In the realm of medical mysteries, there are rare conditions that leave us baffled and intrigued, pushing the boundaries of our understanding.
One such enigma is uteroplacental apoplexy.
With its intriguing name and elusive nature, this condition dives deep into the intricate workings of the womb, captivating the minds of doctors and researchers alike.
Prepare to embark on a journey into the unknown as we unravel the mysteries of uteroplacental apoplexy.
uteroplacental apoplexy
Uteroplacental apoplexy, also known as placental abruption, is a medical condition where the placenta partially or completely separates from the uterine lining.
This premature separation can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the fetus.
Key Points:
- Uteroplacental apoplexy is another term for placental abruption, a medical condition where the placenta separates from the uterine lining.
- This condition can occur when the placenta partially or completely detaches from the uterus.
- Uteroplacental apoplexy can lead to severe complications for both the mother and the fetus.
- Premature separation of the placenta can result in serious health risks.
- It is important to promptly diagnose and treat uteroplacental apoplexy to minimize potential harm.
- Close monitoring of the mother and fetus is essential in cases of uteroplacental apoplexy.
uteroplacental apoplexy – Watch Video
💡
Pro Tips:
1. Uteroplacental apoplexy is a rare condition that involves the sudden rupture of blood vessels within the placenta, causing hemorrhage and potentially endangering the life of both the mother and the fetus.
2. This condition most commonly occurs during the third trimester of pregnancy, but can also happen during labor and delivery.
3. Uteroplacental apoplexy can lead to a range of symptoms, including severe abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, low blood pressure, and a decrease in fetal movements.
4. Studies suggest that some risk factors for developing uteroplacental apoplexy include advanced maternal age, pregnancies with multiple fetuses, and certain medical conditions such as hypertension and preeclampsia.
5. While uteroplacental apoplexy is rare, prompt medical intervention, such as an emergency cesarean section, can help improve the outcome for both the mother and the baby.
Definition Of Uteroplacental Apoplexy
Uteroplacental apoplexy, also known as retroplacental hematoma or placental abruption, is a condition in pregnancy where the placenta detaches from the uterine wall. This can range from a partial detachment to a complete separation, causing significant bleeding and potential complications for both the mother and the fetus. It most commonly occurs in the third trimester, but can also happen earlier in the pregnancy.
The placenta plays a vital role in delivering oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus, forming a crucial connection between the mother and the baby. However, in cases of uteroplacental apoplexy, this connection is disrupted, affecting blood flow and nutrient delivery to the fetus. Immediate medical attention is necessary to ensure the well-being and safety of both the mother and the baby.
Causes Of Uteroplacental Apoplexy
Although the exact cause of uteroplacental apoplexy remains unknown, several risk factors have been identified. High blood pressure, smoking, drug use, advanced maternal age, trauma to the abdomen, and previous cases of placental abruption are some of the factors that can increase the likelihood of experiencing uteroplacental apoplexy. Additionally, certain medical conditions such as pre-eclampsia, blood clotting disorders, and uterine fibroids may also contribute to the development of uteroplacental apoplexy.
The condition is thought to be related to the disruption of the blood vessels that connect the placenta to the uterine wall. This disruption can be caused by various factors, including inflammation, high blood pressure, and mechanical stress. Once the blood vessels rupture, bleeding occurs between the placenta and the uterine wall, leading to the detachment of the placenta.
Symptoms And Diagnosis Of Uteroplacental Apoplexy
Uteroplacental apoplexy is a condition that presents with a range of symptoms of varying severity. The most common symptom is vaginal bleeding, which can range from light to heavy, depending on the extent of placental detachment. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, back pain, uterine contractions, and a decrease in fetal movement.
Upon suspicion of uteroplacental apoplexy, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination and review of medical history. Diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, blood tests, to assess blood clotting factors, and fetal monitoring may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment and management options.
Risk Factors For Uteroplacental Apoplexy
Several factors can increase the risk of developing uteroplacental apoplexy. One of the primary risk factors is maternal age, with women over 35 being more susceptible to placental abnormalities. Other risk factors include:
- high blood pressure
- smoking
- drug use
- multiple pregnancies
- trauma to the abdomen
- certain medical conditions like pre-eclampsia and blood clotting disorders
Women who have had a previous case of uteroplacental apoplexy are also at a higher risk of recurrence. It is important for pregnant women with these risk factors to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their condition and take appropriate preventive measures.
“It is important for pregnant women to work closely with their healthcare providers.”
Complications Associated With Uteroplacental Apoplexy
Uteroplacental apoplexy can have significant implications for both the mother and the fetus. Maternal complications may include severe hemorrhage requiring blood transfusions and the potential development of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), a serious condition that impairs the body’s ability to clot properly. DIC can lead to excessive bleeding and organ damage.
