Hidden beneath the surface of the world of sexual health lies a notorious parasite known as trichomoniasis.
This stealthy culprit, capable of causing havoc in women’s bodies without so much as a whisper in men, warrants our attention.
Anticipate a journey through the realm of this unsolicited infection, with an emphasis on prevention and protection.
trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by a parasitic infection.
In women, it can lead to symptoms such as foul-smelling vaginal discharge, genital itching, and painful urination.
Men may not experience any symptoms.
Pregnant women with trichomoniasis have a higher risk of premature delivery.
Treatment usually involves antibiotics like metronidazole, tinidazole, or secnidazole.
It is important to treat all sexual partners simultaneously to prevent reinfection.
Using condoms consistently and correctly can help reduce the risk of infection.
Key Points:
- Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by a parasitic infection.
- Women may experience symptoms such as foul-smelling vaginal discharge, genital itching, and painful urination.
- Men may not have any symptoms.
- Pregnant women with trichomoniasis are at a higher risk of premature delivery.
- Treatment usually involves antibiotics like metronidazole, tinidazole, or secnidazole.
- Treating all sexual partners simultaneously is important to prevent reinfection.
- Consistent and correct condom use can help reduce the risk of infection.
trichomoniasis – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
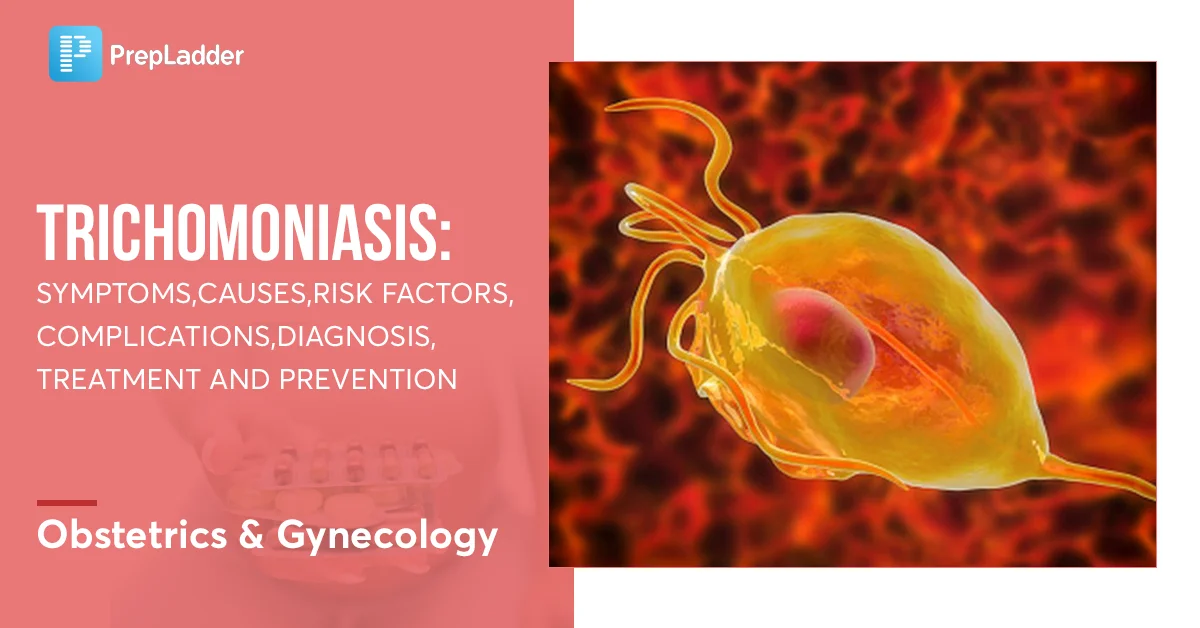
1. Trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection (STI), is caused by a single-celled protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis.
2. While trichomoniasis can affect both males and females, women are at a higher risk of experiencing symptoms. Men typically exhibit milder symptoms or remain asymptomatic carriers.
