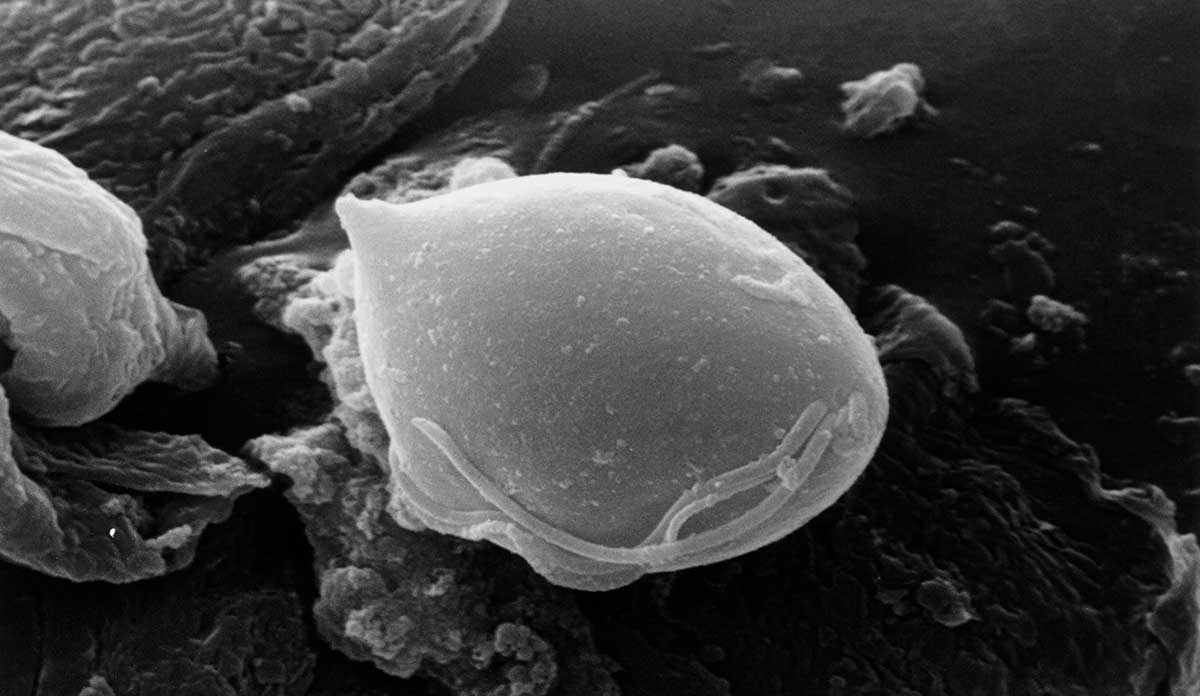
Trichomonas vaginalis: a name that seems almost outlandish, yet it holds the power to wreak havoc on our bodies.
This microbe, this tiny parasite, silently invades the intimate spaces of our lives, causing a storm of uncomfortable symptoms for women.
But what about the men?
Join us as we uncover the secrets of trichomoniasis, the enigmatic STI that hides in the shadows, threatening to unravel the very fabric of our well-being.
trichomonas vaginalis
Trichomonas vaginalis is a parasite that causes trichomoniasis, a common sexually transmitted infection.
In women, it can lead to symptoms such as foul-smelling vaginal discharge, genital itching, and painful urination.
Men typically do not show symptoms.
Pregnant women with trichomoniasis are more likely to have premature deliveries.
The infection can be treated with antibiotics such as metronidazole, tinidazole, or secnidazole.
To prevent reinfection, it is important to treat all sexual partners at the same time.
Consistent condom use can also help reduce the risk of infection.
Key Points:
- Trichomonas vaginalis causes trichomoniasis, a common sexually transmitted infection.
- Women may experience symptoms like foul-smelling discharge, genital itching, and painful urination.
- Men usually do not show symptoms of trichomoniasis.
- Pregnant women with trichomoniasis are more likely to have premature deliveries.
- Antibiotics such as metronidazole, tinidazole, or secnidazole can be used to treat trichomoniasis.
- Treating all sexual partners at the same time and consistent condom use can help prevent reinfection and reduce the risk of infection.
trichomonas vaginalis – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Trichomonas vaginalis is a parasitic protozoan that primarily affects the urogenital tract and is responsible for the sexually transmitted infection known as trichomoniasis.