Complications for the fetus can range from intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) to preterm birth. In severe cases, uteroplacental apoplexy can even result in fetal death. The severity of the complications depends on the extent of placental detachment and the promptness of medical intervention.
Treatment Options For Uteroplacental Apoplexy
The treatment of uteroplacental apoplexy depends on the severity of the condition and the gestational age of the fetus. In some cases, if the mother and the fetus are stable, conservative management may be possible, with close monitoring of both the mother and the baby.
However, if there are signs of fetal distress or maternal complications, immediate delivery may be necessary. The mode of delivery can vary depending on the circumstances, including the gestational age of the fetus and the severity of placental detachment. Vaginal delivery or cesarean section (C-section) may be chosen by the healthcare team.
During the treatment process, close monitoring of vital signs, fetal heart rate, and uterine contractions is essential. Women who experience severe bleeding may require blood transfusions and medications to manage clotting abnormalities. The healthcare team will work together to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances.
- Conservative management may be possible if the mother and fetus are stable.
- Immediate delivery may be necessary if there are signs of fetal distress or maternal complications.
- The mode of delivery depends on gestational age and severity of placental detachment.
- Close monitoring of vital signs, fetal heart rate, and uterine contractions is essential.
- Severe bleeding may require blood transfusions and medications to manage clotting abnormalities.
- The healthcare team will determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances.
“The treatment of uteroplacental apoplexy depends on the severity of the condition and the gestational age of the fetus.”
Prevention Strategies For Uteroplacental Apoplexy
While uteroplacental apoplexy cannot be completely prevented, pregnant women can take steps to reduce the risk and promote a healthy pregnancy. Regular prenatal care is crucial for monitoring the development of the pregnancy and identifying any potential risk factors or complications.
In addition to prenatal care, optimizing overall health is important. This can be achieved by maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise (with healthcare provider approval), and avoiding tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs. These lifestyle choices can contribute to a healthier pregnancy.
Furthermore, managing chronic medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, under the guidance of a healthcare professional is important to reduce the risk of complications.
By following these recommendations, pregnant women can proactively work towards a healthy pregnancy and reduce the risk of uteroplacental apoplexy.
Prognosis And Recovery From Uteroplacental Apoplexy
The prognosis and recovery from uteroplacental apoplexy vary depending on the severity of placental detachment and the timeliness of medical intervention. In cases where the condition is diagnosed early and appropriate treatment is initiated promptly, the prognosis is generally better, with successful outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
However, the long-term effects and recovery can differ for each individual. It is essential for women who have experienced uteroplacental apoplexy to work closely with their healthcare providers during the recovery period and follow any recommended postpartum care guidelines. Regular check-ups and monitoring are important to ensure any complications are promptly addressed.
- It is important to diagnose uteroplacental apoplexy early and provide prompt treatment.
- Successful outcomes are possible when appropriate medical intervention is initiated in a timely manner.
- Long-term effects and recovery may vary for each individual.
- Close collaboration with healthcare providers and adherence to postpartum care guidelines are crucial for recovery.
- Regular check-ups and monitoring are necessary to identify and address any potential complications.
Research And Advances In Uteroplacental Apoplexy
Ongoing research in obstetrics and gynecology is contributing to our understanding and management of uteroplacental apoplexy. Some key points to note include:
- Researchers are investigating potential risk factors, preventive measures, and treatment options for uteroplacental apoplexy.
- Diagnostic tools, like prenatal screening tests and imaging techniques, are advancing and enabling early detection and intervention.
- Studying the underlying mechanisms of uteroplacental apoplexy is providing valuable insights for preventative strategies.
By focusing on these areas, medical professionals are working to improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Importance Of Early Detection And Management Of Uteroplacental Apoplexy
Early detection and prompt management of uteroplacental apoplexy are critical for the well-being of both the mother and the baby. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking immediate medical attention can help prevent potential complications and improve outcomes.
Pregnant women should be aware of the risk factors associated with uteroplacental apoplexy and report any concerning symptoms to their healthcare providers. Regular prenatal care appointments and open communication with the healthcare team are essential in monitoring the progress of the pregnancy and addressing any issues that may arise.
💡
You may need to know these questions about uteroplacental apoplexy
What is another name for uteroplacental apoplexy?
