Are you tired of worrying about getting pregnant?
Looking for a reliable, permanent solution?
Well, look no further!
Tubal resection, a female sterilization surgery, might just be the answer you’ve been searching for.
Not only does it offer a long-term birth control solution, but it can also reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
In this article, we’ll explore the techniques used by the University of Chicago Medicine and discuss the recovery process.
So, if you’re interested in learning more about tubal resection and its potential benefits, read on!
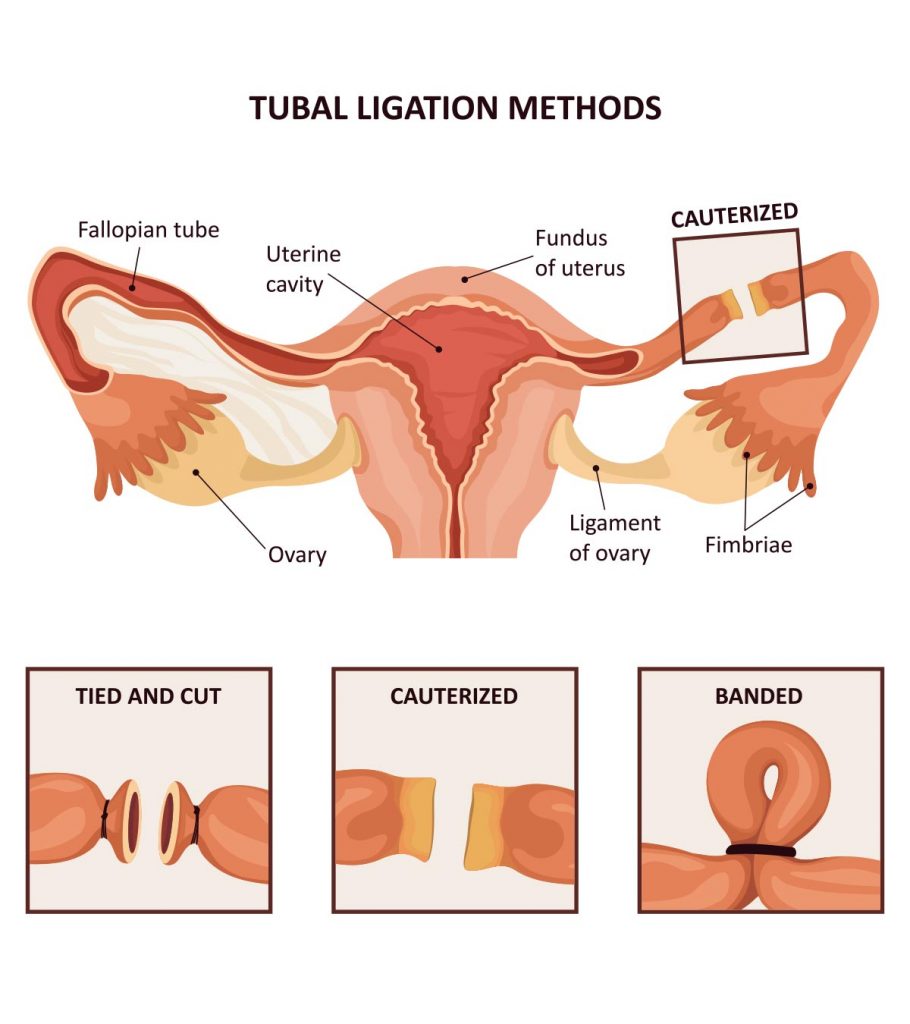
tubal resection
Tubal resection, also known as female sterilization surgery, is a permanent method of birth control.
It is offered to individuals who do not wish to have further pregnancies or have medical conditions that make pregnancy risky.
The University of Chicago Medicine provides two laparoscopic techniques for sterilization surgery, namely tubal ligation and tubal removal.
Both methods may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Recovery time is generally a few hours, and most patients can return to work within a week or less.