3. The World Health Organization estimates that around 276 million cases of trichomoniasis occur worldwide each year, making it the most common non-viral STI globally.
4. Trichomoniasis can have serious consequences during pregnancy. Pregnant women infected with the parasite have an increased risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and passing the infection to their newborns.
5. Surprisingly, although trichomoniasis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, it can also be contracted by sharing damp towels, bathing suits, or other objects that have come into contact with the parasite.
Introduction To Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis, also known as “trich,” is a sexually transmitted infection caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, a microscopic parasite. This infection can be spread through various forms of sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Trichomoniasis is considered one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections globally, with millions of individuals affected annually.
Symptoms Of Trichomoniasis In Women
Trichomoniasis is a common infection in women that can cause a range of symptoms. The most common and prominent symptom is a foul-smelling vaginal discharge. This discharge is typically frothy and yellow-green in color, and it is often accompanied by itching and irritation. Additionally, many women with trichomoniasis experience discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse and may feel a burning sensation while urinating. The severity of these symptoms can range from mild to severe, and if left untreated, they may persist for weeks.
One important thing to note is that trichomoniasis can lead to complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can cause long-term reproductive health problems. Therefore, it is crucial for women to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any of these symptoms. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further complications and ensure overall health.
Lack Of Symptoms In Men With Trichomoniasis
Men infected with trichomoniasis typically do not show any signs, unlike women who may experience noticeable symptoms. This often leads to the infection going undiagnosed and untreated in men, which increases the risk of unknowingly transmitting the parasite to their partners. Therefore, it is crucial for both men and women to undergo regular STI screenings, particularly if they are involved in situations with multiple sexual partners.
To summarize:
- Women may experience symptoms, while men usually do not show any signs of trichomoniasis.
- Undiagnosed and untreated trichomoniasis in men increases the risk of transmission to their partners.
- Regular STI screenings are essential for both men and women, especially in situations involving multiple sexual partners.
Trichomoniasis And Pregnancy
Pregnant women with trichomoniasis may face additional risks. Studies suggest that trichomoniasis during pregnancy could potentially increase the chances of premature delivery or having a low birth weight baby. It is crucial for pregnant women to receive proper medical care and screening for trichomoniasis to ensure early detection and appropriate treatment to minimize these risks.
Antibiotic Treatment For Trichomoniasis
Thankfully, trichomoniasis is a curable infection. The primary treatment for trichomoniasis involves the use of antibiotics, such as metronidazole, tinidazole, or secnidazole. These medications work by killing the parasite responsible for the infection. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional, even if the symptoms subside before the treatment is finished. This ensures complete eradication of the parasite and reduces the likelihood of reinfection.
Importance Of Treating All Sexual Partners
Treating all sexual partners simultaneously is crucial to prevent reinfection and further transmission of trichomoniasis. Even if one partner is asymptomatic, they can still carry and transmit the parasite. Therefore, it is recommended that anyone diagnosed with trichomoniasis informs their sexual partners so that they can seek medical attention and receive treatment promptly. Open and honest communication is vital to address the infection effectively and prevent its spread within sexual networks.
Role Of Condoms In Reducing Trichomoniasis Risk
Correct and consistent use of condoms during sexual intercourse can significantly reduce the risk of contracting trichomoniasis. While condoms do not provide 100% protection, they form a barrier that can prevent the exchange of bodily fluids and reduce contact with the parasite. It is important to note that condoms must be used from start to finish during every sexual encounter to maximize their effectiveness in preventing not only trichomoniasis but also other sexually transmitted infections.
Prevention And Education For Trichomoniasis
Prevention of trichomoniasis entails a combination of safe sexual practices and adequate education on the infection. Some key points to consider are:
- Regular STI screenings, especially for high-risk individuals or those with multiple sexual partners, can aid in early detection and prompt treatment.
- Comprehensive sexual health education, which includes information about trichomoniasis, should be provided to individuals of all ages. This will help promote responsible sexual behavior and reduce the risk of infection for themselves and their partners.
Remember to follow these measures to prevent trichomoniasis:
- Practice safe sex such as using condoms or practicing abstinence.