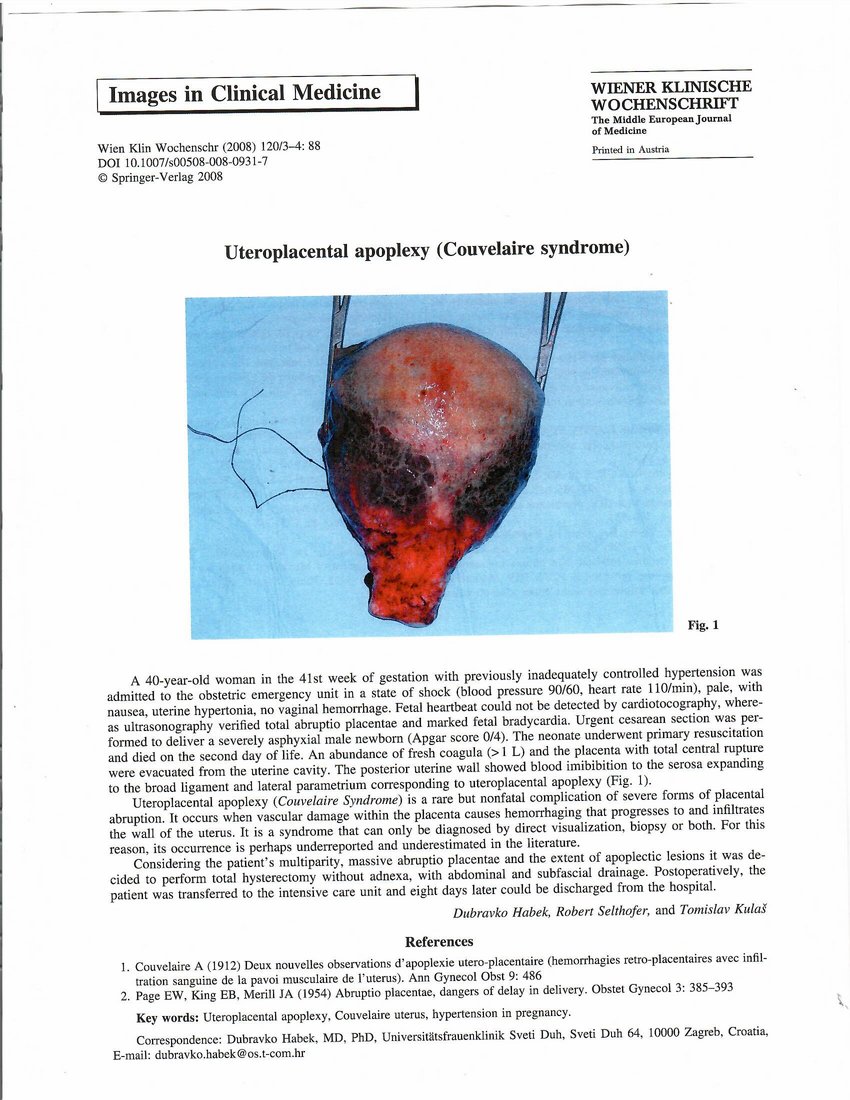
Another name for uteroplacental apoplexy is Couvelaire syndrome. This medical condition is characterized by severe bleeding into the myometrium, which can extend to the parametrium and peritoneum. Couvelaire syndrome is commonly linked to abruptio placentae, which is the premature separation of the placenta.
Is Couvelaire uterus the same as uteroplacental apoplexy?
Couvelaire uterus and uteroplacental apoplexy are related but not the same condition. Couvelaire uterus refers specifically to a rare complication of abruptio placentae, where there is bleeding into the uterine muscle and surrounding tissues. This condition is diagnosed through visual inspection of the uterus and is generally managed conservatively without the need for a hysterectomy. On the other hand, uteroplacental apoplexy, also known as maternal uterine bleeding, involves bleeding within the uterine cavity due to the rupture of blood vessels in the placenta. While they share similarities in terms of uterine bleeding, they are distinct in terms of the specific underlying causes and management approaches.
What causes Couvelaire uterus?
Couvelaire uterus is primarily caused by placental abruption, where bleeding from placental blood vessels infiltrates the decidua basalis, leading to separation of the placenta. This infiltration then spreads to the lateral portions of the uterus. Placental abruption is often triggered by trauma or high blood pressure, which can result in the detachment of the placenta from the uterine wall. This condition can be serious and requires immediate medical attention to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the fetus.
What are the symptoms of Couvelaire uterus?
Symptoms of Couvelaire uterus, also known as uteroplacental apoplexy, may include severe pain caused by uterine contractions or tenderness. These signs can be attributed to the detachment of the placenta, leading to uterine hypertonus and potential fetal distress or death. In rare cases, severe blood loss can result in hypovolemic shock. Prompt medical attention is crucial to manage this condition and mitigate potential complications.
Reference source
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9313351/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2210261222011087
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3975566/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8383572/