Side effects, such as abdominal pain, can be managed with medication, and potential risks will be addressed by the doctor.
On the other hand, salpingo-oophorectomy involves removing the fallopian tubes and ovaries and is considered major surgery.
This procedure requires anesthesia, an overnight hospital stay, and a recovery time of 3-6 weeks.
However, laparoscopic salpingo-oophorectomy is a less invasive option with a shorter recovery time.
Post-surgery, some discomfort around the incision may persist for a few days, but most women will be able to start walking within three days and resume normal activities within 6 weeks, following the doctor’s advice.
It is important to note that salpingo-oophorectomy, like any major surgery, carries potential complications.
Key Points:
- Tubal resection is a permanent method of birth control.
- It is offered to individuals who do not want to have more pregnancies or have medical conditions that make pregnancy risky.
- There are two laparoscopic techniques for sterilization surgery: tubal ligation and tubal removal.
- Both methods may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Recovery time for tubal resection is generally a few hours, and most patients can return to work within a week or less.
- Salpingo-oophorectomy is a more invasive option that involves removing the fallopian tubes and ovaries and requires a longer recovery time.
tubal resection – Watch Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GxRJH2f–P0
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Tubal resection, a surgical procedure used in female sterilization, was first performed in the 19th century by Dr. Isaac Marion in the United States.
2. The term “tubal” in tubal resection refers to the fallopian tubes, which are the small ducts connecting the ovaries to the uterus in females.
3. Tubal resection is an alternative to tubal ligation, commonly known as having one’s “tubes tied.” However, unlike tubal ligation, tubal resection is considered reversible in some cases.
4. A study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology in 1998 found that tubal resection has a lower rate of surgical complications compared to tubal ligation.
5. Tubal resection is often performed laparoscopically, which is a minimally invasive surgical technique that involves making small incisions in the abdomen.
Female Sterilization Surgery As A Permanent Birth Control Method
Female sterilization surgery, including tubal resection, is a permanent method of birth control. It is a safe and effective option for individuals who do not desire future conception or have medical conditions that make pregnancy dangerous. By removing or blocking the fallopian tubes, this procedure prevents the sperm from reaching the egg, thus preventing pregnancy. Tubal resection is a popular choice for women looking for a long-term contraceptive method.
- Female sterilization surgery, such as tubal resection, is a permanent method of birth control.
- It is a safe and effective option for individuals who do not want to have children in the future or have medical conditions that may pose risks during pregnancy.
- The procedure involves removing or blocking the fallopian tubes, preventing the sperm from reaching the egg and thereby impeding pregnancy.
- Tubal resection is a popular choice among women seeking a reliable, long-term contraceptive method.
Indications For Tubal Resection
The main indications for tubal resection are individuals who have completed their family or have decided not to have children in the future. Additionally, women with certain medical conditions, such as uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or pelvic inflammatory disease, may undergo tubal resection to alleviate symptoms or reduce the risk of complications. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if tubal resection is the right option based on individual circumstances.
Two Techniques Offered: Tubal Ligation And Tubal Removal
The University of Chicago Medicine offers two sterilization surgery techniques: tubal ligation and tubal removal. Tubal ligation is a procedure in which the fallopian tubes are tied or sealed, while tubal removal involves the complete removal of the fallopian tubes. Both methods are performed laparoscopically, a minimally invasive approach that significantly reduces recovery time and complications compared to open surgery. The choice between the two techniques depends on various factors, including the patient’s medical history and preferences.
Decreased Risk Of Ovarian Cancer
One of the benefits of tubal resection is its potential to decrease the risk of ovarian cancer. Research suggests that the removal of the fallopian tubes may reduce the likelihood of developing this type of cancer. This is particularly valuable for women with a family history of ovarian cancer or those at higher risk due to genetic mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2.