2. Trichomonas vaginalis is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide, affecting approximately 156 million people annually according to the World Health Organization.
3. The parasite Trichomonas vaginalis was first discovered in 1836 by an Austrian physician named Alfred Donn??.
4. Trichomonas vaginalis can survive outside the human body for brief periods of time, making transmission possible through contaminated objects such as moist towels or shared underwear.
5. Interestingly, Trichomonas vaginalis only infects humans and cannot survive in other hosts, distinguishing it from many other parasites that can affect multiple species.
Introduction To Trichomonas Vaginalis And Trichomoniasis
Trichomonas vaginalis is a microscopic parasite that causes a common sexually transmitted infection known as trichomoniasis. This infection often goes unnoticed due to the lack of symptoms in men and the mild symptoms in women. However, if left untreated, trichomoniasis can lead to serious complications, making it essential for individuals to be aware of the risks and seek appropriate treatment.
- Trichomonas vaginalis is a microscopic parasite.
- It causes a common sexually transmitted infection called trichomoniasis.
- This infection often goes unnoticed, especially in men.
- Women may experience mild symptoms.
- If left untreated, trichomoniasis can lead to serious complications.
- It is important for individuals to be aware of the risks and seek treatment.
Symptoms Of Trichomoniasis In Women
When women contract trichomoniasis, they may experience a range of symptoms that can significantly impact their daily lives. One of the most common symptoms is a foul-smelling vaginal discharge. This discharge may be frothy, yellowish-green, or gray in color. Additionally, women with trichomoniasis often suffer from genital itching, which can be uncomfortable and disruptive. Painful urination is another symptom that can occur, causing discomfort and distress.
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Discharge may be frothy, yellowish-green, or gray in color
- Genital itching
- Painful urination
Lack Of Symptoms In Men With Trichomoniasis
Unlike women, men with trichomoniasis usually do not have any symptoms. This is referred to as asymptomatic trichomoniasis, which makes it difficult to prevent the transmission of the infection. Unknowingly, infected men can unknowingly transmit the infection to their sexual partners, leading to a higher chance of complications and reinfection. As a result, regular testing and open communication about sexual health are essential for both men and women.
Increased Risk Of Preterm Delivery In Pregnant Women With Trichomoniasis
Pregnant women infected with trichomoniasis are at an elevated risk of premature delivery. Studies have demonstrated that the presence of trichomonas vaginalis can cause inflammation in the cervix and other reproductive structures, potentially leading to early labor and preterm birth. Hence, it is important to screen pregnant women for trichomoniasis. If diagnosed, prompt treatment is necessary to minimize the associated risks.
- Pregnant women infected with trichomoniasis have an increased risk of premature delivery.
- Trichomonas vaginalis can cause inflammation in the cervix and other reproductive structures.
- This inflammation may trigger early labor and result in preterm birth.
- Screening for trichomoniasis is crucial for pregnant women.
- Prompt treatment is necessary for diagnosed cases to reduce associated risks.
Antibiotic Treatment For Trichomoniasis
Fortunately, trichomoniasis can be effectively treated with antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics for this infection are metronidazole (Flagyl), tinidazole (Tindamax), or secnidazole (Solosec). These medications work by eliminating the parasite from the body, relieving the symptoms, and preventing further complications. It is crucial for individuals diagnosed with trichomoniasis to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure successful treatment.
Simultaneous Treatment Of Sexual Partners To Prevent Reinfection
To prevent reinfection and minimize the risk of transmitting trichomoniasis to others, it is vital for all sexual partners to be treated simultaneously. Even if one partner is asymptomatic, they may still be carrying the parasite and spread it unknowingly. Treating both partners reduces the chance of recurrence and helps break the cycle of infection. Additionally, it is essential to abstain from sexual activity until both partners have completed the prescribed treatment to ensure maximum effectiveness.
Importance Of Using Condoms To Reduce Infection Risk
Consistent and correct use of condoms is an effective way to reduce the risk of trichomoniasis and other sexually transmitted infections. Condoms act as a barrier, preventing the exchange of bodily fluids that may contain the parasite. However, it is important to note that condoms do not offer complete protection against trichomoniasis as the parasite can still infect areas not covered by the condom.
Therefore, it is important to prioritize regular testing, open communication, and a combination of preventive measures to maintain sexual health.
Some key points to remember include:
- Consistent and correct condom use: Ensuring that condoms are used correctly and consistently during sexual activity can significantly reduce the risk of trichomoniasis and other sexually transmitted infections.