- Get regular STI screenings, particularly if you are at a higher risk or have multiple sexual partners.
- Educate yourself and others about trichomoniasis by seeking information from reliable sources and healthcare professionals.
For further support or more information, consult with your healthcare provider.
“Regular STI screenings, especially in high-risk individuals or those with multiple sexual partners, can aid in early detection and prompt treatment.”
Trichomoniasis: A Common STI
Trichomoniasis is a highly prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) that affects both men and women worldwide. While symptoms tend to be more common in women, it is important to understand that it can impact both genders. Untreated trichomoniasis can lead to discomfort, complications, and negative effects on reproductive health.
To address this issue, it is crucial to raise awareness about trichomoniasis and its potential consequences. Regular screenings and practicing safe sex are key in preventing transmission and minimizing the spread of the infection.
In summary, it is imperative to prioritize education and preventive measures to combat the global burden of trichomoniasis:
- Trichomoniasis is a highly prevalent STI that affects both men and women.
- Untreated trichomoniasis can lead to discomfort, complications, and negative effects on reproductive health.
- Regular screenings and practicing safe sex are essential in preventing transmission.
- Increasing awareness about trichomoniasis and its consequences is crucial.
“Educating individuals about trichomoniasis and promoting safe sexual practices can greatly reduce its impact on public health.”
Trichomoniasis: Parasitic Infection’s Impact On Health
The impact of trichomoniasis extends beyond the immediate symptoms and complications. For pregnant women, it poses additional risks to both mother and baby, potentially leading to preterm birth and low birth weight. Furthermore, the social and psychological burden should not be overlooked. Trichomoniasis can cause embarrassment, anxiety, and strain on personal relationships. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, we can work towards minimizing the prevalence and adverse effects of this parasitic infection on individual and public health.
💡
You may need to know these questions about trichomoniasis
What are 3 trichomoniasis symptoms?
Trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, presents itself through various symptoms. One common indication is the presence of a significant amount of thin, often unpleasant-smelling vaginal discharge. This discharge may vary in color from clear, white, gray, yellow, to green. Additionally, individuals infected with trichomoniasis may experience genital redness, burning, and itching, which can significantly affect their overall well-being and comfort. Furthermore, they may encounter pain during urination or sexual intercourse, along with discomfort in the lower stomach area. These symptoms collectively serve as crucial signs for individuals to recognize and seek appropriate medical attention to treat trichomoniasis effectively.
Is Trichomonas an STD?
Yes, Trichomonas is indeed an STD. Trichomoniasis, commonly referred to as trich, is caused by a parasite that spreads easily during sexual activity. It can be transmitted through various sexual fluids, such as semen, pre-cum, and vaginal fluids. Trichomoniasis is the most common curable STD, emphasizing the significance of preventative measures and regular testing to maintain sexual health.
How did you get trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis, also known as trich, is primarily acquired through intimate sexual contact. The transmission occurs when the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis is present in semen or vaginal fluids and is exchanged during unprotected anal, oral, or vaginal sex. Interestingly, it is important to note that ejaculation is not necessary for the parasite to pass from one partner to another, underscoring the ease of transmission. Therefore, ensuring the use of barrier methods, such as condoms, can greatly reduce the risk of contracting trichomoniasis.
Is trichomoniasis a female STD?
Trichomoniasis, indeed, qualifies as a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Although it is more frequently diagnosed in women and individuals assigned female at birth (AFAB), it is essential to note that men and individuals assigned male at birth (AMAB) can also acquire this infection. Trichomoniasis does not discriminate between genders and can affect anyone engaging in sexual activity, regardless of their assigned sex at birth. Therefore, proper education and awareness about this STI are crucial for everyone, as it can have significant implications on overall sexual health.
Reference source
https://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stdfact-trichomoniasis.htm
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/trichomoniasis/symptoms-causes/syc-20378609
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/stds-hiv-safer-sex/trichomoniasis
https://www.healthline.com/health/how-can-you-get-trichomoniasis-if-no-one-cheats