By choosing tubal resection, individuals can not only achieve permanent birth control but also potentially reduce their risk of developing a life-threatening disease.
- Tubal resection can decrease the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Removal of the fallopian tubes may reduce the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer.
- Particularly valuable for women with a family history of ovarian cancer or genetic mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2.
- It provides permanent birth control.
- Potential reduction in the risk of developing a life-threatening disease.
“By choosing tubal resection, individuals can not only achieve permanent birth control but also potentially reduce their risk of developing a life-threatening disease.”
Recovery Time And Return To Work
The recovery time for tubal resection is relatively short. Most patients can expect to spend a few hours in the hospital and return to work within a week or even less. However, it is important to note that recovery time can vary depending on individual factors, such as overall health and the specific technique used. Patients are typically advised to take it easy during the first few days after surgery, gradually increasing their activity level as they feel comfortable. It is essential to follow the doctor’s post-operative instructions to ensure a smooth recovery.
Managing Abdominal Pain And Rare Risks
Following tubal resection, some patients may experience abdominal pain. This discomfort can be managed with prescribed pain medication, which helps alleviate any discomfort or mild soreness. However, it is essential to report any severe or worsening pain to the healthcare provider, as it could indicate a rare complication. Although the risks associated with tubal resection are generally low, it is crucial to discuss potential complications with the doctor before undergoing the surgery.
Salpingo-Oophorectomy: Removing Fallopian Tubes And Ovaries
Salpingo-oophorectomy is a major surgical procedure that involves the removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. This surgery requires the administration of anesthesia and is typically performed with an overnight hospital stay for post-operative care.
Salpingo-oophorectomy is recommended for individuals who have specific medical conditions, such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or ovarian cancer. However, before making a decision, it is crucial to discuss the implications and potential consequences of this procedure with a healthcare professional.
Benefits of Salpingo-oophorectomy:
- Removal of the source of pain or discomfort caused by conditions like ovarian cysts or endometriosis.
- Reduction in the risk of developing ovarian cancer for individuals at high risk due to family history or genetic predisposition.
Risks and considerations associated with Salpingo-oophorectomy:
- Early menopause due to the removal of the ovaries, leading to hormonal changes and potential long-term effects on bone health.
- Loss of fertility for individuals who have not completed their family-building plans.
- Potential complications related to surgery and anesthesia, such as infection or blood clots.
It is important to weigh the potential benefits and risks of Salpingo-oophorectomy and make an informed decision in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional.
“Discussing the implications and potential consequences of Salpingo-oophorectomy with a healthcare professional is crucial.”
Major Surgery Requiring Anesthesia And Hospital Stay
Salpingo-oophorectomy is a surgical procedure that is more complex than tubal resection and requires general anesthesia. This means that the patient will be unconscious during the entire procedure. Furthermore, due to the invasiveness of the surgery, patients are required to stay in the hospital overnight.
Staying in the hospital allows patients to receive proper pain management and essential support for their recovery process.
To summarize the key points:
- Salpingo-oophorectomy is a more complex surgical procedure than tubal resection.
- General anesthesia is administered to keep the patient unconscious throughout the procedure.
- An overnight hospital stay is necessary due to the invasiveness of the surgery.
- This allows for appropriate pain management and crucial recovery support.
“By staying in the hospital, patients can receive appropriate pain management and crucial support for their recovery process.”
Recovery Time And Discomfort After Laparoscopic Salpingo-Oophorectomy
The recovery time for laparoscopic salpingo-oophorectomy is typically longer compared to tubal resection. The average recovery period ranges from 3 to 6 weeks.
During this time, it is crucial to prioritize rest, gradually increasing activity levels as advised by the healthcare provider.
Some discomfort around the incision site is normal and can persist for a few days following the procedure. However, any severe pain, persistent bleeding, or signs of infection should be promptly reported to the healthcare provider.