- Regular testing: Regular testing is essential to detect any potential infections early and receive appropriate treatment.
- Open communication: Having open and honest communication with sexual partners about sexual health can help in making informed decisions and taking appropriate preventive measures.
- Combination of preventive measures: Along with condom use, it is advisable to consider other preventive measures, such as getting vaccinated for other sexually transmitted infections like HPV, practicing abstinence or mutual monogamy, and getting tested and treated for any existing infections.
In summary, condoms are effective in reducing the risk of trichomoniasis and other sexually transmitted infections, but they do not provide complete protection. To maintain sexual health, it is important to combine the use of condoms with regular testing, open communication, and other preventive measures.
Understanding The Foul-Smelling Vaginal Discharge Symptom
Trichomoniasis in women is characterized by a hallmark symptom: foul-smelling vaginal discharge. The discharge is often accompanied by a distinct odor that is described as fishy or unpleasant. This odor is a direct result of the infection and can cause embarrassment and discomfort for the affected individuals. It is important to recognize this symptom as it serves as an indication to seek medical attention and receive prompt treatment.
- Key Points:
- Hallmark symptom: foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Odor described as fishy or unpleasant
- Source of embarrassment and discomfort
- Important to seek medical attention and receive prompt treatment
“Recognizing the foul-smelling vaginal discharge and distinct odor is crucial, as it serves as an indication for seeking timely medical attention.”
Genital Itching Indication Of Trichomoniasis In Women
Genital itching is a common symptom experienced by women infected with trichomoniasis. This itching sensation can be persistent and irritating, leading to a constant urge to scratch. It is crucial to refrain from scratching, as it can worsen irritation and potentially cause skin damage or secondary infections. Seeking medical advice and appropriate treatment can alleviate this symptom and prevent its escalation.
- Genital itching is a common symptom experienced by women with trichomoniasis.
- The itching sensation can be persistent and irritating.
- Refraining from scratching is important to avoid further irritation and potential skin damage.
- Seeking medical advice and appropriate treatment can help alleviate the symptoms and prevent escalation.
Painful Urination As A Symptom Of Trichomoniasis In Women
Trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection, can lead to painful urination in women. This is due to inflammation and irritation of the urethra, the tube responsible for transporting urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The pain or burning sensation during urination can be distressing and a clear indication of trichomoniasis infection. Seeking immediate medical evaluation is crucial in order to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
💡
You may need to know these questions about trichomonas vaginalis
Is Trichomonas a serious STD?
Trichomonas, while not typically causing noticeable symptoms or significant problems, should still be taken seriously as an STD. Although individuals may not experience any signs of infection, if left untreated, it can increase the risk of acquiring or transmitting other sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV. Thus, seeking timely treatment for trichomonas is crucial in preventing potential complications and further spread of infections.
What causes you to get Trichomonas?
Trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the parasite Trichomonas, is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual activity. Engaging in sexual intercourse without using a condom increases the risk of contracting the infection. Additionally, sharing sex toys that have not been properly cleaned or covered with a new condom before use can also lead to the spread of Trichomonas. It is important to note that one does not need to have multiple sexual partners to acquire trichomoniasis; anyone who is sexually active can become infected and potentially transmit it to others.
Is trichomoniasis a form of chlamydia?
Trichomoniasis, also known as trich, is caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, while chlamydia is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. Although both infections are sexually transmitted and may have similar symptoms, they are distinct diseases caused by different organisms. Therefore, trichomoniasis is not a form of chlamydia.
How did I get trichomoniasis without cheating?
Trichomoniasis is widely known as a sexually transmitted disease, but recent research has shed light on alternative modes of transmission. Although it may seem perplexing, it is possible to contract trichomoniasis without engaging in infidelity or risky sexual behavior. Extensive literature reviews have revealed that nonsexual transmission of the parasite can occur through various fomites such as towels and toilet seats, as well as through exposure to contaminated swimming pools. Hence, it is crucial to consider these alternative transmission routes when questioning how one might have obtained trichomoniasis without any involvement in sexual activities.
Reference source
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/trichomoniasis/symptoms-causes/syc-20378609
https://www.webmd.com/sexual-conditions/trichomoniasis
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/trichomoniasis/
https://www.medicinenet.com/is_trichomoniasis_the_same_as_chlamydia/article.htm