Resuming Normal Activities And Possible Complications
After laparoscopic salpingo-oophorectomy, most women can start walking by the third day after surgery. However, it is important to remember that recovery times may vary depending on individual factors. Normal activities such as driving, exercising, and returning to work can typically be resumed within 4 to 6 weeks, following the advice of the healthcare provider. It is crucial to attend all follow-up appointments to monitor the recovery progress and discuss any concerns or potential complications that may arise.
Potential complications of salpingo-oophorectomy are similar to those associated with any major surgery and should be thoroughly discussed with the healthcare provider beforehand.
Tubal resection, as a form of female sterilization, is a permanent method of birth control. It offers individuals the opportunity to avoid future pregnancies if desired or necessary for medical reasons. The University of Chicago Medicine provides two techniques, tubal ligation and tubal removal, which reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. Recovery times vary between these procedures, with tubal resection typically having a shorter recovery period compared to salpingo-oophorectomy. It is crucial to consult with healthcare providers to determine the best course of action based on individual circumstances and preferences.
- Laparoscopic salpingo-oophorectomy allows women to start walking by the third day after surgery
- Recovery times may vary depending on individual factors
- Normal activities can be resumed within 4 to 6 weeks
- Attending follow-up appointments is crucial
- Potential complications should be discussed beforehand
“Tubal resection is a permanent method of birth control and reduces the risk of ovarian cancer”
“Recovery times vary between tubal ligation and tubal removal”
Consult with healthcare providers to determine the best course of action.
💡
You may need to know these questions about tubal resection
What is the difference between tubal ligation and tubal removal?
Tubal ligation involves altering the fallopian tubes by cutting, tying, clipping, or blocking them, while tubal removal, or bilateral salpingectomy, entails the complete removal of both fallopian tubes. In tubal ligation, the tubes remain in place but are modified to prevent eggs from reaching the uterus. On the other hand, tubal removal eliminates the possibility of eggs being fertilized by completely removing the fallopian tubes. Both procedures are performed by gynecologic surgeons at the University of Chicago Medicine for sterilization purposes.
Is tubal removal a major surgery?
Yes, tubal removal is considered a major surgery. Salpingo-oophorectomy involves the removal of both the fallopian tubes and ovaries, which are essential reproductive organs in females. Due to the need for anesthesia, overnight hospital stay, and the removal of body parts, it is categorized as a major surgical procedure. Recovery from this surgery typically takes around 3-6 weeks to fully heal.
What is the failure rate of tubal resection?
The failure rate of tubal resection, also known as tubal ligation, is extremely low. Although it is a highly effective permanent contraceptive method, there is still a minor risk of pregnancy. In rare cases, the tubes may grow back together, resulting in a failure rate of 0.5%. This occurrence is infrequent and indicates that tubal resection is a reliable contraceptive option for the majority of individuals.
What are the benefits of having your fallopian tubes removed?
Having your fallopian tubes removed can provide several benefits. Firstly, it can serve as a permanent form of birth control, as removing the fallopian tubes prevents eggs from traveling to the uterus, thereby eliminating the possibility of fertilization and pregnancy. This option can be especially beneficial for individuals who have completed their desired family size or for those who do not wish to pursue other forms of contraception.
Additionally, removing the fallopian tubes can significantly lower the risk of ovarian cancer. Since some types of ovarian cancer are believed to originate in the fallopian tubes, their removal can reduce the likelihood of developing this type of cancer. This option may be chosen by individuals who have a family history of ovarian cancer or who want to take proactive steps in reducing their risk of this disease.
Reference source
https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/conditions-services/obgyn/minimally-invasive-gynecologic-surgery/female-sterilization-tubal-ligation-tubal-removal
https://www.nccrm.com/long-term-side-effects-of-tubal-ligation/
https://www.medicinenet.com/is_salpingo_oophorectomy_considered_major_surgery/article.htm
https://www.webmd.com/sex/birth-control/what-is-tubal-ligation